Custom Vaccinia Virus Vector Production Service
Introduction
Creative Biolabs' Custom Vaccinia Virus Vector Production Service accelerates vaccine and gene therapy development with advanced recombinant DNA technology. The service delivers high-titer, clinically validated vectors (such as attenuated MVA strains), addressing challenges in vector design, expression, and safety.
[Discover How We Can Help - Request a Consultation]
Custom Vaccinia Virus Vector Production Service
 Fig.1 VACV with additional safety properties as well as characteristics of wild-type VACV.1,3
Fig.1 VACV with additional safety properties as well as characteristics of wild-type VACV.1,3
The Vaccinia Virus (VV) serves as an exceptional vector due to its large DNA genome, capable of accommodating 25-30 kb of foreign DNA, making it ideal for multi-gene delivery or large therapeutic constructs. Its broad tropism allows infection of various mammalian cells. Importantly, VV replicates exclusively in the cytoplasm, eliminating the risk of genomic integration and enhancing its safety profile for gene therapy.
Workflow
 Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the cloning strategy for generating recombinant poxvirus vectors.2,3
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of the cloning strategy for generating recombinant poxvirus vectors.2,3
-
Production
- Strategic Vector Design: Advanced molecular techniques to create shuttle vectors for vaccinia genome integration, using BACYAC backbones for flexible propagation.
- Optimized Cell Culture: Primary chicken embryo fibroblasts cells for MVA, with culture conditions optimized for max virus replication and transgene expression.
- Efficient Recombination: Homologous recombination in infected cells ensures stable, accurate gene insertion.
- Rigorous Selection: Fluorescent markers and multi-round plaque purification to isolate pure recombinant virus clones.
-
Purification
The purification stage is critical for ensuring the safety and efficacy of the final vector. We offer two main purification grades:
- PEG Concentration: Suitable for in vitro research applications, this method efficiently concentrates viral particles while removing bulk impurities.
- Ultra-Purification via Sucrose Density Gradient Centrifugation: Gold-standard method for in vivo/clinical use, removing cellular debris and contaminants to minimize immune responses. Ensures high safety and performance.
-
Quality Control
- Titer Determination: Precise quantification of infectious viral particles to guarantee consistent dosing and experimental reproducibility.
- Sterility Testing: Thorough screening to confirm the absence of bacterial and fungal contamination.
- Mycoplasma Testing: Essential testing to detect and prevent mycoplasma contamination, which can severely compromise cell health and experimental integrity.
- Fluorescence Transduction Testing: Functional assay to verify the efficiency of gene delivery and expression in target cells.
- Endotoxin Testing: A critical safety test for in vivo applications, ensuring endotoxin levels are below regulatory thresholds to prevent inflammatory responses.
What We Can Offer
As a leading provider of Custom Vaccinia Virus Vector Production Service, Creative Biolabs offers unparalleled advantages designed to accelerate your therapeutic development and ensure the highest quality for your projects:
[Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage - Get a Quote Today]
Case Study
| Construction of Recombinant Virus |
|---|
|
|
| Transfection and Imaging |
|
|
Customer Reviews

FAQs
Q1: How to address genomic rearrangement issues in vaccinia virus vectors with multi-antigen insertion?
A: The ITRs of the VACV genome prone to recombination are managed by:
- Three-site insertion strategy: Insert different antigen genes into non-essential regions of the Tiantan strain genome (e.g., TK, HA, F13L loci) to avoid overloading a single region.
- loxP-Cre system: Add loxP sites to both ends of the inserted fragment for Cre recombinase-mediated single-copy integration, reducing rearrangement rates caused by tandem repeats.
- Temperature-sensitive screening: Construct tsE mutant strains (thermosensitive DNA polymerase) to allow only single-copy recombinants to replicate at 39°C, eliminating multi-copy mutants.
Q2: How to remove residual bovine serum albumin (BSA) contamination during vaccinia vector production?
A: Our serum-free purification process includes:
- Column chromatography combination: Use Q Sepharose anion-exchange column to adsorb BSA first, then capture viruses with Butyl Sepharose hydrophobic column.
- Affinity elution: Employ anti-VV A33 antibody-conjugated magnetic beads for specific viral particle capture.
- Mass spectrometry verification: Detect residual proteins via LC-MS/MS.
Q3: How to resolve purification efficiency fluctuations caused by viral particle polymorphism during vaccinia virus vector production?
A: Vaccinia viruses exist in two morphologies (brick-shaped and ovoid), and their density differences are addressed by:
- Gradient Centrifugation Optimization: 30%-60% sucrose continuous gradient, 40,000×g for 3h separates particle morphologies by density, achieving 95% purity (vs. 70% with traditional methods).
- Affinity Magnetic Bead Capture: Anti-A33 Ab-conjugated beads bind infectious brick-shaped particles, increasing infectious titer/total protein ratio 3-fold.
- Cryo-EM Production Monitoring: Quantify morphology ratios per batch; adjust MOI=5 and harvest at 48h when ovoid particles exceed 30%.
[Contact us to discuss your project]
References
- Wang, Yuxiang. "Rendezvous with Vaccinia Virus in the Post-smallpox Era: R&D Advances." Viruses 15.8 (2023): 1742. DOI: 10.3390/v15081742
- Jiménez-Cabello, Luis, et al. "Viral vector vaccines against bluetongue virus." Microorganisms 9.1 (2020): 42. DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9010042
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.

 Fig.3 Schematic representation of the genome structure of the recombinant VACV expressing reporters.
Fig.3 Schematic representation of the genome structure of the recombinant VACV expressing reporters.
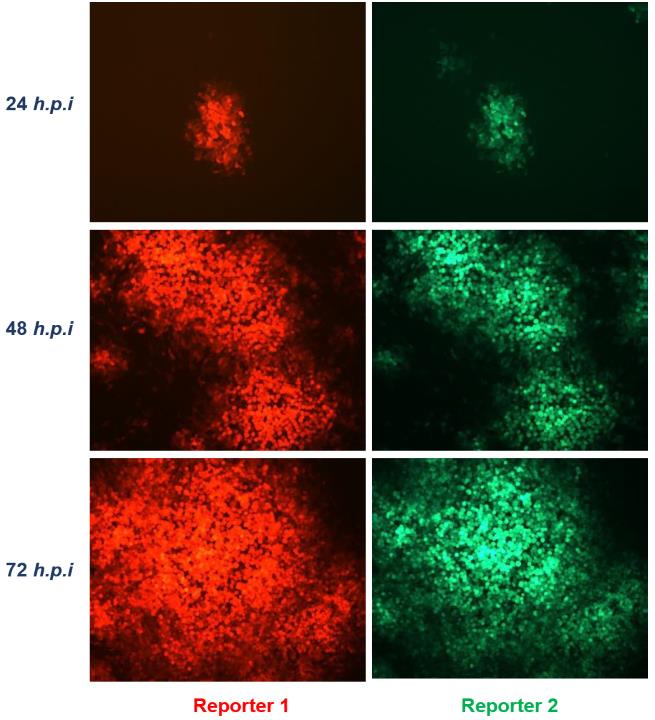 Fig.4 The expression of reporters in cells infected with recombinant VACV was observed under a fluorescence microscope.
Fig.4 The expression of reporters in cells infected with recombinant VACV was observed under a fluorescence microscope.