Creative Biolabs has successfully constructed a series of improved and innovative aptamer platforms to provide fast and better 3D structure determination services for our worldwide customers. Our high-quality services can help you get satisfactory results without repeated redundant trials and obtain a milestone development in your aptamer development.
Brief Introduction to Aptamer
Aptamers are a small segment of oligonucleotide sequences or short polypeptides synthesized and screened in vitro, which are capable of binding to ligands or target molecules with high affinity and strong specificity. The discovery of aptamers provides a new efficient and rapid target recognition approach for biological research and novel target therapy development, exhibiting promising application prospects in many aspects, such as disease treatment, drug target delivery, molecular imaging, microbiological analysis, and so forth.
Currently, the method for aptamer synthesis and screening is the in vitro Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment (SELEX). Firstly, there is a synthetic “combinatorial library” that refers to the initial oligonucleotide pool (IOP) which contains 1014-1015 random oligonucleotides with different lengths. Then, the library is converted into single-strand nucleotides that consist of random or variable sequence regions usually 30-40 mers. The variable regions are flanked by the primer binding sites for amplification and transcription. Secondly, the target molecules are added to and incubated with the single-strand nucleotide library to screen the interest aptamer sequence. And the target-aptamer complexes are separated from the unbound components, and the bound aptamer was eluted from the target molecule. Thirdly, the eluted aptamer sequences are amplified using the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and the enriched sequences were further screened for several rounds (10-15 rounds). Then the interest aptamers will be obtained.
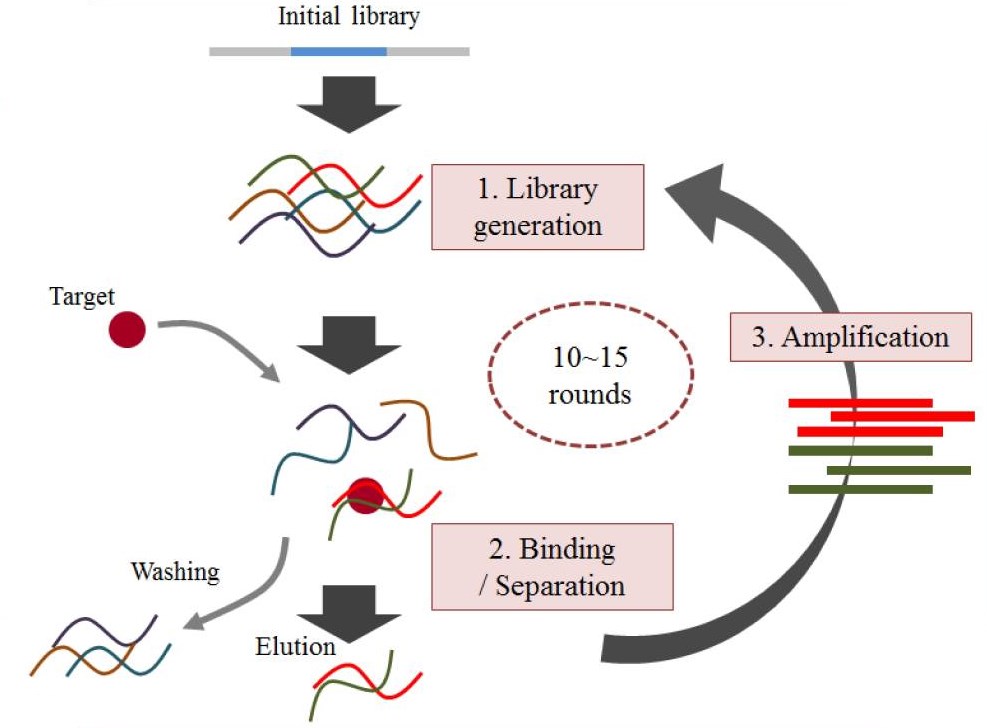 Fig. 1 The general SELEX strategy.1, 3
Fig. 1 The general SELEX strategy.1, 3
3D Structure Determination Services for Aptamer Characterization
After obtaining the target aptamer by SELEX, it is necessary to characterize it to fully understand its properties before the application. Firstly and basically, structure determination is preferred. The method for aptamer structure determination is similar to that of nucleic acid. For atomic resolution structure analysis, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy and electron microscopy or electron crystallography of two-dimensional (2D) crystals are useful. X-ray crystallography can be used for the 3D structure determination for aptamer-based on the aptamer crystals that provide suitable quality diffraction data. Recently, computational modeling based on base pairing and other interactions analysis has been developed to predict tertiary structures. 3D structure determination of aptamer is an elaborate and complex process, which is usually performed by the combination of these methods and technologies.
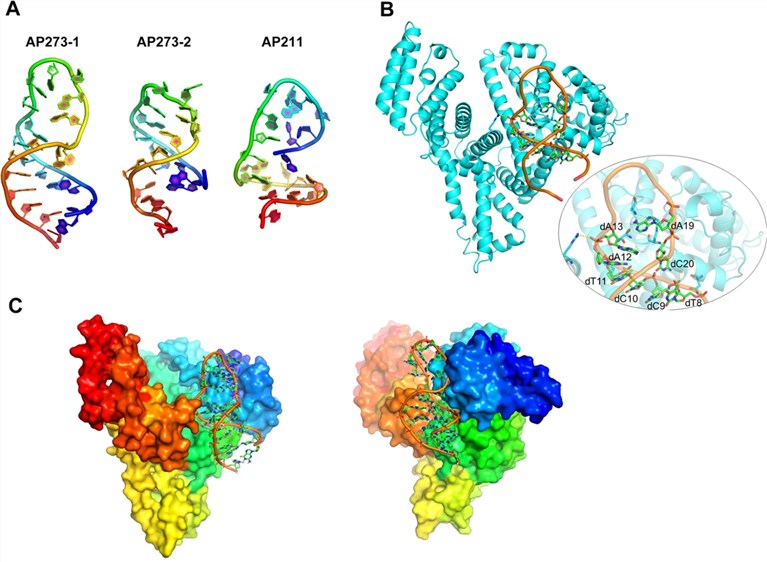 Fig. 2 The general SELEX strategy.2, 3
Fig. 2 The general SELEX strategy.2, 3
Why Choose Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs, a leading biotechnology company dedicated to novel therapy discovery, has devoted to the investigations and applications of aptamers for several years. Our optimized technology platform and scientist team can offer professional and comprehensive 3D aptamer structure analysis services to help you get satisfactory results in further research. Besides, our custom aptamer services for you are all based on the “4A” advantages of:
-
Advanced technologies for aptamer structure analysis
-
Abundant experience in aptamer development
-
An excellent expert team supports the whole process
-
A perfect service system covering from product to application
To discuss your interest or questions about aptamer development, please contact us or send us an inquiry directly. Our scientists are confident in offering satisfying and the best answers and services.
References
-
Song, Kyung-Mi, Seonghwan Lee, and Changill Ban. "Aptamers and their biological applications." Sensors 12.1 (2012): 612-631.
-
Dong, Lili, et al. "Screening and identifying a novel ssDNA aptamer against alpha-fetoprotein using CE-SELEX." Scientific reports 5.1 (2015): 15552.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Aptamer binding is determined by its three-dimensional structure, not its primary sequence. Both target recognition and binding involve three-dimensional, shape-related interactions as well as hydrophobic interactions, base stacking and embedding. Therefore, it is useful to characterize the structural information of the aptamer.
A: The three most common methods used to study the three-dimensional structure of biological macromolecules are X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, and cryo-electron microscopy. Generally the structure of short aptamers can be determined by nuclear magnetic resonance. Aptamers that are generally too large cannot be resolved by NMR, and structural determination by crystallography and X-ray crystallography may be helpful. The combination of NMR and X-ray crystallography may be feasible when conformational rearrangements of aptamers occur during interaction with proteins.
A: When determining the structure of aptamers, it is critical to maintain the stability of the aptamer. Both the temperature and concentration of the sample affect the stability of the aptamer structure in the structure determination. Typically, samples are stabilized by heating at 95°C for 5 minutes and then continuously cooling to room temperature prior to measurement.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 The general SELEX strategy.1, 3
Fig. 1 The general SELEX strategy.1, 3
 Fig. 2 The general SELEX strategy.2, 3
Fig. 2 The general SELEX strategy.2, 3