Three-dimensional (3D) aptamer structures provide invaluable insights into the molecular basis of aptamer functions. Powered by cutting-edge technologies and the rich expertise in 3D modeling, we offer the best aptamer structural 3D modeling services, helping our clients investigate the mechanisms of functions of aptamers.
Introduction of 3D Structure Modeling
3D structure modeling is a powerful technology that is used to model 3D structure of aptamers in silico, which helps to understand the mechanisms of functions and aptamer-target interactions. In a study, scientists revealed the molecular interactions of anti-HER2 ssDNA aptamers (H1-H7) that specifically bind to the extracellular domain of HER2 protein. Molecular docking and molecular dynamics (MD) simulations showed the stable HER2 binding nature of H1, H2, and H6 aptamers and the amino acid residues (Asn37, Gln59, Arg81-Gln84, Asp88, and Lys128) of Site 2a were found to be crucial for high-affinity binding. In another study, the authors used computational RNA structure and RNA/protein docking modeling to guide the truncation of the A9 prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) RNA aptamer. Furthermore, the modeled RNA 3D structure and protein/RNA docking modeling also indicated key nucleotides within the aptamer that are essential for binding to PSMA and inhibiting its enzymatic activity.
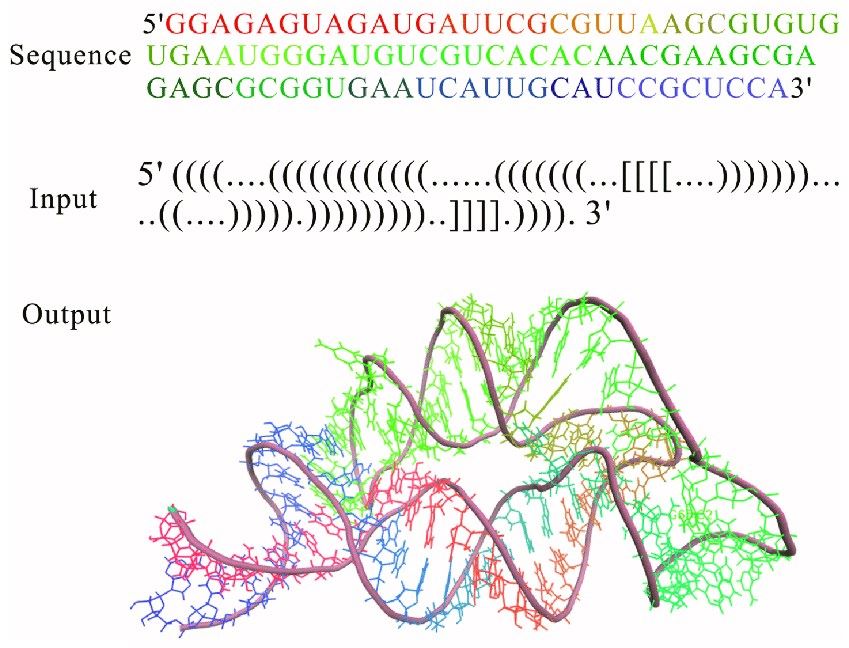 Fig. 1 3D structure for THF riboswitch aptamer predicted by using RNAComposer program online.1, 2
Fig. 1 3D structure for THF riboswitch aptamer predicted by using RNAComposer program online.1, 2
3D Structure Modeling Services at Creative Biolabs
Equipped with solid professional knowledge in aptamer 3D structure modeling and state-of-the-art technologies, Creative Biolabs provides a variety of solutions for aptamer 3D modeling for studying the mechanism of aptamer-target binding. There are two strategies for aptamer 3D modeling at Creative Biolabs:
-
Template-based modeling, also called homology modeling or comparative modeling. The procedure of template-based modeling generally consists of the following steps: (1) identification of a template structure associated with the target sequence; (2) alignment of the sequences of the target and templates; (3) constructing a 3D model of the aptamer from the alignment; (4) optimization of the models.
-
Free-based modeling, also called abinitio modeling. The strategy is used in the case of a lack of structural analogs in the reference libraries. The modeling mechanism is based on biophysical rules that simulate the process of folding using minimum free energy.
Table 1. Methods that have been used for modeling 3D structure for aptamers.1
|
Methods
|
Description
|
Availability
|
|
RNA Composer
|
A motif library-based method that uses the dictionary tailored from RNA FRABASED database to build initial 3D structure.
|
Web server
|
|
Rosetta
|
A fragment-based method that uses FARFAR optimizes RNA conformations in the context of a physically realistic energy function.
|
Local installation
|
|
RMdetect
|
A bioinformatics tool for identifying known 3D structural modules on genomic sequences.
|
Local installation
|
|
JAR3D
|
Scoring sequences to motif groups based on sequences’ ability to form the same pattern of interactions in motif.
|
Web server
|
|
RAGTOP
|
Predicting RNA topologies by a coarse-grained sampling of 3D graphs guided by statistical knowledge-based potentials.
|
Not available online
|
|
iFoldRNA
|
Incorporating SHAPE into discrete molecular dynamics to predict RNA structure.
|
Web server
|
Based on a variety of well-established 3D modeling methods such as RNA Composer, Rosetta, JAR3D, and iFoldRNA, we provide the best and affordable 3D modeling services for aptamers to support their functional research.
Advantages
-
Extensive experience in 3D modeling of aptamers
-
Strong project management
-
All-around services from the first concept to the final result
-
Short turnaround time
If you are interested in our aptamer 3D modeling services, please contact us for more details.
References
-
Gong, Sha, et al. "Computational methods for modeling aptamers and designing riboswitches." International journal of molecular sciences 18.11 (2017): 2442.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: When developing aptamers into drugs, information about the mechanism and structure of aptamer-target interactions is very useful. 3D structural modeling of aptamers can contain aptamer data as potential drug candidates and can be used to predict the unknown structure of aptamer-target molecule complexes. This leads to the design of optimal aptamers for target molecules and increases the efficiency and productivity of drug candidate selection.
A: We can consider aptamers with different targets, such as proteins, antibiotics, organophosphates, nucleobases, amino acids and drugs. Based on theoretical and experimental studies, it is possible to design aptamers that specifically bind to target molecules with high affinity and selectivity and to extend the design possibilities.
A: It starts with the structural prediction of the aptamer. Then, perform the docking of the target and aptamer. Next, perform MD simulations, which allow us to assess the stability of the aptamer/ligand complex and to determine the binding energy with a higher degree of accuracy. Then, analyze the aptamer/ligand interactions and mutate the studied aptamer. Subsequently, the entire process of molecular modeling can be repeated.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 3D structure for THF riboswitch aptamer predicted by using RNAComposer program online.1, 2
Fig. 1 3D structure for THF riboswitch aptamer predicted by using RNAComposer program online.1, 2