Creative Biolabs is proud to offer a range of anaphylatoxin receptor antagonist development services in a timely and cost-effective manner. With years of ample experiences in drug development, our scientists are confident in providing a full range of anaphylatoxin receptor antagonist development services to promote your complement therapeutics project success. We offer turn-key or ala carte services customized to our client’s needs.
Anaphylatoxins, or complement peptides, are fragments that are produced as part of the activation of the complement system. Complement components are large glycoproteins that have important functions in the immune response and host defense. They have a wide variety of biological activities and are proteolytically activated by cleavage at a specific site, forming a- and b-fragments. They cause smooth muscle contraction, histamine release from mast cells, and enhanced vascular permeability. C5aR and C3aR are the membrane-bound receptors for the complement system protein C5aR and C3aR, which are the target of inhibition against inflammatory diseases.
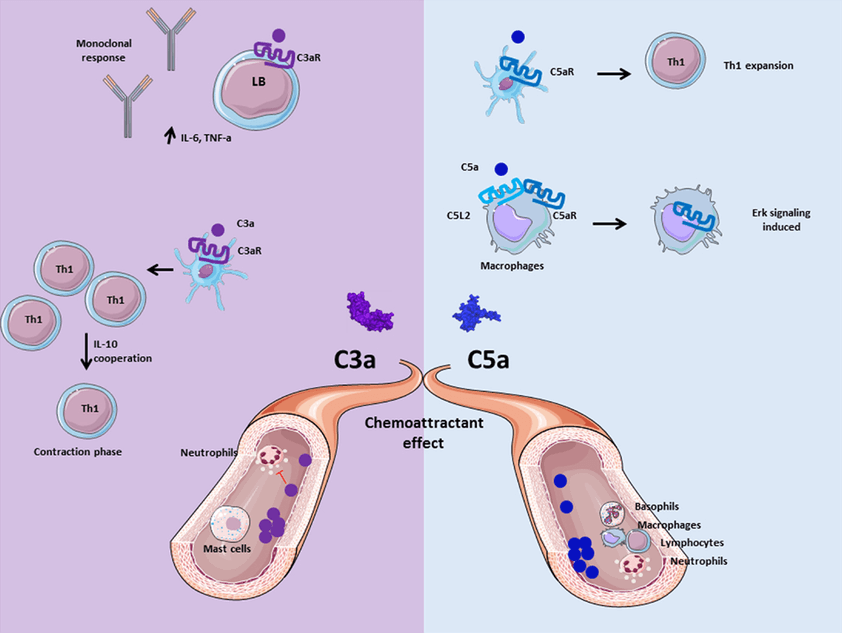
Fig. 1 Aptamers targeting coagulation factors.1, 2
C5aR
C5a binds two receptors, which are C5aR and C5L2. Most of the C5a functional effects occur through C5aR, and the pharmaceutical industry has focused on this receptor for the development of new anti-inflammatory therapies. However, the detrimental effects of uncontrolled C5a production have been implicated in various pathological conditions, making C5a and its receptors attractive targets for therapeutic intervention for inflammatory diseases. C5aR can be widely expressed, on both immune and nonimmune cells, and shows a dramatic pattern of regulation, especially in the tissues from mice undergoing the cecal ligation/puncture sepsis model. Signaling of C5aR involves intracellular calcium mobilization and activation of different pathways. So C5aR was the predominant, if not the only, receptor for chemotactic responses to C5a.
C3aR
Recent studies have pointed to a role for G-protein-coupled receptors in the trafficking of HSPCs, and recently presented evidence for the involvement of the G-protein-coupled complement C3a receptor (C3aR) in this process. The C3a anaphylatoxin is a 78-amino-acid peptide derived from the proteolytic cleavage of the complement protein C3, which mediates various immunoregulatory functions through its binding to C3aR. C3aR is predominantly expressed on the surface of human mast cells, eosinophils, monocytes, and activated T lymphocytes. Its major functions include chemotaxis of eosinophils and the recruitment and degranulation of mast cells.
Overproduced or upregulated C5aR and C3aR expression has been implicated in the pathogenesis of many inflammatory conditions, autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases. These include rheumatoid arthritis, respiratory distress syndrome, inflammatory bowel diseases and so on. So the receptors are attractive targets for therapeutic intervention in many diseases. Also, the antagonists for C5aR and C3aR have been studied and developed, which including:
-
PMX53
-
SB290157
Based on our advanced anaphylatoxin receptor antagonists strategy and well-developed complement therapeutic platform, Creative Biolabs is confident in proving anaphylatoxin receptor antagonist development services against a variety of complement component, especially for those which are essential for complement activities. Please contact us for more information or a detailed quotation.
References
-
Merle, Nicolas S., et al. "Complement system part II: role in immunity." Frontiers in immunology 6 (2015): 257.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: The pro-inflammatory activity of the allergenic toxin C5a is a driver of many complement-related diseases. Selective inhibition of C5a binding to its receptor offers a very promising opportunity to suppress the inflammatory response without depleting the defence potential of the complement. Macromolecular biologics either inhibit C5a production (anti-C5 antibodies and aptamers) or neutralise C5a-C5aR interactions by blocking the relevant binding sites.
A: C5aR and C3aR inhibitors are potential therapeutic targets for a variety of diseases, especially those with a common underlying mechanism of inflammation. These include conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, inflammatory bowel disease, multiple sclerosis, and asthma.
A: Recent advances in the development of anaphylatoxin receptor antagonists have focused on several different approaches. One approach involves the development of small molecule antagonists that can block the activation of anaphylatoxin receptors. For example, a number of compounds that act as antagonists of the C3a and C5a receptors have been identified and are being evaluated in preclinical and clinical studies. Another approach involves the use of monoclonal antibodies to block the activity of anaphylatoxins. Several anti-C5 antibodies are in development for the treatment of diseases such as paroxysmal nocturnal.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

