Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing long drug development cycles, difficulty in protein expression and purification, challenges in antibody development, or complex clinical trials? Our Creative Biolabs Complement Therapeutic services help you accelerate drug discovery, obtain high-quality recombinant proteins, develop highly specific antibodies, and streamline clinical trial processes through advanced recombinant DNA technology, high-throughput screening platforms, and innovative protein engineering techniques.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system, a vital component of the innate immune system, serves as a first line of defense against pathogens and plays a crucial role in maintaining tissue homeostasis. This complex network of soluble proteins and membrane-bound receptors, upon activation, orchestrates a rapid and potent immune response via three main pathways: classical, lectin, and alternative.
Click here to learn more information about specific inflammatory diseases:
While essential for host protection, the complement system's potent functions, including opsonization, direct cell lysis (MAC), and inflammatory mediator generation (anaphylatoxins C3a, C5a), become detrimental if dysregulated. Uncontrolled activation drives inflammation and tissue damage in conditions like autoimmune diseases (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus), inflammatory bowel disease, psoriasis, and ischemia-reperfusion injury. C3a and C5a act as chemoattractants, increasing vascular permeability and amplifying inflammation, while MAC causes cell lysis. Given its central role in inflammatory pathogenesis, the complement system is a key therapeutic target. Strategies involve inhibiting specific components or receptors to dampen excessive responses, precisely modulating the system to prevent pathogenic activation while preserving protective functions.
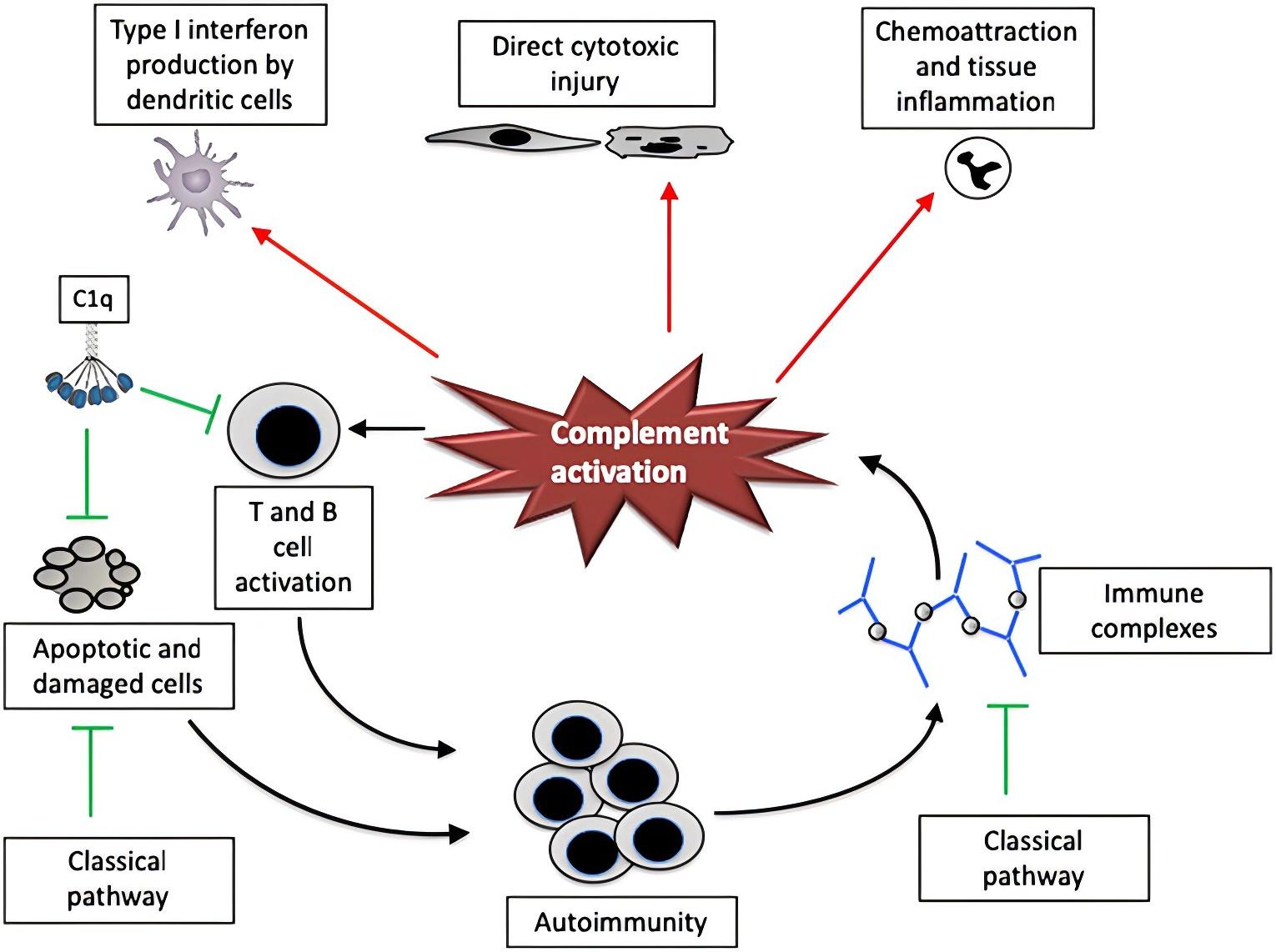
Fig. 1 The complement system plays a role in the pathogenesis of paradigmatic autoimmune disease.1
Complement elements fundamentally engage in multiple stages of inflammation, partially explaining their implication in inflammatory disorder pathogenesis. Complement's pathogenic contributions to inflammatory conditions may be analyzed from diverse viewpoints.
Complement Activation
During inflammation, complement triggering promotes inflammatory-mediated damage, evident in ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury, varied-etiology vasculitides, nephritis, and arthritis. Post-I/R injury, all three complement initiation routes participate in commencing complement cascade proteolytic cleavage.
Complement Deficiency
Shortages in inherent complement components or essential activation proteins may likewise provoke tissue damage, as evidenced in autoimmune responses.
Complement Regulator Dysregulation
Modified expression of complement control proteins, causing unchecked complement activation, can similarly induce tissue injury.
What We Can Offer?
Selecting Creative Biolabs signifies collaborating with a pioneer in cutting-edge biologic innovations. Our deep expertise and state-of-the-art platforms offer unparalleled advantages for your research:
-
Comprehensive Service Portfolio: A Full spectrum of services, from recombinant protein expression to in vivo disease models, provides a seamless therapeutic development workflow.
-
Advanced Technology Platforms: Cutting-edge technologies, including high-throughput screening, protein engineering, and robust assay development, ensure high-quality, accelerated results.
-
Precision Targeting: Focus on highly specific inhibitors and antibodies against key complement components (e.g., C3, C5, Factor B, Factor D, MASP-2) minimizes off-target effects, enhancing therapeutic safety and efficacy.
-
Proven Track Record: Our commitment to excellence is reflected in successful collaborations and impactful published data showcasing our capabilities.
-
Customized Solutions: Flexible approach allows us to tailor services to your unique research objectives, ensuring optimal outcomes.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive products and services for complement system research and therapeutic development in inflammatory diseases, designed to accelerate your progress and ensure reliable results:
Products:
-
Recombinant Complement Proteins: A wide range of high-purity recombinant human and animal complement proteins for in vitro studies.
-
Complement-Related Antibodies: Highly specific monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies targeting complement components for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic applications.
-
Complement Inhibitors: Small molecule and biologic inhibitors to block specific complement pathways, valuable for mechanistic studies and drug discovery.
Services:
-
Complement Protein Expression and Purification: Customized services ensuring high yield and biological activity.
-
Complement Activity Assays: Comprehensive functional assays for pathway activity and inhibition.
-
Developing and Engineering Antibodies: Custom solutions for medicinal antibody identification and enhancement.
-
Custom Research Services: Flexible partnerships to address unique complement biology challenges.
FAQs
Q: How can modulating the complement system specifically benefit inflammatory disease treatment?
A: Targeting the complement system offers a precise approach to disrupting the inflammatory cascade at its source. By inhibiting key components, it's possible to reduce the production of potent inflammatory mediators and prevent tissue damage, leading to more effective and potentially safer treatments for chronic inflammatory conditions.
Q: What are the primary challenges in developing therapeutics that target the complement system?
A: The complement system is highly complex, with multiple intertwined pathways. Challenges include ensuring specificity to avoid off-target effects, maintaining essential immune functions, and overcoming potential compensatory mechanisms. Careful design and rigorous testing are crucial for successful therapeutic development.
Q: Can complement-targeted therapies be applied to a broad range of inflammatory diseases?
A: Yes, given the complement system's fundamental role in inflammation, therapies designed to modulate its activity hold promise for a wide spectrum of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. The specific target within the complement cascade may vary depending on the disease's underlying pathology, allowing for tailored approaches.
Q: What kind of data is typically generated during the development of complement therapeutics?
A: Development involves generating extensive data, including in vitro functional assays (e.g., pathway activity, anaphylatoxin generation, MAC formation), binding kinetics, cell-based assays, and in vivo efficacy studies in relevant disease models. This information is essential for validating mechanisms of action and treatment prospects.
Q: How do these therapeutic approaches compare to conventional anti-inflammatory treatments?
A: While conventional treatments often focus on broad immunosuppression, complement-targeted therapies offer a more specific mechanism of action by directly addressing a key driver of inflammation. This specificity can lead to improved efficacy with potentially fewer systemic side effects, representing a significant advancement in inflammatory disease management.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner in advancing Complement System Therapeutic research and development for inflammatory diseases. We offer a comprehensive suite of products and services, backed by extensive expertise and cutting-edge technology, designed to accelerate your project from discovery to preclinical validation.
Featured Services
Feature Products
Reference
-
Thurman, Joshua M, and Roshini Yapa. "Complement Therapeutics in Autoimmune Disease." Frontiers in Immunology vol. 10 672. 3 Apr. 2019, DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00672. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: