Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in developing effective treatments for inflammatory conditions, particularly those involving complex immune responses like Salpingo-Oophoritis? Creative Biolabs' Complement System Therapeutic solutions help you advance your research and therapeutic development by precisely modulating the complement system, a key driver of inflammation and tissue damage. Our advanced antibody-based technologies offer a targeted approach to control pathological immune responses, leading to more effective and safer therapeutic interventions.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system, a crucial component of innate immunity, plays a dual role in host defense and inflammatory pathology. Comprising over 50 plasma and cell-surface proteins, it acts as a rapid and potent effector mechanism against pathogens and aberrant cells, while also contributing to tissue homeostasis and immune regulation. However, uncontrolled or inappropriate activation of the complement cascade can lead to significant tissue damage and contribute to the progression of various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Salpingo-Oophoritis, an inflammatory condition affecting the fallopian tubes (salpingitis) and ovaries (oophoritis), is often caused by ascending infections but can also have non-infectious inflammatory etiologies. The pathogenesis of Salpingo-Oophoritis involves a complex interplay of immune cells and inflammatory mediators, where the complement system is increasingly recognized as a significant contributor. During inflammation, complement activation, particularly through the classical and alternative pathways, leads to the generation of potent anaphylatoxins (C3a, C5a) and the formation of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC, C5b-9). C3a and C5a are powerful chemoattractants and activators of immune cells, promoting leukocyte recruitment and inflammatory cytokine release, which exacerbates tissue injury in the reproductive organs. The MAC can directly lyse cells, contributing to cellular damage within the fallopian tubes and ovaries. Dysregulation of complement control proteins can further amplify this destructive cycle. Understanding and therapeutically modulating the complement system in Salpingo-Oophoritis offers a promising avenue to mitigate inflammation, prevent fibrotic changes, and preserve reproductive health.
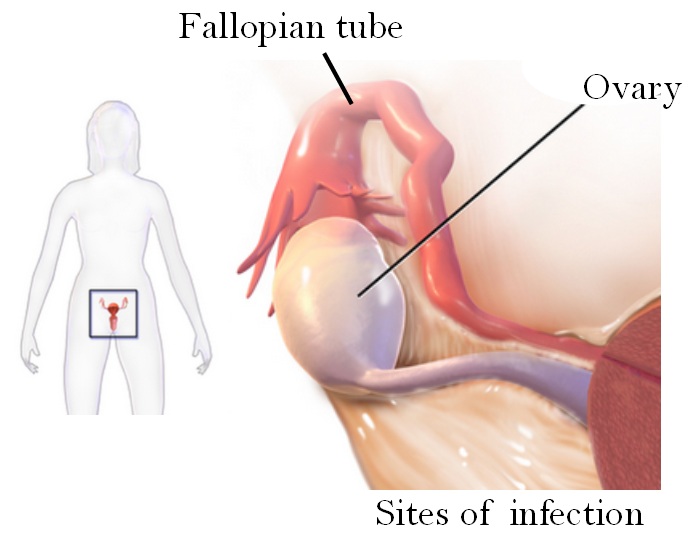 Distributed under Open Access license CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Fig.1 Sites of tubo ovarian abscess.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing comprehensive products and services to empower your research and therapeutic development in the field of complement system modulation.
-
Recombinant Complement Proteins: A wide array of high-purity recombinant human and animal complement proteins, including C1q, C3, C4, C5, Factor B, Factor D, Properdin, and various complement regulators, essential for research and assay development.
-
Anti-Complement Antibodies: A diverse catalog of highly specific antibodies targeting various complement components (e.g., anti-C3, anti-C5, anti-Factor B, anti-C1q), available for research, diagnostic, and potential therapeutic applications.
-
Complement Assay Kits: Ready-to-use ELISA kits and functional assay kits for measuring complement activation, C3/C4 deposition, MAC formation, and specific complement pathway activities (classical, alternative, lectin pathways).
-
Complement Drug Discovery Services: Comprehensive services including target identification and validation, high-throughput screening for complement inhibitors/activators, lead optimization, and in vitro / in vivo efficacy testing.
-
Antibody Development Services: Custom antibody generation (monoclonal, polyclonal, recombinant) against specific complement targets, including antibody engineering for enhanced specificity and affinity.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs leads in complement system therapeutic development, leveraging unparalleled expertise and cutting-edge platforms. Our commitment to scientific rigor ensures your projects benefit from the highest standards.
-
Advanced Therapeutic Modalities: We develop diverse complement modulators—monoclonal antibodies, recombinant proteins, and small molecules—tailored to specific therapeutic needs.
-
High-Throughput Screening Platforms: Our state-of-the-art screening capabilities accelerate discovery by rapidly identifying and optimizing lead compounds.
-
Comprehensive Functional Assays: We provide a full suite of in vitro and in vivo assays to rigorously evaluate complement therapeutic efficacy, specificity, and safety, including activation, hemolytic, and cell-based models.
-
Proven Track Record: Our success, supported by Published Data, demonstrates our ability to deliver high-quality, effective solutions for client projects.
-
Customized Project Support: We offer tailored solutions, collaborating closely with clients from concept to preclinical validation to meet unique project requirements.
Acquire the Creative Biolabs Edge – Inquire for Particulars Promptly
FAQs
Below are frequent inquiries about complement-targeting therapeutic strategies:
Q: How does modulating the complement system offer a therapeutic advantage in inflammatory diseases?
A: The complement system, while essential for immunity, can also drive inflammation and tissue damage when dysregulated. By specifically inhibiting or modulating key components of this cascade, it's possible to reduce excessive inflammatory responses, prevent bystander tissue injury, and mitigate disease progression without broadly immunosuppressing the patient. This directed methodology seeks to reestablish immunological equilibrium.
Q: Are there different strategies for targeting the complement system, and how do they differ in application?
A: Yes, various strategies exist, including inhibiting specific complement proteins (e.g., C3, C5, Factor B), blocking receptors for complement fragments (e.g., C5aR), or enhancing regulatory proteins. The choice of strategy depends on the specific disease pathology, the pathway predominantly involved, and the desired therapeutic outcome, allowing for tailored interventions.
Q: What are the potential challenges or precautions associated with complement-targeted therapies?
A: While highly targeted, modulating the complement system requires careful consideration to avoid compromising essential host defense mechanisms. Potential challenges include the risk of increased susceptibility to certain infections, particularly encapsulated bacteria, and off-target effects. Careful design, rigorous testing, and precise dosing are crucial to maximize therapeutic benefit while minimizing adverse effects.
Q: How do complement-targeted therapies compare to conventional anti-inflammatory treatments?
A: Conventional anti-inflammatory treatments often provide broad immunosuppression, which can lead to significant side effects. Complement-targeted therapies offer a more specific approach, aiming to interrupt a precise inflammatory pathway. This specificity can potentially lead to fewer systemic side effects and more effective control of complement-driven inflammation, particularly in diseases where complement plays a central role.
Q: In what types of inflammatory conditions is complement modulation most promising?
A: Complement modulation shows significant promise in conditions where uncontrolled complement activation is a primary driver of pathology. This includes various autoimmune diseases, certain kidney diseases, neurological disorders, and acute inflammatory conditions. Research continues to expand the understanding of the complement's role across a broader spectrum of inflammatory and infectious diseases.
Creative Biolabs' Complement System Therapeutic solutions provide advanced, targeted approaches for managing inflammatory conditions like Salpingo-Oophoritis. Our comprehensive suite of products and services, backed by deep scientific expertise, positions us as your ideal partner in developing innovative and effective therapies.
Featured Services
Feature Products
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: