Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing long drug development cycles, difficulty in protein expression and purification, challenges in antibody development, or complex clinical trials? Our Creative Biolabs Complement Therapeutic services help you accelerate drug discovery, obtain high-quality recombinant proteins, develop highly specific antibodies, and streamline clinical trial processes through advanced recombinant DNA technology, high-throughput screening platforms, and innovative protein engineering techniques.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
Pyoderma Gangrenosum (PG) is a rare, chronic, and debilitating inflammatory skin disease characterized by rapidly enlarging, painful, necrotic ulcers with undermined borders. Classified as a neutrophilic dermatosis, its pathogenesis is complex and involves significant dysregulation of both innate and adaptive immune responses. While the exact triggers remain elusive, an aberrant inflammatory response, particularly involving neutrophils, is a hallmark of the condition.
Recent research highlights the critical involvement of the complement system in the inflammatory cascade of PG. The complement system, a vital part of innate immunity, consists of a cascade of proteins that, when activated, play a crucial role in host defense but can also contribute to inflammatory tissue damage if dysregulated. In PG, evidence suggests an overactivation of complement pathways, leading to the generation of potent pro-inflammatory mediators. Specifically, the anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a are believed to be central players. C5a, a powerful chemoattractant, recruits and activates neutrophils, leading to their excessive infiltration into the skin lesions, a characteristic feature of PG. Furthermore, the formation of the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC, C5b-9) can contribute to cellular damage and perpetuate the inflammatory cycle. This sustained complement activation and subsequent neutrophil-driven inflammation contribute significantly to the non-healing nature and tissue destruction observed in PG ulcers. Understanding these intricate interactions provides a strong rationale for targeting specific complement components as a therapeutic strategy for PG.
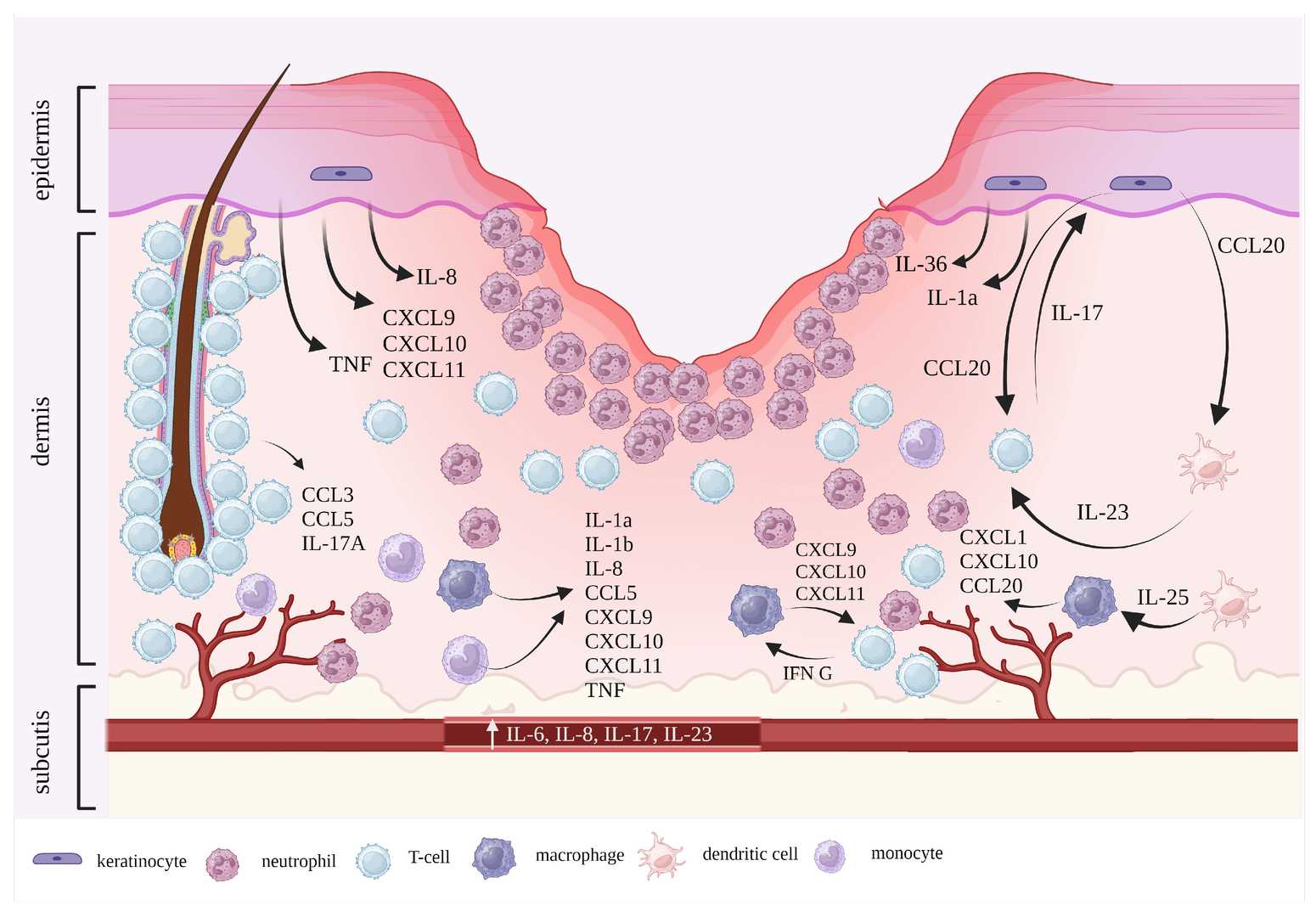
Fig. 1 PG pathogenesis in a contemporary perspective.1
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to support your therapeutic development efforts targeting the complement system in Pyoderma Gangrenosum and other inflammatory conditions:
-
Complement Component Assays: Quantitative analysis of complement proteins (e.g., C3, C4, C5, Factor B, Factor D) and activation products (e.g., C3a, C5a, sC5b-9) in various biological samples.
-
Complement Pathway Activity Assays: Functional assays to assess the activity of classical, alternative, and lectin pathways, and their modulation by test compounds.
-
Antibody and Small Molecule Development: Custom development and screening of therapeutic antibodies or small molecule inhibitors targeting key complement factors (e.g., anti-C5, anti-C5aR, anti-Factor D).
-
Recombinant Complement Proteins: Production of high-quality recombinant complement proteins and fragments for research and drug screening purposes.
-
Cell-Based Assays for Complement Biology: Development of specialized cell lines and assays to study complement-mediated cellular responses and inflammation.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of complement system therapeutics, offering unparalleled expertise and cutting-edge platforms specifically tailored for complex inflammatory conditions like Pyoderma Gangrenosum. Our dedication to methodological precision, advancement, and client achievement differentiates us.
-
Deep Scientific Expertise: Our team comprises seasoned immunologists and biochemists with extensive experience in complement biology and inflammatory disease mechanisms, ensuring a profound understanding of your project needs.
-
Advanced Technological Platforms: We utilize state-of-the-art high-throughput screening, protein engineering, and in vitro and in vivo assay systems for precise complement activity measurement and therapeutic candidate evaluation.
-
Customized Solutions: We offer flexible and bespoke service packages, adapting our capabilities to the unique requirements and objectives of each client's research and development pipeline.
-
Proven Track Record: Our methodologies have consistently yielded high-quality results, contributing to successful therapeutic development programs. (Published Data available upon request).
-
Quality and Reliability: Creative Biolabs adheres to stringent quality control standards at every stage, ensuring the integrity and reproducibility of all data and deliverables.
Obtain the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Request Details Immediately
FAQs
Q: How does modulating the complement system offer a new approach for treating inflammatory skin conditions?
A: Targeting specific components of the complement system can interrupt the inflammatory cascade at its source, reducing the recruitment and activation of immune cells like neutrophils that contribute to tissue damage. This offers a more precise therapeutic strategy compared to broad immunosuppression, potentially leading to better outcomes and fewer side effects.
Q: What are the primary challenges in developing complement-targeted therapies for complex inflammatory disorders?
A: Key challenges include ensuring target specificity to avoid off-target effects, understanding the intricate balance of complement activation and regulation, and developing robust in vitro and in vivo models that accurately reflect human disease pathology. Additionally, the complex nature of these disorders often requires a deep understanding of multiple interacting pathways.
Q: Can complement-targeted therapies be combined with existing treatments for inflammatory skin diseases?
A: In many cases, yes. Complement-targeted therapies are often designed to address specific mechanisms of inflammation, which can be complementary to existing treatments that may act through different pathways. Combination therapies could potentially offer enhanced efficacy and allow for lower doses of individual agents, thereby reducing side effects.
Q: Are there specific biomarkers that can indicate the effectiveness of complement-targeted interventions?
A: Yes, monitoring levels of complement activation products (e.g., C3a, C5a, sC5b-9) in patient samples can serve as valuable biomarkers to assess the engagement of the therapeutic agent with its target and the subsequent reduction in complement activation. Clinical markers related to inflammation and disease activity would also be crucial for evaluating therapeutic efficacy.
Q: What considerations are important when evaluating the safety of complement-modulating drugs?
A: Safety evaluation is paramount. It's crucial to assess potential risks, such as increased susceptibility to infections (especially encapsulated bacteria) due to the complement system's role in host defense. Careful dose titration, target specificity, and comprehensive preclinical and clinical safety assessments are essential to ensure a favorable risk-benefit profile.
Featured Services
Feature Products
Reference
-
Łyko, Magdalena et al. "The Pathophysiology and Treatment of Pyoderma Gangrenosum-Current Options and New Perspectives." International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 25,4 2440. 19 Feb. 2024, DOI:10.3390/ijms25042440. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: