Aptamers are short synthetic single-stranded (ss) DNA or RNA sequences that can specifically bind to a variety of substances such as proteins, chemical compounds, cells, and micro-organisms. They have been used in various fields of biology and medicine such as targeted gene therapy and drug delivery. Creative Biolabs is an excellent service provider and committed to providing the best custom aptamer development services for protein targets.
Introduction of Protein-based SELEX
SELEX is a well-established method for aptamer development. Conventional SELEX is, however, time and labor-consuming. Therefore, it is required to develop a high-performance SELEX approach to overcome these shortcomings. Protein-based SELEX is an improvement over traditional SELEX and is used for identifying new aptamers for a known purified intracellular or extracellular protein. Typically, target proteins are immobilized on the surface of beads and then incubated with an ssDNA/RNA library. After washing away unbound nucleic acids, the target-bound nucleic acid mixture is amplified by PCR. After approximately 3-4 rounds of selection, the enriched sublibrary is sequenced and the aptamers that specifically bind to the target protein are identified.
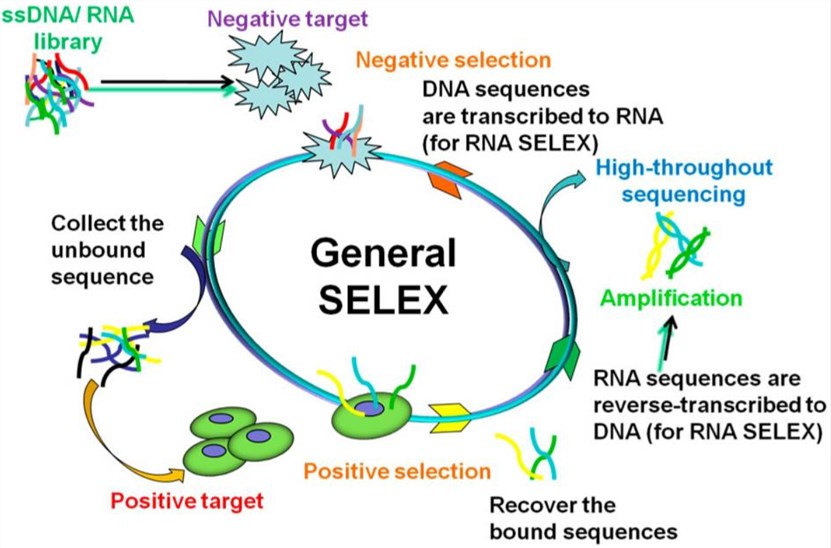
Fig. 1 General SELEX procedures.1, 2
Services
Creative Biolabs has a wealth of expertise in identifying high-affinity and high-specificity aptamers against the target protein through the SELEX method. Our excellent expert staff provides a variety of flexible and reliable selection strategies to meet the different purposes of your project. To improve the binding specificity and sensitivity of aptamers, a counter-target is used to perform a negative selection. Furthermore, we also can optimize some critical factors of SELEX procedure, such as library construction, separation scheme, ssDNA/RNA preparation, PCR amplification, and selection conditions to increase the success rate of high-specific aptamer screening.
Get your high-affinity aptamers by sending us a purified protein or just tell us the protein sequence, we also provide protein expression and purification services.
|
Service Item
|
Description
|
Time
|
|
Preparation of an ssDNA/RNA library
|
Chemically synthesize an ssDNA/RNA library with the capacity of 1×1013 to 1×1015
|
1 week
|
|
In vitroselection
|
Target incubation, binding sequence elution, and amplification; Repeat above procedures for 3~4 times to select target-bound sequences; Negative selection using counter-target is sometimes required to improve the specificity of target sequences
|
~4-5 weeks
|
|
NGS sequencing
|
Utilizing NGS sequencing, bioinformatics, and biophysical methods to obtain basic information of the candidate.
|
2 weeks
|
|
Aptamer synthesis
|
High-quality Aptamer synthesis and purification by HPLC, with MS report
|
1 week
|
|
Modifications
|
Different needs and applications chose different modifying methods, such as biotin, 5’-NH2, 5’-thiol, Fluorescent dyes…
|
2 weeks
|
|
Binding affinity test
|
Technologies like flow cytometry, ITC, SPR, QCM, etc. are used for KD determination.
|
1 week
|
Advantages
-
Experienced expert team
-
Advanced and powerful technologies
-
Customized experimental scheme according to special purposes
-
More efficient, cost-effective, and less time-consuming
If you are interested in our protein-based SELEX services for aptamer development, please contact us for more details.
References
-
Wu, Xiaoqiu, et al. "Potential diagnostic and therapeutic applications of oligonucleotide aptamers in breast cancer." International journal of molecular sciences 18.9 (2017): 1851.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Protein-based SELEX offers several advantages, including high specificity, customizability, and potential for therapeutic use. The process identifies aptamers with high specificity and affinity for complement proteins.
A: Selection stringency can be controlled by adjusting conditions such as incubation time, temperature, and the concentration of target protein. Increasing stringency selectively amplifies high-affinity aptamers.
A: The key steps include incubating a random library of oligonucleotides with the target protein, partitioning bound and unbound oligonucleotides, amplifying the bound oligonucleotides, and repeating these steps through multiple rounds to enrich for aptamers with high affinity and specificity.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

