Product List Background CRIg Functional Service
Background
Complement receptor of immunoglobulin family (CRIg), also known as V-set and immunoglobulin domain-containing protein 4 or Z39Ig, is a member of B7 family proteins encoded by VSIG4 gene located on the human X chromosome. CRIg was later identified as a novel complement receptor expressed by macrophages, which binds to C3b, iC3b, and C3c molecules. CRIg is a type 1 transmembrane protein composed of 399 amino acids, presenting in two alternatively spliced forms, CRIg(L) and CRIg(S). Both two human CRIg isoforms contain an N-terminal IgV-type immunoglobulin domain, and CRIg(L) contains an additional IgC-type immunoglobulin domain at the membrane-proximal end. Mouse CRIg lacks the IgC-type immunoglobulin domain, resembling the CRIg(S) form. The IgV-type immunoglobulin domain is significant for the binding of CRIg to complement fragments and CRIg-related phagocytosis.
CRIg specifically recognizes the beta chain of C3b and iC3b that are deposited on particle surfaces, playing a critical role in C3-mediated opsonization. The extracellular domain of CRIg was found to block the activation of complement alternative pathway, of which inhibitory mechanism is unclear. Moreover, CRIg also has been indicated to be implicated in multiple functions, including the clearance of the intracellular pathogens by Kupffer cells, the regulation of T-cell proliferation, and adaptive immune responses. The IgV domain of CRIg fusion with other functional proteins has been shown to have relieved effects on diseases in animal models, such as traumatic brain injury, arthritis, uveitis, and so forth.
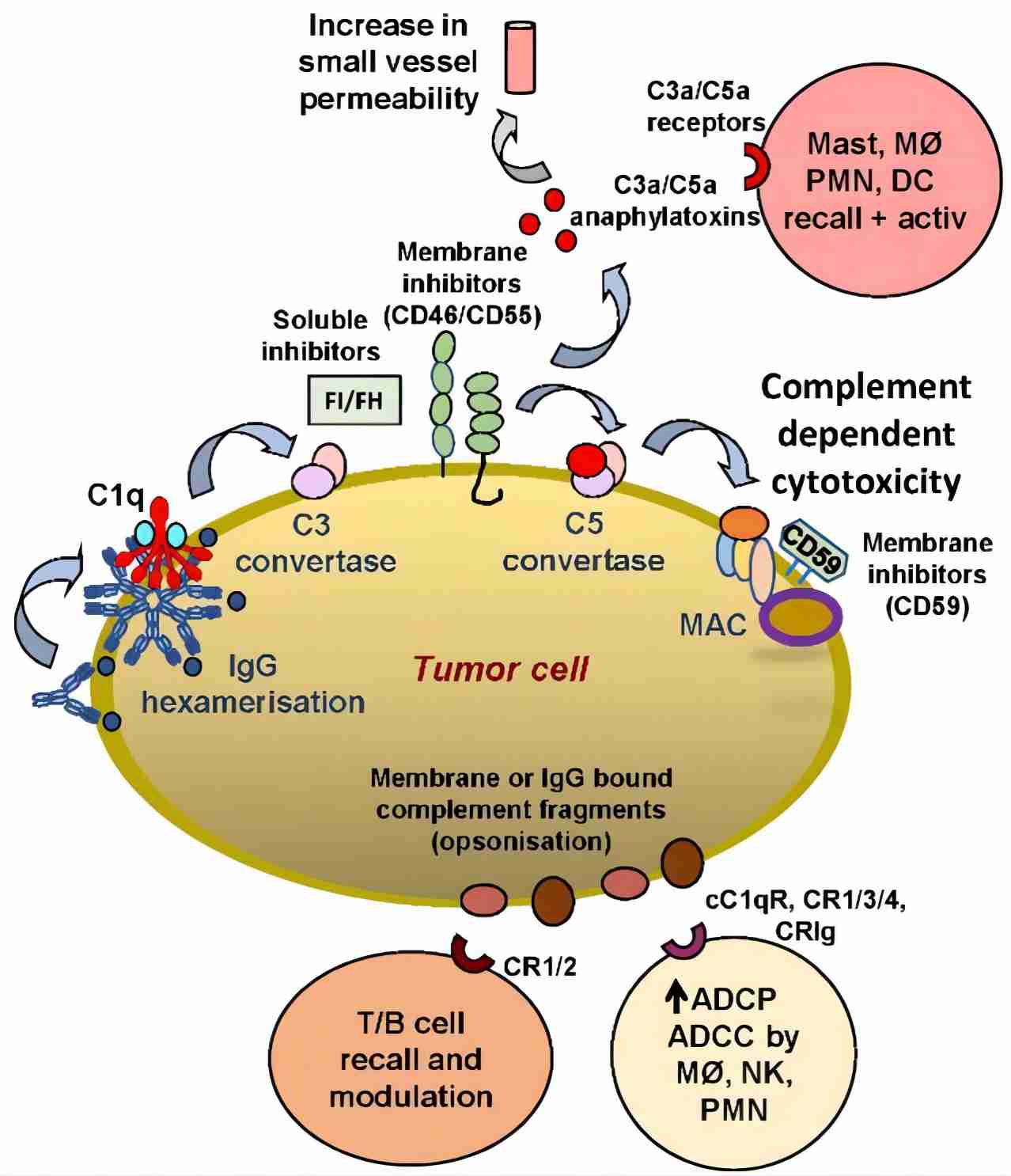 Fig. 1 CRIg’s functionality in tumor cells.1, 3
Fig. 1 CRIg’s functionality in tumor cells.1, 3
CRIg Functional Service
Creative Biolabs delivers a comprehensive suite of CRIg-related offerings, including anti-CRIg antibodies, CRIg detection ELISA kits, and CRIg proteins. These carefully crafted resources are essential in advancing research endeavors aimed at formulating therapeutic strategies for a broad spectrum of diseases.
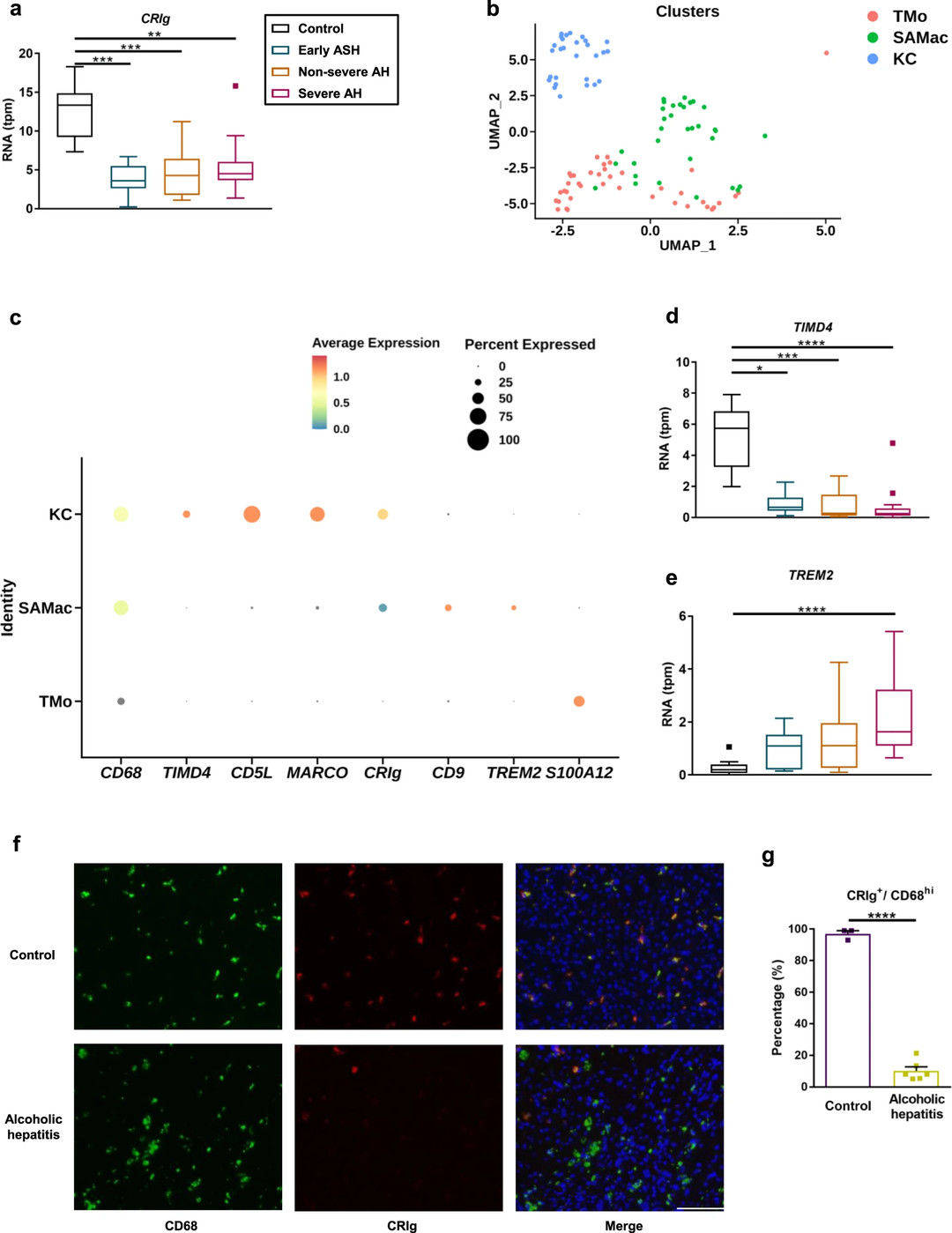 Fig.2 Reduced CRIg expression on hepatic macrophages in individuals with alcohol-induced liver pathology.2, 3
Fig.2 Reduced CRIg expression on hepatic macrophages in individuals with alcohol-induced liver pathology.2, 3
Researchers have elucidated that the complement receptor, CRIg, part of the immunoglobulin superfamily and located on liver macrophages, is vital for immune competency by binding complement C3b or Gram-positive bacteria to facilitate phagocytosis. While pivotal in several immune-mediated diseases, its precise mechanism in maintaining physiological balance remains mysterious. Through RNA sequencing and immunofluorescence staining of CRIg in liver sections, researchers uncovered diminished CRIg in patients’ liver tissues. CRIg-deficient mice faced aggravated alcohol-related liver disease compared to wild types, with a reduction in severity observed upon toll-like receptor 2 loss. These mice also showed reduced efficacy in eliminating Enterococcus faecalis from the liver. Treatment with soluble CRIg–Ig protein mitigated ethanol-induced hepatic damage, suggesting that reduced hepatic CRIg hampers pathogen clearance and accelerates liver disease progression.
Creative Biolabs offers a suite of customized services focusing on CRIg, including comprehensive interaction evaluations and complementary functional solutions. These services are precisely designed to assist prestigious clients in their scientific investigations and clinical endeavors.
References
-
Golay, Josée, and Ronald P. Taylor. "The role of complement in the mechanism of action of therapeutic anti-cancer mAbs." Antibodies 9.4 (2020): 58.
-
Duan, Yi, et al. "CRIg on liver macrophages clears pathobionts and protects against alcoholic liver disease." Nature communications 12.1 (2021): 7172.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig. 1 CRIg’s functionality in tumor cells.1, 3
Fig. 1 CRIg’s functionality in tumor cells.1, 3
 Fig.2 Reduced CRIg expression on hepatic macrophages in individuals with alcohol-induced liver pathology.2, 3
Fig.2 Reduced CRIg expression on hepatic macrophages in individuals with alcohol-induced liver pathology.2, 3
