Adriamycin induced Nephropathy (AN) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers reliable platforms to assess drug efficacy across various mechanisms, ensuring high-quality, reproducible data for informed decision-making in the drug development pipeline.
Introduction
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive, debilitating condition defined by persistent structural or functional abnormalities of the kidney, lasting for three months or more, with profound implications for global health. The primary measure of disease severity is the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and the level of albuminuria. CKD is stratified into five stages (G1 to G5) based on declining GFR, and three categories (A1 to A3) based on albumin excretion, with stages G4 and G5 representing advanced renal failure requiring renal replacement therapy. The most prevalent forms of CKD include Diabetic Nephropathy, which accounts for up to 50% of cases globally, and Hypertensive Nephropathy, both characterized by progressive glomerulosclerosis and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Other significant forms include various types of primary and secondary Glomerulonephritis, Polycystic Kidney Disease, and drug-induced kidney injury. The pathogenesis of CKD is complex, involving chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, podocyte damage, and the activation of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS), all contributing to the irreversible scarring of renal tissue. The lack of highly effective treatments capable of halting or reversing fibrosis underscores the critical need for robust preclinical models.
Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy (AN) Model
This advanced research platform is created by administering a single intravenous or intraperitoneal injection of the chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin (Adriamycin) to susceptible rodent strains, typically Balb/c mice or Sprague-Dawley rats, which induces reproducible and progressive renal injury. A key feature of this model is the development of a nephrotic syndrome phenotype, including hyperlipidemia and edema, within a few weeks, making it an excellent system for studying glomerular basement membrane integrity and podocyte-specific interventions. The model's main strength lies in its high reproducibility, relatively short induction time compared to diabetic models, and its specific relevance to studying the mechanism of podocyte injury and the progression of glomerulosclerosis. However, a drawback is that it primarily represents non-inflammatory proteinuric nephropathy, thus limiting its application for treatments specifically targeting systemic inflammatory CKD causes.
Simulates:
- Primary and secondary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
- Podocyte-mediated Proteinuric Nephropathy
- Glomerular basement membrane injury and foot process effacement
- Nephrotic Syndrome phenotype (proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, hyperlipidemia)
Evaluates Drugs:
- Anti-proteinuric agents (e.g., specific RAAS inhibitors, novel endothelin receptor antagonists)
- Podocyte-protective agents and cytoskeleton stabilizers
- Anti-fibrotic compounds that target the TGF-β or Wnt/β-catenin pathways
- Anti-oxidative stress therapies (e.g., Nrf2 activators)
- Potential immunosuppressants for nephrotic syndrome
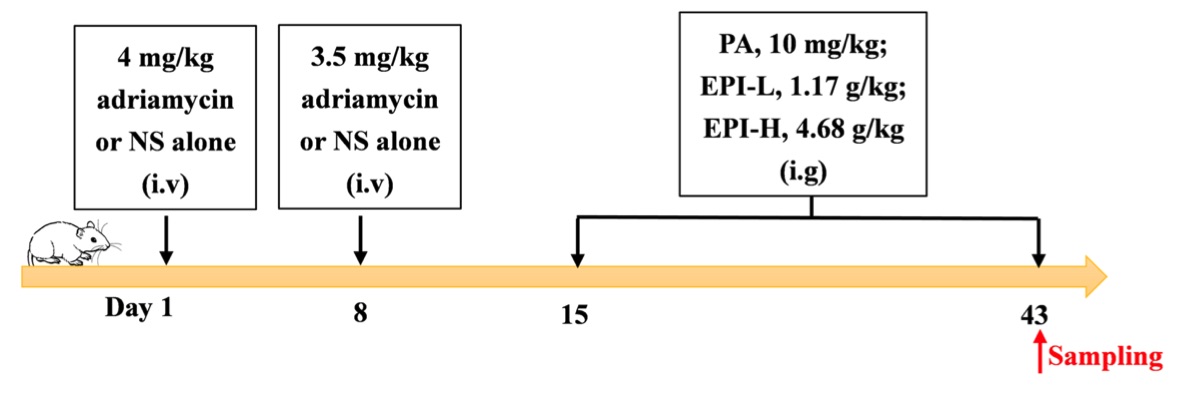 Fig. 1 Timeline of the adriamycin‐induced nephropathy model.1,3
Fig. 1 Timeline of the adriamycin‐induced nephropathy model.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We offer a diverse range of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the renal disease model, employing a suite of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:- General Observations: Monitoring of body weight, survival rate, presence, and severity of ascites/edema, and 24-hour urine output volume.
- Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry (IHC): Evaluation of the Glomerulosclerosis Index (GSI) via Periodic acid–Schiff (PAS) staining, assessment of tubulointerstitial fibrosis using Masson's Trichrome staining, and quantification of podocyte density or injury markers (e.g., WT1, Synaptopodin) via IHC.
- Biochemistry and Urine Analysis (ELISA/Kits): Measurement of 24-hour total urine protein excretion (Proteinuria), Urinary Albumin-to-Creatinine Ratio (UACR), Serum Creatinine, Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN), Total Serum Cholesterol, and Serum Albumin levels.
- Molecular Analysis: Gene and protein expression profiling of key fibrosis mediators (e.g., α-SMA, Collagen I/III, TGF-β1), podocyte injury markers (e.g., Nephrin, Podocin), and inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α) via RT-qPCR and Western Blot techniques.
Related Services
While this model is invaluable for studying podocyte injury, we recognize that CKD pathogenesis is multifactorial. Therefore, we also offer alternative established models to cover a broader spectrum of renal pathologies.
- Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) Model
- Bilateral Ureteral Obstruction induced Renal Fibrosis Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Folic Acid (FA) induced Renal Fibrosis Model
- Adenine induced Chronic Renal Failure Model
Our advantages
- Deep Expertise in Glomerular Diseases: Our dedicated nephrology team possesses specialized, hands-on knowledge in podocyte biology and glomerulosclerosis, ensuring accurate model execution, interpretation, and troubleshooting.
- Rigorous Quality Control: We utilize standardized operating procedures (SOPs) and internal metrics for baseline measurements (e.g., proteinuria onset) to guarantee model consistency and reproducibility across all study cohorts.
- Translational Endpoint Panel: Beyond standard histological and biochemical analysis, we offer advanced, state-of-the-art molecular profiling (e.g., spatial transcriptomics) to identify novel and clinically relevant biomarkers.
- Comprehensive Data Analysis: Full-service support is provided from initial study design to final report generation, including rigorous statistical analysis and personalized scientific consultation to accelerate client decision-making.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the primary advantage of this model over other CKD models?
The main advantage is its specific and early induction of a nephrotic syndrome phenotype, primarily due to direct podocyte damage, making it uniquely suited for testing therapeutics aimed at preserving podocyte health and reducing proteinuria.
-
2. Are there any strain limitations for implementing this model?
Yes, susceptibility varies significantly. We primarily use Balb/c or C57BL/6 mice and Sprague-Dawley rats, as these strains reliably develop proteinuria and subsequent glomerulosclerosis following drug administration.
-
3. Can you perform long-term efficacy studies with this model?
While the acute injury is rapid, the subsequent glomerulosclerosis progresses over several weeks. We commonly run therapeutic studies for 6 to 10 weeks to assess long-term anti-fibrotic effects, though the model severity is high.
Published Data
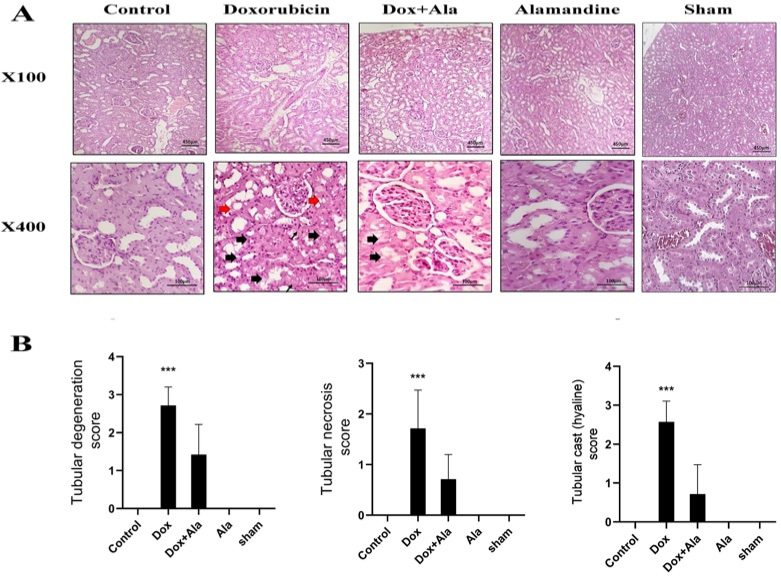 Fig. 2 Histopathologic sections of kidneys from different experimental groups.2,3
Fig. 2 Histopathologic sections of kidneys from different experimental groups.2,3
Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stained kidney sections from various experimental groups were analyzed histologically. Kidney sections from the alamandine-treated group exhibited no significant histopathological changes. In contrast, the kidneys of animals treated with doxorubicin (DOX) showed severe tubular degeneration, the presence of tubular casts, and moderate tubular necrosis. Co-treatment with alamandine significantly reduced these pathological changes, as evidenced by improved tissue morphology (Fig. 2).
References
- Soltani Hekmat, Ava et al. "Protective effect of alamandine on doxorubicin‑induced nephrotoxicity in rats." BMC Pharmacology & Toxicology vol. 22,1 31. 29 May. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40360-021-00494-x
- Wang, Ru et al. "Epimedium sagittatum Maxim ameliorates adriamycin-induced nephropathy by restraining inflammation and apoptosis via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway." Immunity, Inflammation, and Disease vol. 11,6 (2023): e904.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
