Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of advanced models, including those for diabetic nephropathy, hypertensive nephropathy, and the unilateral ureter obstruction (UUO) model, to assess drug efficacy and facilitate preclinical research on chronic kidney disease therapies.
Introduction
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a progressive condition characterized by the gradual deterioration of kidney function, which can eventually lead to end-stage renal failure if not managed properly. The disease is commonly caused by underlying conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, glomerulonephritis, and polycystic kidney disease. In its early stages, CKD often remains asymptomatic, making early diagnosis challenging. As the disease advances, symptoms such as fatigue, edema, high blood pressure, and changes in urine output become more evident. The most common laboratory indicators of CKD include elevated serum creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels, as well as the presence of proteinuria. CKD can lead to severe complications, including cardiovascular disease and electrolyte imbalances, and often requires dialysis or kidney transplantation at advanced stages.
Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) Model
The Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) model is a widely used animal model to study the progression of kidney fibrosis and chronic kidney disease. This model is typically induced by obstructing one of the ureters in rodents, leading to hydronephrosis and renal injury. The UUO model closely mimics the pathological processes of CKD, including tubulointerstitial fibrosis, glomerulosclerosis, and inflammation. It is commonly used to evaluate the efficacy of potential drug candidates aimed at mitigating fibrosis and improving kidney function. The UUO model allows for monitoring the onset of renal damage and fibrosis over time, offering insights into the molecular mechanisms involved in CKD. However, a limitation of this model is that it primarily represents unilateral injury, which may not fully replicate bilateral renal damage seen in some human cases of CKD.
- Simulates: The UUO model simulates chronic kidney disease, specifically focusing on kidney fibrosis, inflammation, and functional impairment.
- Evaluates Drugs: The model is ideal for testing anti-fibrotic agents, anti-inflammatory drugs, and nephroprotective compounds. It can evaluate therapies aimed at reversing or preventing fibrosis, reducing inflammation, or improving renal function. Drug candidates targeting pathways such as TGF-β signaling, oxidative stress, and apoptosis are often tested in this model.
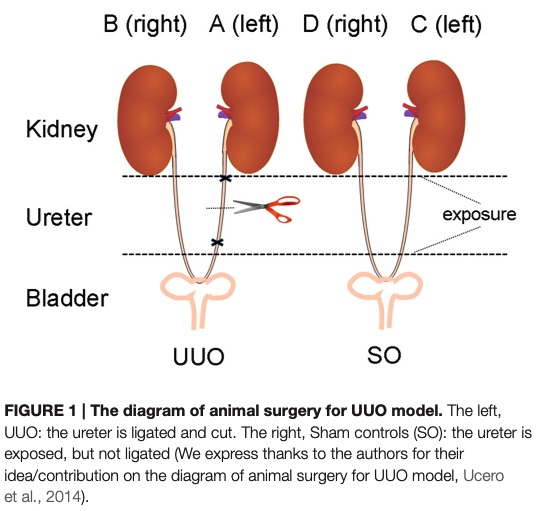 Fig. 1 The diagram of animal surgery for UUO model.1,3
Fig. 1 The diagram of animal surgery for UUO model.1,3
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We offer a range of measurements to assess the effectiveness of treatments in the UUO model, utilizing advanced techniques such as:- General Observations: Monitoring body weight, renal function (creatinine and blood urea nitrogen), and urine output.
- Histological Assessment: Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining to evaluate structural changes, as well as Masson's trichrome for fibrosis.
- Immunohistochemistry: Analyzing immune cell infiltration (macrophages, T-cells) and markers of fibrosis (e.g., collagen I, α-SMA).
- Gene Expression Profiling: RT-qPCR for markers of inflammation (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1β) and fibrosis (e.g., TGF-β, Col1a1).
- Protein Analysis: Western blot for detecting the expression of key proteins involved in fibrosis and inflammation.
- Functional Parameters: Measurement of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) and renal blood flow (RBF).
Additionally, our expert team provides custom experimental design, model selection, and data analysis to ensure accurate and tailored results.
Related Services
In addition to the UUO model, we offer other CKD models. These models complement the UUO system for comprehensive drug evaluation.
- Bilateral Ureteral Obstruction-Induced Renal Fibrosis Model
- 5/6 Nephrectomy Model
- Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy (AN) Rodent Model
- Folic acid (FA)-Induced Renal Fibrosis Model
Our advantages
- Established Model: The UUO model is a well-validated and reproducible platform widely used in renal research.
- Tailored Solutions: Our team offers customized protocols and analytical services to meet specific research needs.
- Comprehensive Assessment: We provide a full range of histological, molecular, and functional assays to evaluate drug effects.
- Cutting-Edge Technology: Access to advanced tools such as gene expression profiling and live animal imaging.
- Expert Support: Benefit from our team's expertise in study design, data interpretation, and result validation.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the UUO model used for?
The UUO model is primarily used to simulate kidney fibrosis and study chronic kidney disease, enabling researchers to test various drugs targeting fibrosis, inflammation, and kidney function.
-
2. How long does it take to observe significant fibrosis in this model?
Significant fibrosis typically becomes evident within 7 to 14 days post-ureteral obstruction, depending on the severity of the injury and the study design.
-
3. Can the UUO model be used for testing gene therapies?
Yes, the UUO model is suitable for evaluating gene therapies targeting renal fibrosis and inflammation, as well as assessing the molecular mechanisms of disease progression.
-
4. Is this model applicable to human kidney diseases?
While the UUO model is a useful preclinical tool, it primarily represents unilateral kidney injury, which may not fully mimic bilateral CKD observed in humans. However, it is highly relevant for understanding fibrotic processes.
Published Data
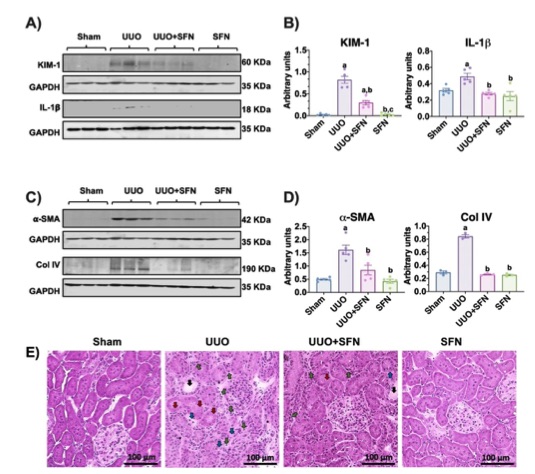 Fig. 2 Sulforaphane (SFN) reduces kidney damage in the unilateral ureteral obstruction.2,3
Fig. 2 Sulforaphane (SFN) reduces kidney damage in the unilateral ureteral obstruction.2,3
Renal damage induced by UUO and its potential improvement with SFN were evaluated through histological analysis and biomarker measurements. These markers were significantly elevated in the UUO group, whereas SFN treatment effectively prevented this increase (Figure 2A, B). In addition, fibrosis markers such as α-SMA and Col IV were significantly reduced in the UUO + SFN group compared to the UUO group (Figure 2C, D). Histological examination using H&E staining revealed that UUO caused notable structural damage, including loss of tubular integrity, epithelial cell loss, tubular dilatation, leukocyte infiltration, and increased connective tissue deposition. However, these alterations were less pronounced in the UUO + SFN group, indicating a protective effect of SFN treatment. These findings suggest that SFN significantly mitigates renal damage in the UUO model.
References
- Li, Zhenyu et al. "Kidney Tissue Targeted Metabolic Profiling of Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction Rats by NMR." Frontiers in pharmacology vol. 7 307. 15 Sep. 2016. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2016.00307
- Aranda-Rivera, Ana Karina et al. "Sulforaphane Protects against Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction-Induced Renal Damage in Rats by Alleviating Mitochondrial and Lipid Metabolism Impairment." Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 11,10 1854. 20 Sep. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101854">https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox11101854
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
