Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced Cystitis Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Creative Biolabs offers a variety of advanced models to evaluate the efficacy of drugs targeting cystitis, including both acute and chronic models, providing comprehensive solutions for preclinical research and drug development.
Introduction
Cystitis refers to the inflammation of the bladder, commonly caused by bacterial infections, but it can also result from non-infectious causes such as chemical irritation, trauma, or autoimmune disorders. The most common form of cystitis is urinary tract infection (UTI)-associated cystitis, which often manifests with symptoms like frequent urination, burning sensations, pelvic pain, and hematuria (blood in urine). Other forms of cystitis, such as interstitial cystitis, are chronic and non-infectious, characterized by bladder pain and discomfort, often with a difficult-to-diagnose origin. The inflammation in cystitis is typically driven by immune responses to infections or irritants, leading to the release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators that exacerbate symptoms.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Cystitis Model
The LPS-induced cystitis model is constructed by administering LPS intraperitoneally or intravesically, leading to inflammation in the bladder tissue. This model accurately represents the acute inflammatory phase of cystitis, displaying classic symptoms such as bladder edema, neutrophil infiltration, and increased cytokine production. The model's strength lies in its ability to replicate key features of human cystitis, making it a reliable tool for testing potential therapies. However, one limitation is that it may not fully replicate chronic cystitis, and long-term observations are required to assess the model's complete range of potential applications.
- Simulates: This model effectively simulates bladder inflammation and infection, providing insights into conditions like interstitial cystitis, bacterial cystitis, and inflammatory bladder diseases.
- Evaluates Drugs: It is used to evaluate various pharmacological interventions, including anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, and treatments targeting bladder pain.
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat.
-
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in the LPS-induced cystitis model, utilizing advanced technologies, including but not limited to:- General observations: Bladder weight, gross tissue appearance, and behavioral changes such as micturition frequency and pain response.
- Histopathological analysis: Hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining to evaluate bladder tissue morphology, inflammation, and edema.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): Levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and other mediators.
- Gene expression analysis: RT-qPCR to assess the expression of key inflammatory genes, including TLR4, NF-kB, and other markers of immune activation.
- Urinary biomarkers: Detection of urinary protein, cytokines, or other markers that correlate with inflammation.
In addition to these, our scientific team is available to assist with experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your research.
Related Services
In addition to the LPS-induced cystitis model, we also provide services for other models of cystitis, including chemical-induced models and infection models, each tailored to specific research objectives.
Cyclophosphamide (CYP)-Induced Cystitis Model
Our advantages
- Expertise: A dedicated team of scientists ensures customized solutions tailored to your research needs.
- Comprehensive Data Analysis: In-depth data collection and analysis to support all stages of your research.
- Reliable Results: Reproducible outcomes to ensure the validity of your findings.
- Flexible Options: Multiple models available to evaluate both acute and chronic cystitis.
- State-of-the-art Facilities: Cutting-edge research tools and technologies for advanced measurements.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What is the LPS-induced cystitis model used for?
This model is used to study bladder inflammation and evaluate the efficacy of potential drugs for treating cystitis, interstitial cystitis, and other inflammatory bladder conditions.
-
2. How long does it take to observe the effects of LPS treatment in the model?
The inflammatory response is typically observed within 24-48 hours after LPS administration, with peak effects seen in the first few days.
-
3. Can this model be used to study chronic cystitis?
While this model primarily simulates acute inflammation, it can be adapted for chronic studies with prolonged treatment and observation.
Published Data
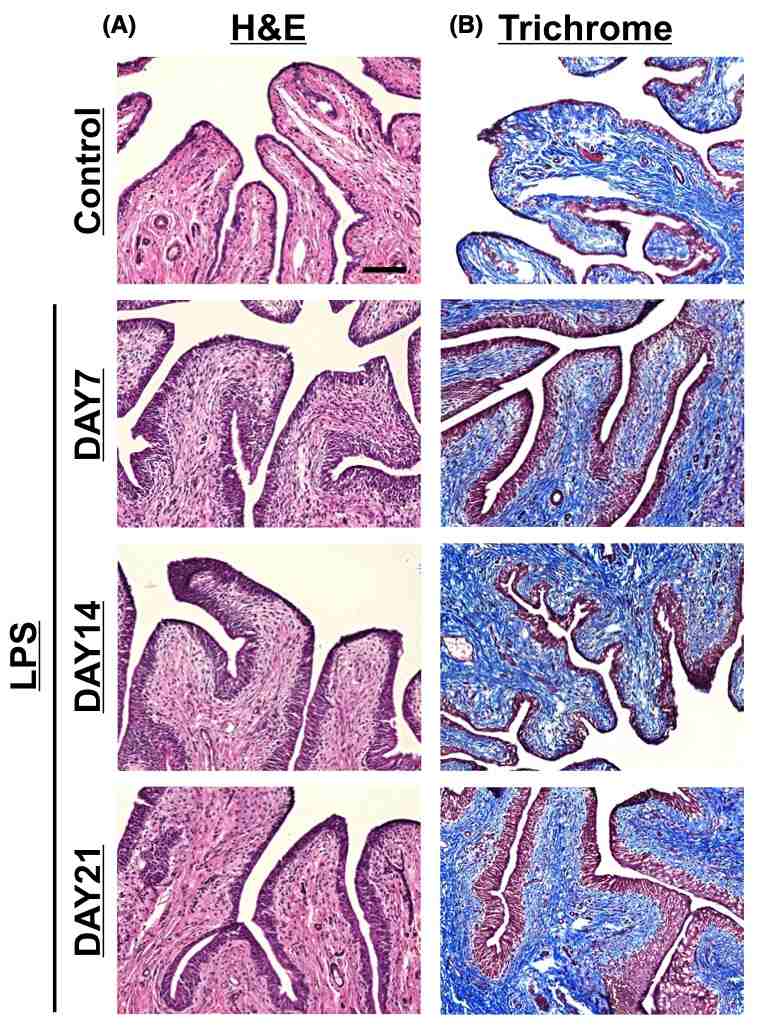 Fig. 1 Histological findings of LPS-induced chronic bladder inflammation. 1
Fig. 1 Histological findings of LPS-induced chronic bladder inflammation. 1
Chronic inflammation induced by repeated intravesical administrations of LPS was observed to persist for up to 21 days after the initial injection (Figure 1). Histological examination using H&E staining revealed a mixed inflammatory cell infiltrate, predominantly consisting of macrophages and lymphocytes. Additionally, an increased number of urothelial cells and abnormal thickening of the re-epithelialization layer were noted in the LPS-injected group compared to the saline-treated control group (Figure 1A). Masson's trichrome staining demonstrated an increase in bladder tissue fibrosis, highlighted by the blue coloration, in the LPS-treated group relative to the control group (Figure 1B).
Reference
- Yoshizumi, Masaru et al. "Gabapentin reduces painful bladder hypersensitivity in rats with lipopolysaccharide-induced chronic cystitis." Pharmacology Research & Perspectives vol. 9,1 (2021): e00697. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1002/prp2.697
For Research Use Only.
