Urological System Disease Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Services
Creative Biolabs provides a variety of advanced models, including rodent, large animal, and humanized models, to assess the efficacy of treatments for urological system diseases. These models are designed to support drug development and therapeutic evaluation, offering comprehensive solutions for preclinical research.
Introduction
The urological system encompasses the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, and diseases of this system can significantly impact overall health. Common urological disorders include urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, bladder cancer, interstitial cystitis, and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Kidney diseases like chronic kidney disease (CKD) and glomerulonephritis are also prevalent, often leading to renal failure. Urological cancers, such as bladder and prostate cancer, are major concerns due to their high incidence and significant impact on quality of life. These diseases can result from genetic, environmental, or lifestyle factors, and they often present with symptoms like frequent urination, pain, blood in the urine, or difficulty urinating. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to managing these conditions effectively and preventing complications such as kidney failure or metastasis in cancers.
Urological System Disease Models
Creative Biolabs offers a wide range of well-established models for urological system diseases, including models for urinary tract infections (UTIs), kidney stones, bladder cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and other urological disorders. These models are meticulously developed to mirror critical aspects of human urological diseases, providing a reliable platform for preclinical evaluation of therapeutic candidates. Our models come with comprehensive assessments of urological parameters such as kidney function, urinary biomarkers, bladder function, and tumor progression, offering valuable insights into the effects of potential treatments. Our expert team of scientists will guide you through every stage of the project, from experimental design to data analysis, ensuring high-quality and reproducible results. To learn more about the urological disease models available for preclinical research, please explore the links below:
- Gentamicin Induced Acute Renal Failure Model
- Cisplatin Induced Acute Renal Injury Model
- Glycerol Induced Acute Renal Failure Model
- Contrast Agent Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Folic Acid Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Cecal Ligation & Puncture (CLP) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Growth Hormone-Releasing Hormone (GHRH) Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Anti-TSHR Antibody Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Aristolochic Acid A Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- Renal Ischemia-Reperfusion (IR) Model
- Obesity related Glomerulopathy Model
- Diabetic Nephropathy Model
- HDF-CHOL & Salt Feed & 5/6 Nephrectomy Induced Nephropathy Model
- Rat Warm Kidney Graft Transplant Model
- Rat Delayed Kidney Graft Transplant Model
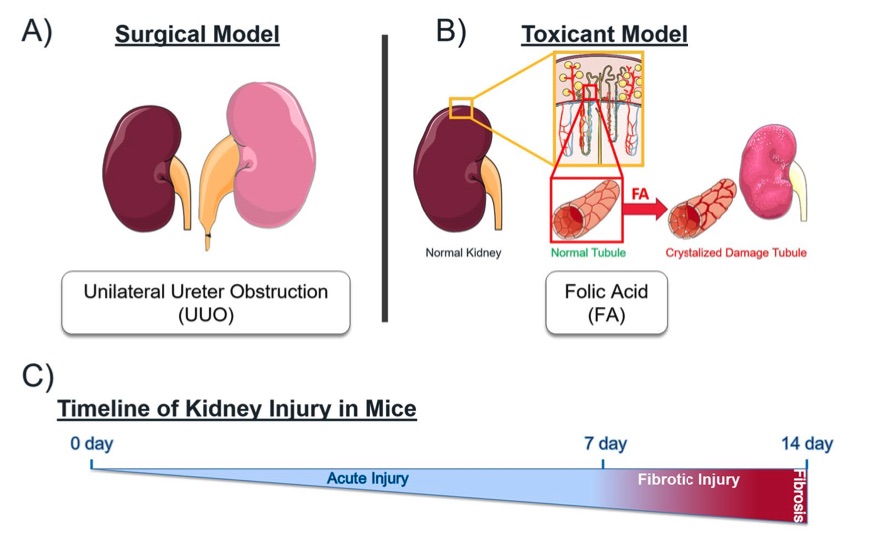
Fig. 1 Mechanistically distinct mouse models of kidney injury.1
Evaluation Platform
- Animals: Mouse, Rat, Hamster, Rabbit, Dog, NHPs.
-
Measurements
We offer a variety of measurements for evaluating drug efficacy in urological system disease models, utilizing a range of advanced technologies, including but not limited to:- General observations: body weight, urination frequency, urine color, presence of hematuria or proteinuria, and mortality rate.
- Immunohistochemistry: infiltration of immune cells (e.g., T-cells, macrophages) in the kidney, bladder, and prostate tissues.
- Cytokine profiling (e.g., ELISA): expression levels of inflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-17 in urological tissues.
- Urine analysis: proteinuria, urinary pH, and specific gravity.
- Hematology analysis and serum biomarkers: serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and kidney function indicators.
- Gene/protein expression profiling: RT qPCR and Western blot techniques to assess the expression of kidney and bladder-specific markers, such as aquaporins, uroplakins, and pro-inflammatory cytokines.
- Histopathology: evaluation of tissue damage and fibrosis in the kidney, bladder, and prostate through H&E, Masson's Trichrome staining, and fibrosis scoring.
In addition to the established urological disease models, our expertise extends to the development of novel animal models tailored to specific research needs, guided by literature and prior studies. Our scientific team is available to assist in experimental design, model selection, and data analysis, ensuring a customized and effective approach to your project at every stage.
Related Services
In addition to urological system disease models, we also offer comprehensive models for a wide range of related diseases. These models provide robust platforms for drug efficacy testing and disease mechanism studies.
Inflammation & Immunological Disease Models
Metabolic/Liver Disease Models
Musculoskeletal Disease Models
Infectious Disease Animal Models
Ear Disorder Models
Reproductive System Disease Models
Skin Disease Models
Products
With a full understanding of the importance of choosing appropriate disease models based on a specific research objective, Creative Biolabs provides various and well-characterized urological system disease models. The serum, urine, and tissue samples of these models listed below can help you to select models and verify mechanisms. Please contact us for more information or a detailed quote.
| Rodent Kidney Disease Models | Modeling | Species | Sample types | Catalog # | |||
| Thy-1 Nephritis Models | 3-9 weeks | Mouse | Anti-mouse Thy-1 Mab | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ1 |
|
| Rat | Sheep Anti-Rat Thymocyte (Anti-Thy-1) Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ2 |
|||
| Fx1A Nephritis Models | 3-9 weeks | Rat | Sheep Anti-Rat Fx1A Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ3 |
|
| Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane (GBM) Nephritis Models | 3-9 weeks | Rat | Sheep Anti-Rat GBM Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ4 |
|
| Adriamycin-Induced Nephropathy (AN) Rodent Models | 2 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ5 |
|
| 4 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ6 |
||
| 6 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ7 |
||
| 8 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ8 |
||
| 10 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ9 |
||
| Cisplatin-Induced Acute Renal Failure Models | 3 days | C57BL/6 mouse | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ10 |
|
| 7 days | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ11 |
||
| Acute Kidney Injury Models | 2K2C Models | 3 days | Mouse | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ12 |
| 2K1C Models | / | Mouse | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ13 |
|
| 1K1C Models | / | Mouse | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ14 |
|
| Kidney Ischemic Reperfusion Injury Models | 30min I-72h R | Rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ15 |
|
| 45min I-72h R | Rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ16 |
||
| 60min I-72h R | Rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ17 |
||
| Subcute & Chronic Kidney Ischemic Reperfusion Injury Models | 5/6 Nephrectomy Models | 4 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ18 |
| 8 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ19 |
||
| 12 weeks | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ20 |
||
| 2/3 Branches of Renal Artery Ligation Models | / | SD rat | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ21 |
|
| Adenine Induced CKD Rat Models | 28 days | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ22 |
|
| 37days | SD rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ23 |
||
| / | Lewis rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ24 |
||
| / | Wistar rat | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ25 |
||
| Unilateral Ureter Obstruction (UUO) Mouse Models | 14 days | C57BL/6 mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ26 |
|
| 10 days | C57BL/6 mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ27 |
||
| 7 days | C57BL/6 mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ28 |
||
| 3 days | C57BL/6 mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ29 |
||
| 1 day | C57BL/6 mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ30 |
||
| 7 days | CD1 mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ31 |
||
| 2 weeks | Rat | Serum | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ32 |
||
| Renal Transplant Models | 2 weeks | Rat | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ33 |
|
| 4 weeks | Rat | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ34 |
||
| Diabetic nephropathy Models | Streptozotocin induced Type I Diabetes Models | / | Mouse | / | / | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ35 |
| STZ-HFD-induced diabetic nephropathy Models | / | Mouse | Serum | Urine | Kidney [FFPE block] [ Slide] [Snap Frozen] |
ZAJJ-0723-JJ36 |
|
Our Advantages
- Comprehensive Expertise: We offer a wide range of well-established and customized disease models, ensuring tailored solutions for your research needs.
- Advanced Technologies: Our cutting-edge methodologies, including advanced imaging, histology, and biomarker analysis, provide precise and reliable results.
- High-Quality Support: Our team of experienced scientists offers full support, from experimental design to data interpretation, ensuring a smooth and efficient research process.
- Proven Track Record: With a history of successful collaborations across multiple therapeutic areas, we deliver dependable and reproducible results that meet your research goals.
- Tailored Solutions: We develop novel models based on the latest literature and prior studies, adapting to specific research requirements for maximum relevance and impact.
Work with Us
- Summarize the project requirements and fill in the information collection form.
- Sign a CDA from both parties to further communicate information, such as targets.
- Select an animal model, discuss experimental design, and determine assay parameters.
- Project costing and project schedule forecasting.
- We provide a detailed project plan, including the required sample quantities, methods, and protocols.
- Both parties confirm the project details and start the project.
- Confirm the timeline of the project.
- We provide periodic results and information on the animal's condition.
- We will work together to make project adjustments as necessary.
- We provide a comprehensive project report promptly.
- We arrange transportation for the produced samples.
- We provide a discussion of the project results and help to arrange the next steps.
- Data storage and archiving.
FAQs
-
1. What types of disease models do you offer?
We provide a wide range of well-established models for urological diseases, metabolic disorders, liver diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and more. These models are available for both rodent and large animal studies.
-
2. How do I select the right model for my research?
Our scientific team is here to assist you in selecting the most suitable model based on your research objectives. We offer expert guidance from experimental design to data analysis.
-
3. Do you offer customized disease models?
Yes, we can develop customized animal models tailored to your specific research needs, based on the latest scientific literature and prior studies.
-
4. What technologies and assays are used to evaluate drug efficacy?
We utilize advanced technologies such as immunohistochemistry, cytokine profiling, gene/protein expression analysis (RT-qPCR, Western blot), urine analysis, histopathology, and hematology to assess drug efficacy.
-
5. Can your models be used for long-term studies?
Yes, our models are designed for both short-term and long-term studies, providing flexibility to meet the specific timelines of your research.
-
6. How do you ensure the quality and reliability of your models?
We adhere to strict quality control standards in model development and ensure reproducibility through extensive validation and ongoing evaluation in preclinical studies.
Published Data
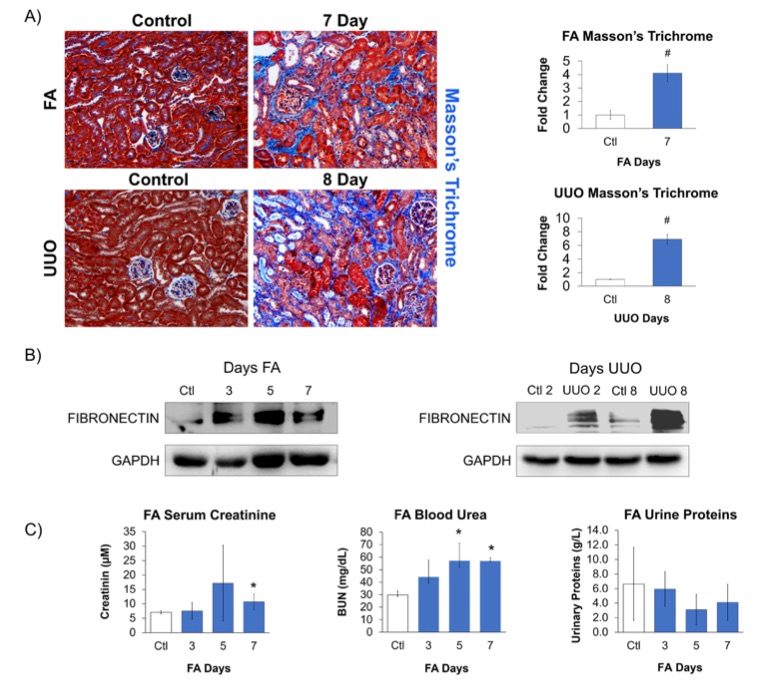 Fig. 2 Confirmation of kidney injury within mouse models.1
Fig. 2 Confirmation of kidney injury within mouse models.1
Fibrosis in the kidney induced by FA and UUO was confirmed through significant pathological changes, particularly tubulointerstitial fibrosis, detected using Masson's trichrome staining (Fig. 2A). Additionally, the classical injury marker, fibronectin, was elevated in both models (Fig. 2B). In the UUO model, fibronectin expression increased progressively over time, while in the FA model, peak fibronectin expression was followed by a recovery phase. Due to the ureter being tied in the UUO model, clearance from the damaged kidney could only be assessed in the FA model. Furthermore, plasma creatinine levels could not accurately measure kidney function in the UUO model, as the contralateral kidney compensates for the loss of function in the obstructed kidney. Consequently, renal function was only analyzed in the FA model, where urine and serum samples were collected to assess kidney injury by measuring serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and urine protein (Fig. 2C). The FA model showed increased serum creatinine and BUN, indicating a decline in kidney function. However, no significant changes in proteinuria were observed, likely because the FA model affects the distal tubule, which is not involved in protein reabsorption. Therefore, while kidney functional analysis in the FA model revealed a decrease in kidney activity followed by recovery, this outcome reflects its role as a regression model.
Reference
- Feng, Daniel et al. "Characterization of Matricellular Protein Expression Signatures in Mechanistically Diverse Mouse Models of Kidney Injury." Scientific Reports vol. 9,1 16736. 13 Nov. 2019. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52961-5
For Research Use Only.
