GTOnco™ Apoptosis Assay Service
For cancer therapy, apoptotic tumor cells are able to prime the anti-tumor immune response and increase the proliferative ability of tumor-specific T cells. In addition, the immune system to some degree relies on apoptosis to prevent autoimmunity and immunopathology. At the end of the immune response, apoptosis drastically reduces the numbers of activated T cells. Apoptosis is a highly regulated process that affects the anti-tumor immune response of gene therapy-based I-O products. At Creative Biolabs, we have developed a large number of apoptosis assays devoted to the identification of apoptotic cells and the analysis of the biochemical, morphological, and molecular changes during this biological process.
Apoptosis Assay Introduction
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is an evolutionarily conserved and highly regulated biological process essential for development, tissue homeostasis, and the clearance of damaged or unwanted cells. Dysregulation of apoptosis is a hallmark of many diseases, including cancer (insufficient apoptosis) and neurodegenerative diseases (excessive apoptosis). Therefore, quantitative and qualitative assessment of apoptotic events—i.e., apoptosis detection—is crucial in pharmacological, toxicological, and clinical research.
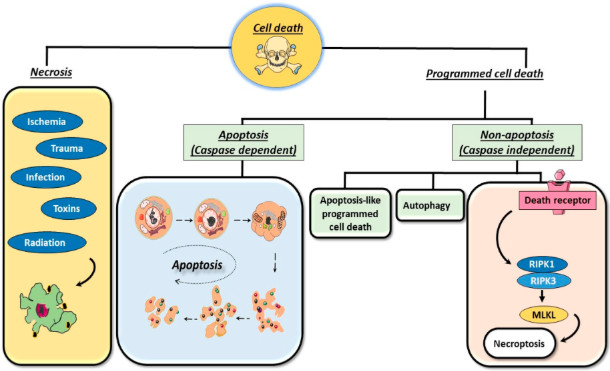 Figure 1. The common types of cell death: programmed cell death and necrosis.1
Figure 1. The common types of cell death: programmed cell death and necrosis.1
What is Apoptosis?
Apoptosis is characterized by a series of unique morphological and biochemical changes. Morphologically, apoptotic cells exhibit cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation (nuclear pyknosis), nuclear fragmentation (nuclear fragmentation), and cell membrane bubbling, ultimately forming small, membrane-bound apoptotic bodies. These bodies can be effectively phagocytosed by neighboring cells or macrophages without inducing an inflammatory response.
Key biochemical features include:
- Caspase Activation: The executors of apoptosis, particularly caspase-3, -6, and -7.
- DNA Fragmentation: Caspase-activated DNase (CAD) cleaves chromosomal DNA into 180 bp oligonucleotide fragments.
- Phosphatidylserine (PS) Externalization: PS migrates from the inner to the outer layer of the plasma membrane, acting as a "take me" signal.
Apoptosis Pathway
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells can induce apoptosis in target cells by secreting perforin and granzymes. Perforin promotes the entry of granzymes into target cells; these serine proteases can directly activate caspase cascades or initiate mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis by cleaving bid.
Table 1: Key Components of Major Apoptotic Pathways
| Pathway | Initiators | Key Mediators | Caspases Activated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intrinsic | DNA damage, oxidative stress | Bax/Bak, Bcl-2, cytochrome c, Apaf-1 | Caspase-9, -3, -7 |
| Extrinsic | FasL, TRAIL | FADD, DISC, caspase-8 | Caspase-8, -3, -7 |
| Perforin/Granzyme | Cytotoxic T cells | Perforin, granzyme B | Caspase-3, -7 (direct) |
Apoptosis vs Necrosis
Understanding the fundamental differences between apoptosis and necrosis is crucial for accurately interpreting cell death test results. These two processes represent distinct patterns of cell death with varying impacts on health and disease.
Different Mechanisms and Effects
Apoptosis is an active, energy-dependent process that can occur under both physiological and pathological conditions and does not induce an inflammatory response. In contrast, necrosis is a passive, incidental form of cell death, triggered by extreme environmental conditions or physical damage, and typically induces an inflammatory response and can lead to tissue damage.
Morphological and Biochemical Differences
Morphological features that distinguish these processes include:
- Membrane Integrity: Apoptotic cells maintain membrane integrity in the late stages, while necrotic cells immediately undergo membrane rupture.
- Inflammatory Response: Apoptosis avoids inflammation through orderly packaging and phagocytosis of cellular remnants, while necrosis releases intracellular substances, triggering a significant inflammatory response.
- Mitochondrial Changes: During apoptosis, mitochondria remain intact and release cytochrome c, while necrosis involves mitochondrial swelling and rupture.
- Execution Time: Apoptosis occurs rapidly (within hours), while necrosis typically takes several days.
A Flexible Suite of Services at Creative Biolabs
Apoptosis is considered as a vital component of various processes including proper development and functioning of the immune system, and normal cell turnover. Creative Biolabs provides a wide array of apoptosis assays for our clients across the world to measure multiple components changes in their gene therapy-based I-O products development. At GTOnco™, our featured apoptosis assays include but not limited to:
Preliminary Assays for Cell Death Detection
The initial indication for the occurrence of cell death is detected by MTS, Vital Dye Exclusion, or Hoechst staining. Meanwhile, these initial observations will be followed-up by more specific assays. For clinical research, this stage integrates TP53 biomarker analysis (≤0.5% VAF detection via NGS/ddPCR for cancer stratification) and liquid biopsy (ctDNA-based non-invasive apoptosis assessment, 87% concordance with tissue biopsies). Annexin V assays (distinguishing early/late apoptosis via PS externalization) are basic tools for lab mechanism studies/screening.
Plasma Membrane Changes Detected by Annexin V Binding Assays and Staining
Generally, by the reaction of phosphatidylserine with Annexin V-fluorochrome conjugates on the plasma membrane, the changes in plasma membrane composition and function are detected. This method can distinguish between the early and late apoptotic events with the combination of propidium iodide (PI) staining.
Morphology and DNA Fragmentation Detected by Flow Cytometry-Based Assays
We provide quick and reliable detection methods to recognize the apoptotic cells, which are based on their reduced DNA-associated fluorescence in cells with diminished DNA content (sub-G1) or morphological changes. In addition to the flow cytometry-based assays, trypan blue, or Hoechst staining are also available at GTOnco™.
Caspase Activity Determination
The best-recognized biochemical hallmark of early-stage apoptosis is the activation of caspase enzymes. The activated caspases cleave many cellular proteins and the resulting fragments may serve as apoptosis markers recognized by a variety of assays, such as colorimetric/fluorometric substrate-based assays, flow cytometry and western blot analysis.
Other Assays Available
Such as mitochondrial membrane potential assays, nuclear condensation, and cleavage of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins are available at GTOnco™.
Our Collaboration Process
Our process is designed to maximize scientific value and efficiency:
- Project Scope Definition: Consult with PhD students to identify specific research questions.
- Detection Design: Select the optimal GTOnco™ detection combination (e.g., MOMP detection, Caspase-8/9 activation, Annexin V/PI).
- Execution and Quality Control: Employ rigorous quality control metrics for high-throughput, robust detection.
- Data Analysis and Reporting: Provide comprehensive scientific reports that include complete analytical data, graphs, and tables, along with mechanistic explanations and relevant data from the GEO database.
GTOnco™ Platform Advantages and Highlights
Creative Biolabs' GTOnco™ platform is a specialized apoptosis screening system focused on oncology, integrating multiple cutting-edge technologies to accelerate cancer drug development. This platform employs a multifaceted approach to assessing apoptosis, meeting the complex needs of modern oncology research.
High-Content Apoptosis Screening
The GTOnco™ platform integrates high-content screening capabilities, combining multi-parameter flow cytometry, automated imaging, and AI-driven analysis. This method can simultaneously assess multiple apoptosis biomarkers in thousands of cells, providing a comprehensive understanding of compound efficacy and mechanisms of action.
TP53 Biomarker Integration
Our platform integrates the advanced TP53 apoptosis biomarker, enabling precise cancer risk stratification and treatment selection. Utilizing targeted next-generation sequencing (NGS) and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR) technologies, we have achieved extremely high sensitivity with a detection limit of less than 0.5% variant allele frequency (VAF).
Liquid Biopsy Applications
The GTOnco™ platform supports liquid biopsy analysis for apoptosis assessment, achieving 87% concordance with conventional tissue biopsies across various analytical platforms. This non-invasive method enables dynamic monitoring of responses through the analysis of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA).
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Which apoptosis detection method is best suited for my research?
A: The choice of apoptosis detection method depends on several factors, including the experimental system, the specific research question, and the available instruments. For general screening, flow cytometry with Annexin V/PI staining can effectively distinguish between early and late apoptosis. For pathway-specific analysis, caspase activation or mitochondrial membrane potential detection may be more suitable.
Q: How does Creative Biolabs ensure the sensitivity and specificity of its assays?
A: We use orthogonal validation methods and validate our assays against established standards to ensure accurate detection of apoptosis. Our platform has extremely high sensitivity; digital PCR can detect mutations in clinical samples with a sensitivity of 0.1%. Furthermore, multi-parameter methods reduce false positives by requiring confirmation from multiple apoptosis signatures.
Q: Can Creative Biolabs develop custom apoptosis detection methods for specific targets?
A: Absolutely. Our custom assay development services leverage our extensive experience in assay design, reagent development, and validation. We have extensive experience developing assays for novel targets using our antibody discovery platform, including advanced phage display and transgenic mouse technology.
Q: What advantages does the GTOnco™ platform bring to cancer drug development?
A: The GTOnco™ platform provides comprehensive apoptosis analysis and is specifically optimized for oncology applications. Its key advantages include: integrated TP53 mutation analysis, high-content screening capabilities, compatibility with liquid biopsy, and AI-enhanced data analysis. This specialized approach generates more physiologically relevant data, thereby facilitating the development of cancer therapeutics.
Q: How does Creative Biolabs support clients throughout the project lifecycle?
A: We assign a dedicated research team to each project to ensure smooth communication and provide technical support throughout the entire process, from experimental design to data interpretation. Our project managers provide regular updates on project progress and answer questions or adjust the plan as needed throughout the collaboration.
Reach Out to Us Now!
Apoptosis detection is an indispensable tool in modern biomedical research, particularly in drug discovery and development. From multiparameter flow cytometry to liquid biopsy, continuous advancements in detection technologies have provided us with increasingly sophisticated methods for analyzing cell death mechanisms. Creative Biolabs leverages these technological advancements, utilizing our professional platform and comprehensive expertise to offer comprehensive apoptosis assessment services, helping clients achieve their research goals. Contact us today for a quotation or any question. Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day!
Reference
- Mustafa M, Ahmad R, Tantry I Q, et al. Apoptosis: a comprehensive overview of signaling pathways, morphological changes, and physiological significance and therapeutic implications. Cells, 2024, 13(22): 1838. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13221838 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
