Large monoclonal antibodies have become one of the most successful and important drugs for the treatment of cancer patients due to their efficacy and safety, but despite their advantages in pharmacokinetics, they may show limited solid tumor permeability, thus compromising its therapeutic efficacy. The successful development of aptamer-antibody conjugates provides a choice to solve this problem. After decades of concentrated researches, Creative Biolabs has now launched a comprehensive and high-quality aptamer-antibody conjugates development service.
Background of Aptamer-Antibody Conjugates
Aptamers have attracted attention as new promising drugs in the field of cancer therapy due to their binding ability, lack of immunogenicity, easy chemical synthesis and adaptive modification procedures. However, it may be due to their rapid elimination properties in the body, there are currently no approved aptamers for cancer treatment.
In order to optimize the specificity, tissue permeability and half-life of drugs (such as antibody drugs) that are critical the efficacy of cancer treatment, current research has begun to test the conjugation of small aptamers (12 kDa) with antibodies targeting different antigens to obtain new bispecific molecular constructs with relatively low molecular weight composed of two antibody-based reagents. On the one hand, it can increase the potential tumor permeability and target accessibility. On the other hand, the presence of antibodies in the aptamer-antibody conjugate increases the molecular size of the aptamer, thus overcoming rapid clearance through renal filtration and prolonging its half-life in circulation.
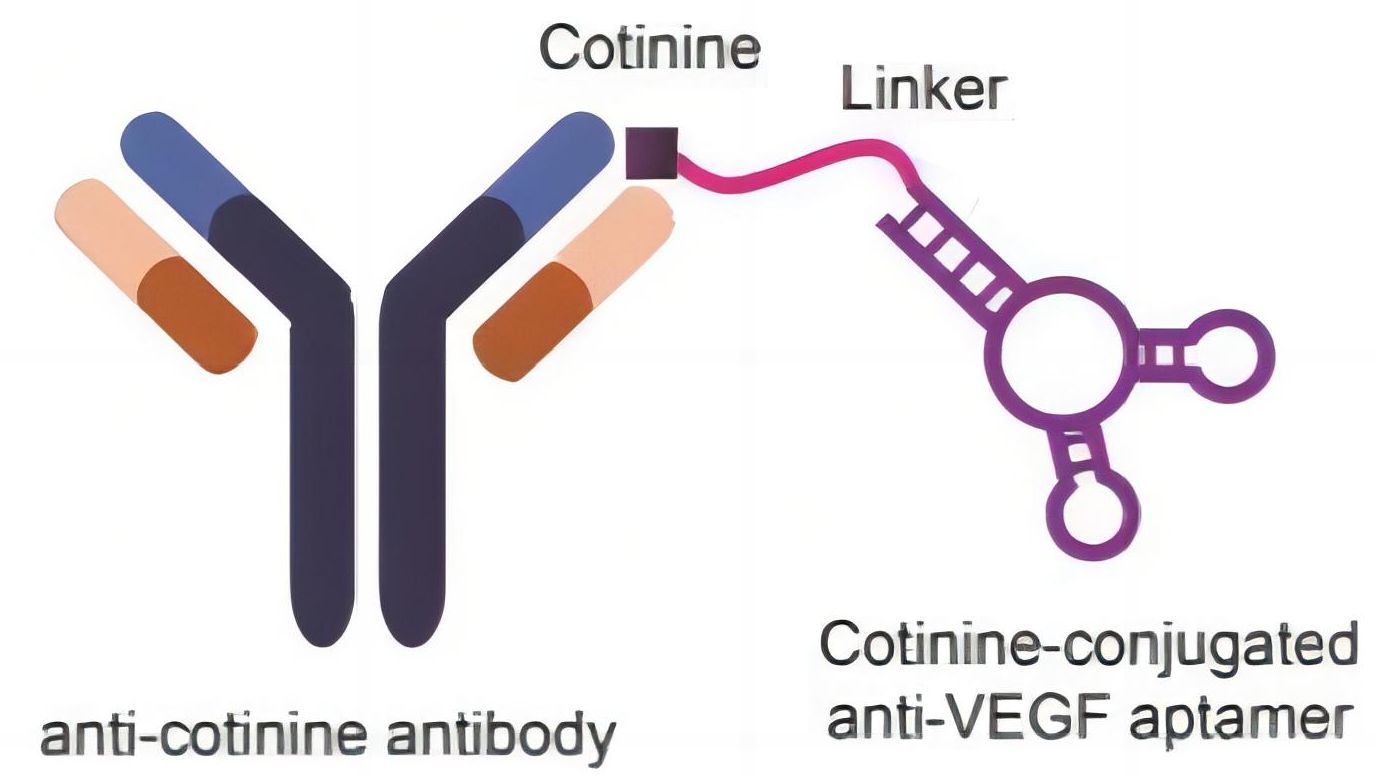 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of aptamer-antibody conjugates.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of aptamer-antibody conjugates.1
Aptamer-Therapeutic Oligonucleotide Conjugates Development Service
The conjugation of aptamer and antibody is a new therapeutic strategy, which is more effective than aptamer or antibody alone in some cases. Antibody-aptamer conjugate can increase the binding affinity and inhibitory effect of antibody or aptamer to its target. We offer antibody-aptamer conjugate development services, which can be applied to almost all desired antibodies and aptamers by using the linker residues of antibody constant region and simple conjugation protocol. Our antibody-aptamer conjugates have the following advantages:
-
Simple and fast procedures for production;
-
Low production cost;
-
Increased specificity;
-
Potentially increased pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties.
Based on our advanced aptamer development service strategy and perfect complement therapy platform, Creative Biolabs is confident to provide aptamer development services for various complement components, especially those vital to complement activities. We deeply understand that each customer has different requirements for their projects, and we are happy to work with you to design a selection process that best suits your needs. If you are interested in our service, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Kim, Minhee, et al. "Applications of cancer cell-specific aptamers in targeted delivery of anticancer therapeutic agents." Molecules 23.4 (2018): 830.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: The development of aptamer-antibody conjugates typically involves the following steps. (1) Selection of appropriate aptamer and antibody: This step involves the selection of an aptamer that selectively binds to the desired target molecule, and an antibody that recognizes a different epitope on the same target molecule. (2) Introduction of chemical modifications: To enable conjugation between the aptamer and the antibody, chemical modifications are introduced to either the aptamer or the antibody. (3) Conjugation: The aptamer and antibody are conjugated using a suitable linking chemistry, such as maleimide-thiol chemistry, biotin-streptavidin binding or click chemistry. (4) Optimization: The conjugation conditions are optimized to ensure maximum conjugation efficiency and retention of the binding affinity of both the aptamer and the antibody. (5) Characterization: The aptamer-antibody conjugates are characterized using techniques such as gel electrophoresis, chromatography, and binding assays to confirm their binding affinity and selectivity for the target molecule.
A: Aptamer-antibody conjugate drugs have shown great promise as a next-generation therapeutic option for a variety of diseases. Some recent research advances in this field include: improved aptamer selection methods and multivalent aptamer-antibody conjugates. There are some new methods for the selection of high-affinity aptamers against specific targets, including in vitro selection methods like SELEX and high-throughput sequencing techniques. Researchers have developed aptamer-antibody conjugates that have multiple aptamer binding sites. These multivalent aptamer-antibody conjugates have shown improved binding affinity and specificity to the target compared to monovalent aptamer-antibody conjugates.
A: Aptamer-antibody conjugates can be used in various areas such as diagnostics, therapeutics, biotechnology, and biosensors. They are specifically useful in research and medical fields for their high specificity and affinity towards their target molecules. They can also be used for targeted drug delivery and as tools for bioimaging.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Schematic representation of aptamer-antibody conjugates.1
Fig. 1 Schematic representation of aptamer-antibody conjugates.1