Aptamer: an Alternative to Antibody
In the 1980s, it was found that some small structured RNAs encoded by human immunodeficiency virus and adenovirus could bind to viral or cellular proteins with high affinity and specificity. And later in 1990, the first aptamer specific for the T4 DNA polymerase was isolated from an 8-nucleotide random region library. Since then, dramatic progress has been made on aptamers development due to the Systematic Evolution of Ligands by EXponential enrichment (SELEX) technology.
Aptamers, also known as chemical antibodies, are small single-stranded RNA or DNA oligonucleotides with specific 3-dimensional structures. Similar to monoclonal antibodies, aptamers are capable of recognizing and binding to ligands or targets with high affinity and specificity. What is different is that the binding of aptamers to targets is achieved by folding and forming stable 3-dimensional structures such as a hairpin, false knot, and convex ring through complementary base pairs in the chain, electrostatic interaction, and hydrogen bonding. Up to now, several therapeutic aptamers have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the disease treatment. And aptamers are now widely considered as alternatives to antibodies since they exhibit plenty of advantages over antibodies, such as:
-
High affinity and specificity
-
High stability
-
A wide range of target types and size
-
Relative lower manufacturing time and cost
Bivalent Aptamer and Related Applications
It is well known that natural nucleic acid is unstable and sensitive to nuclease, which hinders the development and practical application of natural aptamers. Multiple strategies have been developed to improve the stability of aptamers, including chemical modifications and aptamer-based conjugations, among which bivalent or multivalent aptamers have aroused great interest.
The concept of bivalent or multivalent aptamers was proposed and verified in a patent in 1999 by Shi et al., which are defined as modified aptamer structures consisting of two or more identical or different single aptamers, with or without additional structures. Bivalent aptamers are constructed by linking two identical or different aptamers with an optimized spacer, which exhibits higher avidity to targets. And several bivalent aptamers have been reported to enhance the therapeutic responses and reduce side effects. For example:
-
CD28 bivalent aptamer has been shown to co-stimulate CD8 T cells and CD4 lymphocytes and promotes the immune response;
-
OX40 bivalent aptamer has been shown to stimulate OX40 on T cells, promoting T cell proliferation and interferon-γ production;
-
4-1BB bivalent and multivalent aptamer have been shown to co-stimulated CD8+ T cell activation and inhibit tumor growth.
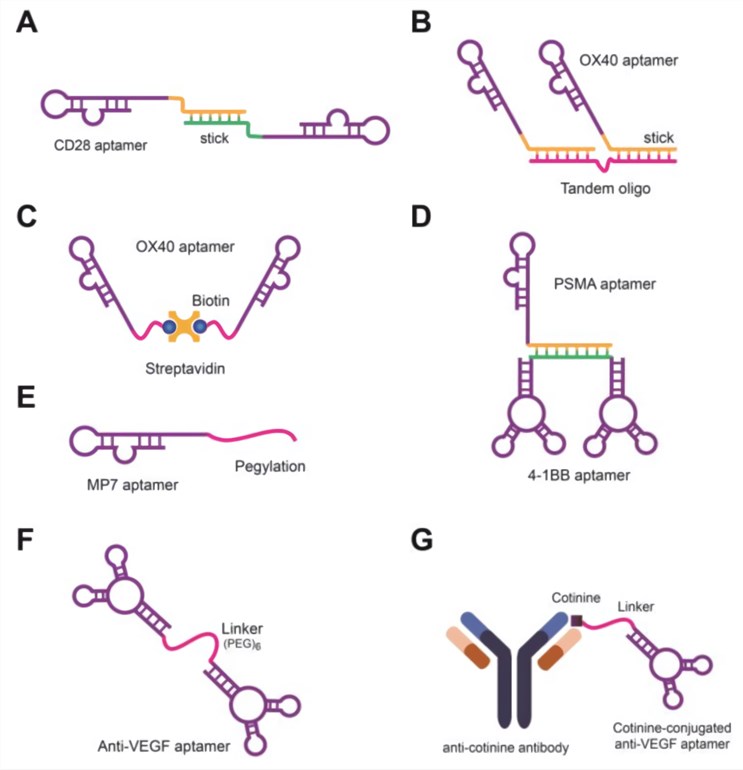 Fig. 1 Schematics of aptamers and bivalent aptamers.1, 2
Fig. 1 Schematics of aptamers and bivalent aptamers.1, 2
Our Highlighted Bivalent Aptamer Development Service
The success of FDA-approved drug Macugen has greatly inspired the development of aptamer. Currently, many therapeutic aptamers and modified aptamers are being evaluated in Phase II and III clinical trials. Creative Biolabs, an expert in the field of novel drug discovery, focuses on providing high-quality and convenient aptamer development services to clients all over the world. Specifically, we offer one-stop custom bivalent aptamer development services, as well as aptamer conjugates development, such as aptamer-oligonucleotide conjugates, aptamer-antibody conjugates, aptamer-drug conjugates, aptamer-cholesterol conjugates, aptamer-nanoparticles conjugates, and aptamer-based biosensors.
If you are interested in our services, please do not hesitate to contact us directly for more details.
References
-
Kim, Minhee, et al. "Applications of cancer cell-specific aptamers in targeted delivery of anticancer therapeutic agents." Molecules 23.4 (2018): 830.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: We offer custom bivalent aptamer development services tailored to specific client requirements. We provide expertise and services in design, synthesis, characterization, and optimization of bivalent aptamers.
A: Developing bivalent aptamers involves challenges such as linker optimization, maintaining individual aptamer functionality, and achieving the desired binding properties. Creative Biolabs has expertise in addressing these challenges during the development process.
A: Bivalent aptamers are typically developed on a custom basis to suit specific research or therapeutic needs. Creative Biolabs offers custom bivalent aptamer development services, but the availability of specific aptamers may vary.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Schematics of aptamers and bivalent aptamers.1, 2
Fig. 1 Schematics of aptamers and bivalent aptamers.1, 2