Current technologies of automated DNA/RNA synthesis enable easy, cost-effective, large-scale manufacture and automated chemical modification of aptamers with low batch-to-batch variations. The relatively simple chemical structures of aptamers entail full conformational recovery even after thermal or chemical denaturation. Aptamers typically have a long shelf life. These features make aptamers intriguing for targeted therapy. As an experienced biopharmaceutical development company, Creative Biolabs has established a comprehensive aptamer development platform with an efficient and sophisticated technical team. We are capable of providing global customers with high-quality aptamer development services.
Introduction of Aptamers as Targeted Drug Delivery
Aptamers have been extensively studied as targeting ligands for drug delivery in the form of aptamer-drug conjugates (ApDCs). A few ApDCs have been already approved by the US FDA for cancer treatment. Compared with counterparts of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), ApDCs present multiple potential advantages. Aptamers can be chemically or enzymatically modified with versatile functional groups for bioconjugation with therapeutics or optimization of biostability; aptamers can be recovered from some extreme thermal or chemical conditions for possible efficient bioconjugation; the relatively small molecular weights of aptamers and ApDCs make them promising for faster and deeper tissue penetration than ADCs. ApDCs have been studied for multiple modalities of therapy, such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, radiotherapy, and phototherapy.
Application of Aptamers as Targeted Delivery
-
ApDCs for chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is one of the mainstream treatment modalities for cancer and has dramatically improved the outcome of cancer treatment. A common limitation with conventional chemotherapy is their toxicity in healthy tissues and the consequent adverse side effects that narrow the therapeutic windows and compromise the overall therapeutic efficacy. Reducing the exposure of healthy tissues to these drugs is thus expected to reduce these side effects and improve therapeutic efficacy. Towards this goal, ApDC-mediated targeted drug delivery has been explored by specifically delivering drugs to diseased tissues or cells, but not/less to healthy tissues.
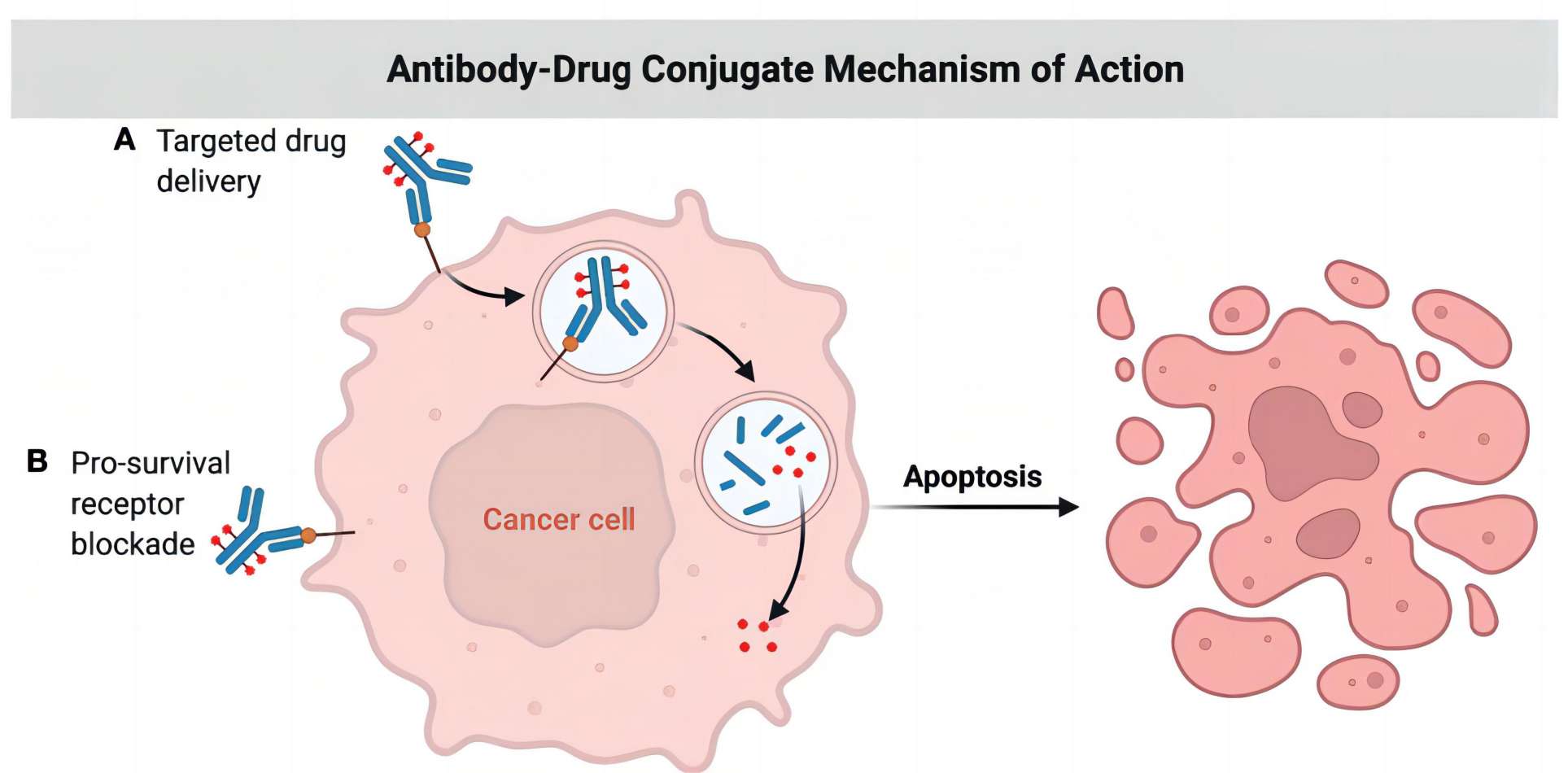 Fig. 1 ApDCs mechanism.1, 2
Fig. 1 ApDCs mechanism.1, 2
-
ApDCs for gene therapy
Gene therapy is an integral part of precision medicine. Like many other therapeutic agents, gene therapy agents by themselves lack specificity towards diseased cells, which makes it critical to deliver the gene therapy agents specifically to diseased cells. To this end, aptamers may serve as the targeting ligands. For example, in viral gene therapy, ApDC approaches may be utilized to reduce the potential off-target effect. Moreover, the implementation of nanocarriers in ApDC-mediated gene therapy may increase the loading capacity of gene therapeutics and hence enhance the therapeutic efficacy.
-
Aptamer conjugates for immunotherapy
Immunotherapy has made historical breakthroughs in the past few years, especially for the treatment of cancer. However, current approaches to immunotherapy are also accompanied by significant immune toxicities. To address this challenge, one strategy is to specifically deliver immune therapeutics to the target tumor or immune cells. Towards this end, ApDC is a promising platform. ApDCs have been studied to deliver immunomodulatory agents to confine immune costimulation to the tumor region, induce the generation of neoantigens in the tumor, block exhaustion-inducing immune checkpoints to reinvigorate functional immune cells, and prolong antitumor immunity.
-
ApDCs for radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is one of the main modalities for cancer treatment in clinics. Systemic radiotherapy, which typically involves the injection of radioisotopes to allow the delivery of radioisotopes into diseased lesions, is often less specific. Such less specific delivery of radioisotopes would harm healthy tissues and cells and cause adverse side effects, making targeted delivery of radioisotopes significant to reduce such side effects and improve the therapeutic efficacy of systemic radiotherapy. Targeting ligands, such as aptamers, are promising for targeted delivery of therapeutic radioisotopes.
-
ApDCs for phototherapy
Phototherapy, such as photodynamic therapy (PDT) and photothermal therapy (PTT), holds great potential for the treatment of a variety of diseases. Due to the potential off-target toxicities of photosensitizers and PTT agents, there remains a need to specifically deliver these agents into diseased tissues or cells. Therefore, targeted delivery of phototherapeutics is the potential to minimize drug toxicity to healthy tissues both by target-specific drug delivery and by precisely controlling the phototherapy-initiating external light source.
Services at Creative Biolabs
Committed to aptamer development for years, Creative Biolabs has accumulated extensive experience in aptamer applications in targeted drug delivery from practice. We provide comprehensive aptamer development services to meet global customers’ detailed requirements such as one-stop aptamer in vitro selection service and aptamer-based conjugation services. Our professional scientists will help with every puzzle during the services.
Advantages:
-
Experienced: Hundreds of satisfying precedents.
-
Reliable: Information security.
-
Convenient: One-stop services.
Aptamer has shown its huge potential in the application of targeted drug delivery. Based on the advanced aptamer development system and mature technology, Creative Biolabs offers high-quality and worry-free aptamer application research services to global customers. If the above services do not meet your requirements, please contact us for your exclusive solution.
References
-
Xie, Duoli, et al. "Targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic agents for osteosarcoma treatment." Frontiers in Oncology 12 (2022): 843345.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Aptamers offer several advantages for targeted delivery compared to other targeting strategies. They have high specificity and affinity for their targets, enabling precise targeting. Aptamers can be easily synthesized, modified, and conjugated to various therapeutic agents or nanoparticles. They exhibit low immunogenicity and toxicity, making them suitable for clinical applications. Aptamers also offer the potential for multi-targeting and simultaneous delivery of multiple payloads.
A: Aptamers can deliver a wide range of payloads, including small molecule drugs, therapeutic nucleic acids (e.g., siRNA, antisense oligonucleotides), peptides, proteins, and imaging agents. By conjugating these payloads to the aptamer, they can be specifically delivered to the target site, improving therapeutic efficacy and minimizing off-target effects.
A: Aptamers for targeted delivery have diverse applications in medicine. They can be used in cancer therapy to selectively deliver chemotherapy drugs to tumor cells while sparing healthy tissues. Aptamers can also target specific pathogens or infected cells for antimicrobial or antiviral therapy. Additionally, they have potential applications in diagnostics, imaging, and regenerative medicine. Ongoing research is exploring the use of aptamers for personalized medicine and targeted therapy in various diseases.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 ApDCs mechanism.1, 2
Fig. 1 ApDCs mechanism.1, 2