Aptamers per se have been developed as therapeutics. Such therapeutic aptamers can readily modulate the biological pathways for the intervention of many types of diseases such as cancer, infectious diseases, and cardiovascular diseases. With extensive experience in aptamer development, Creative Biolabs provides global clients with reliable aptamer development services to promote aptamer applications in therapeutics.
Introduction of Aptamers for Therapeutics
Aptamers are synthetic single-stranded oligonucleotides (DNA or RNA) of short length (20-100 nucleotides) whose three-dimensional disposition confers them high avidity for their targets. Aptamers are gaining importance as therapeutics due to their potential advantages over cell-based products, such as recombinant proteins or antibodies. They can be chemically synthesized, which enables quick productions and versatile chemical modifications. High stability, lack of immunogenicity, flexible structure, and small size increase their penetration strength. Aptamers have been developed as therapeutics, such as for the treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), treatment of cancer and anticoagulants.
Application of Aptamers in Therapeutics
-
Aptamer in Macular Degeneration Research
Pegaptanib sodium (Macugen; Valeant Ophthalmics, Bridgewater, NJ) is a pegylated RNA aptamer that selectively binds VEGF165, which is thought to be one of the primary pathologic VEGF isoforms. Pegaptanib became the first anti-VEGF agent approved by the FDA for the treatment of neovascular AMD.
-
Aptamer in Coagulation Research
In the broad area of cardiovascular diseases, aptamers have also been extensively sought after. For instance, aptamers have been developed for a panel of molecules involved in coagulation. The current clinical practice of anticoagulation uses heparin, which however has drawbacks such as the lack of safe and well-controllable antidotes. Towards this end, anti-FIXa aptamers have been developed. For example, an anti-FIXa aptamer called pegnivacogin was developed to inhibit the function of FIXa to catalyze the conversion of FX to FXa, which enables pegnivacogin to inhibit the intrinsic pathway activation and reduce the propagation of thrombin generation. Pegnivacogin has been clinically investigated for applications such as prevention from arterial thrombosis or venous thrombosis.
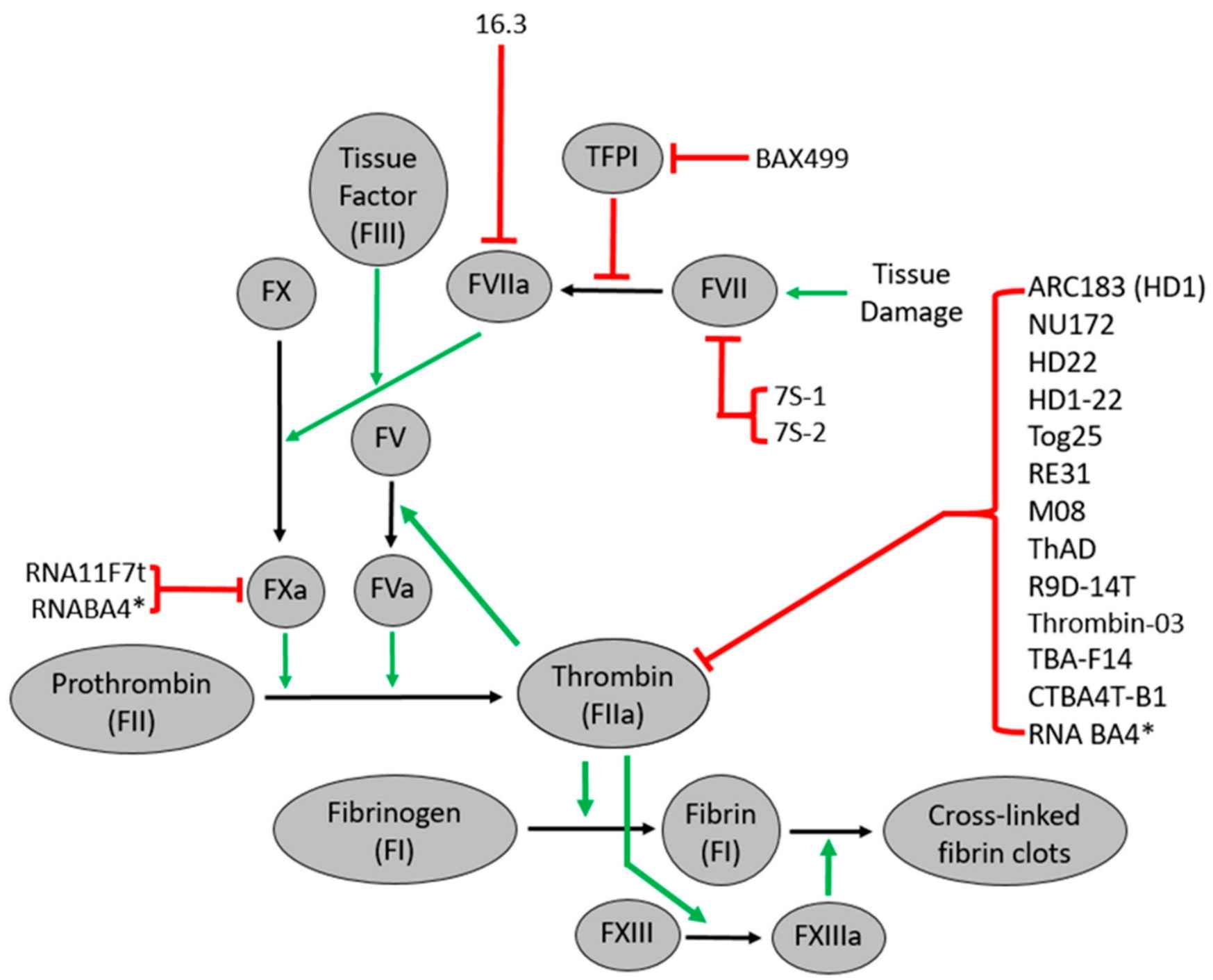 Fig. 1 Aptamers targeting coagulation factors.1, 2
Fig. 1 Aptamers targeting coagulation factors.1, 2
-
Aptamer in Oncology Research
For the development of aptamers as anticancer therapeutics, one example is AS1411 that has been under clinical testing for the treatment of cancers including AML. This aptamer was thought to bind with nucleolin and can be internalized into many types of cancer cells. The underlying mechanisms of the AS1411-mediated antiproliferation effect have not been fully understood, but have been shown to involve the inhibition of cell proliferation via multiple signaling pathways involving BCL-2 mRNA destabilization and NF-κB inhibition.
-
Aptamer in Inflammation Research
Aptamers therapeutics have been developed for the intervention of infectious diseases by targeting proteins related to inflammation and immunity. For instance, HIV-1 viral infection was inhibited using a trans-activation response (TAR) nucleic acid decoy that is essentially an aptamer, or by an aptamer selected against the TAR element. In addition, aptamers have been developed for reverse transcriptase, HIV-1 Gag protein, nucleocapsid protein, integrase, Tat protein, and gp120, all of which are closely related to viral infection.
Services at Creative Biolabs
With extensive professional experience accumulated from hundreds of successful precedents, Creative Biolabs has established a reliable platform offering a full range of aptamer development services for therapeutics applications. By focusing on quality, efficiency, flexibility, and expertise, our excellent scientists are dedicated to providing optimal solutions to meet every customer’s specific requirements.
Applications of aptamers in therapeutics have shown huge potential. Creative Biolabs is a leading custom services provider in the field of aptamer development services. We can provide flexible options for your choice, either single-alone services or integrated projects are available to satisfy every detailed demand from our customers. Please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Liu, Max, Khalequz Zaman, and Yolanda M. Fortenberry. "Overview of the therapeutic potential of aptamers targeting coagulation factors." International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22.8 (2021): 3897.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Aptamers offer several advantages as therapeutic agents. They can be developed to bind with high affinity and specificity to target molecules, similar to monoclonal antibodies. Additionally, aptamers are typically smaller in size, have lower immunogenicity, and can be chemically modified to enhance stability and improve pharmacokinetics.
A: Yes, aptamers can be used in combination with other therapeutics. They can be combined with small molecule drugs, antibodies, or other therapeutic modalities to achieve synergistic effects or enhance the overall therapeutic outcome. Aptamers can serve as complementary agents or targeting components in multi-modal therapeutic approaches.
A: Despite their potential, aptamers also face certain challenges and limitations. One challenge is the delivery of aptamers to target tissues or cells. Strategies such as conjugation to nanoparticles or liposomes are being explored to improve aptamer delivery. Another limitation is the relatively short half-life of aptamers in the bloodstream, which may require frequent dosing. Ongoing research aims to address these challenges and further optimize the development of aptamers for therapeutic use.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Aptamers targeting coagulation factors.1, 2
Fig. 1 Aptamers targeting coagulation factors.1, 2