Aptamers are functional oligonucleotides of single stranded DNA or RNA with high affinity, specificity and selectivity. Aptamers are used in diagnosis and treatment as biomolecular recognizers. Among various modified aptamers, biotin modified aptamers can be labeled with dye or enzyme labeled streptavidin. These streptavidin-specific aptamers can be used as tools to characterize the occupancy of biotinylated target molecules on streptavidin modified surfaces.
Background of Biotin Modified Aptamer
Aptamer-based biosensors have been widely studied and developed for the detection of proteins, small chemicals and metabolites such as nucleic acids and carbohydrates in biological, environmental substances and food. As biomolecular recognition agents, aptamers are used in diagnosis and treatment because of their small size, which may reduce the steric hindrance and make the analyte more accessible. Biotin is commonly used as a modifier for colorimetric-based aptasensors, either in the lateral flow analysis (LFA) or in the Enzyme-linked aptamer assays (ELAA). This is because of its high affinity for streptavidin and avidin, which is very important in many molecular biological applications. It is used for mobility determination and for enrichment, purification and attachment to solid surfaces.
Biotin Modified Aptamer Development in Creative Biolabs
At present, biosensors based on biotinylated aptamers have been successfully developed for detecting a multiplex strain-specific influenza virus. For LFA, the biotinylated aptamer and antibody-bound gold nanoparticles (AuNP) are dried on the coupling pad of LFA, and streptavidin is fixed on the test wire at the same time. In the presence of a target, the virus forms sandwich complexes with biotin modified aptamers and monoclonal antibodies, which are captured at the test line through streptavidin biotin interaction. In the absence of a target, no complex is formed, and there is no visible signal corresponding to the test line.
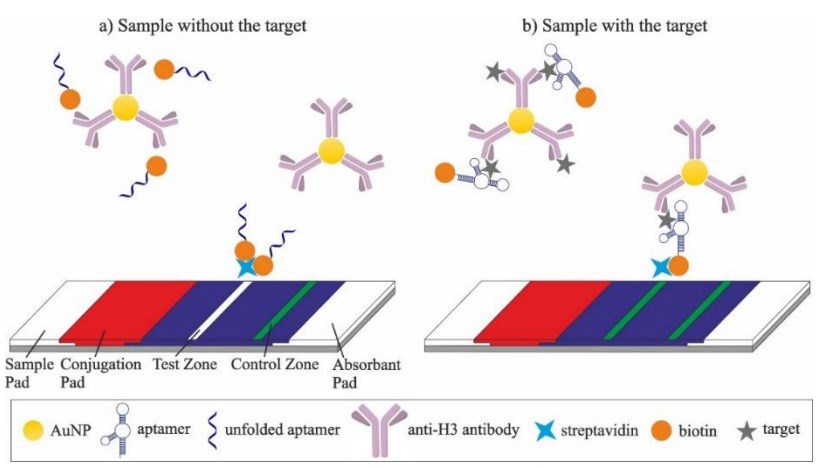 Fig. 1 The principle of the dual recognition LFA.1, 2
Fig. 1 The principle of the dual recognition LFA.1, 2
In the design of aptamer modification, we developed a site-specific modification technology, that is, the biotin group can be attached to the 3’ or 5’ end of the aptamer without affecting the target binding site, and form a one-to-one conjugate similar to gene fusion technology.
Compared with antibodies, the advantages of aptamer design are as follows:
-
The aptamer is highly chemically stable in a wide temperature range and has reversible denaturation;
-
The aptamer can be isolated by in vitro methods without generating an immune response;
-
The aptamer can be obtained within a few days;
-
The aptamer is easy to modify and mark.
Creative Biolabs provides a wide range of services (One-stop Aptamer In Vitro Selection Service, Aptamer-based Conjugation Services, Aptamer Modifications Services, ect.) to support your project and is the best choice for providing high-quality, cost-effective outsourcing/collaboration options for your research projects. Please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
-
Schüling, Torsten, et al. "Aptamer-based lateral flow assays." AIMS Bioengineering 5 (2018), Nr. 2 5.2 (2018): 78-102.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
Related Product
Questions & Answer
A: Yes, biotin-modified aptamers can be easily detected using various detection methods, such as fluorescence, enzyme-linked assays, or magnetic bead-based assays.
A: Some considerations include potential steric hindrance or interference with aptamer-target binding caused by biotin modifications, which can be minimized through careful design and optimization.
A: For more detailed information on Creative Biolabs' biotin modification services, including protocols, timelines, and pricing, you can contact our team directly through the contact information provided on website.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 The principle of the dual recognition LFA.1, 2
Fig. 1 The principle of the dual recognition LFA.1, 2