Product List Background C3A Functional Service
Background
Complement C3a, a small 9 kDa peptide, has 77 amino acids and made up of four anti-parallel helical structures that are trapped by three disulfide bridges. C3a is an important chemotactic mediator in the immune system, and the C3a/C3aR pathway plays crucial anti-inflammatory and proinflammatory roles in different cells and diseases. Generally, C3a/C3aR participates in the response of the immune system in three ways, including (1) activate dendritic cells (DCs), acting on resident innate immune cells to up-regulate or down-regulate different cytokines, and regulate T cell signaling between lymphocytes and antigen presenting cells (APCs).
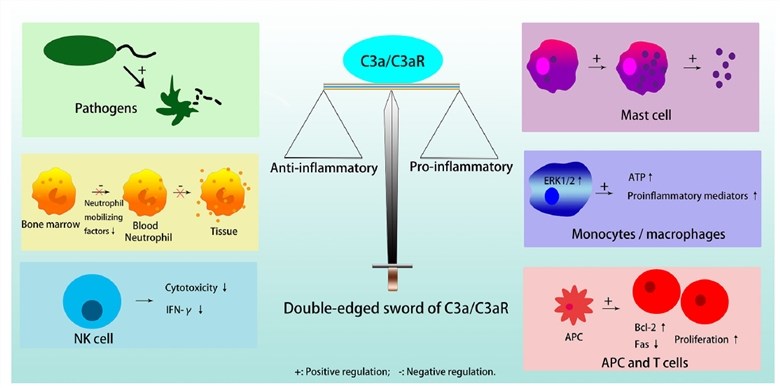 Fig.1 The dual role of C3a and its receptor C3aR.1, 3
Fig.1 The dual role of C3a and its receptor C3aR.1, 3
Besides, C3a also has anti-inflammatory effects in pathogens, such as neutrophils in the bone marrow reservoir, bacteria/fungi, as well as natural killer (NK) cells. What’s more, although there is a high expression of functional C3aR on the neutrophil cell membrane, C3a does not stimulate neutrophil degranulation to activate inflammatory response. Also, through directly inhibiting neutrophil mobilizing factors (e.g., G-CSF), C3a can suppress the migration of neutrophils from the bone marrow into the circulation. Typically, in healthy individuals, the plasma concentration of C3a is 119 ng/mL, and it is generated by the degradation of C3 in the alternative pathway. But in different researches, owning to protocol and sample characteristics, the C3a concentration varies widely, from 20 to 156 ng/mL.
C3A Functional Service
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive array of C3a-centric products, including anti-C3a antibodies, ELISA kits, recombinant C3a proteins and C3a inhibitors. These precisely designed reagents facilitate the detection and examination of interactions between C3a proteins and other molecular factors. They play an essential role in propelling research aimed at devising therapeutic strategies across a variety of diseases.
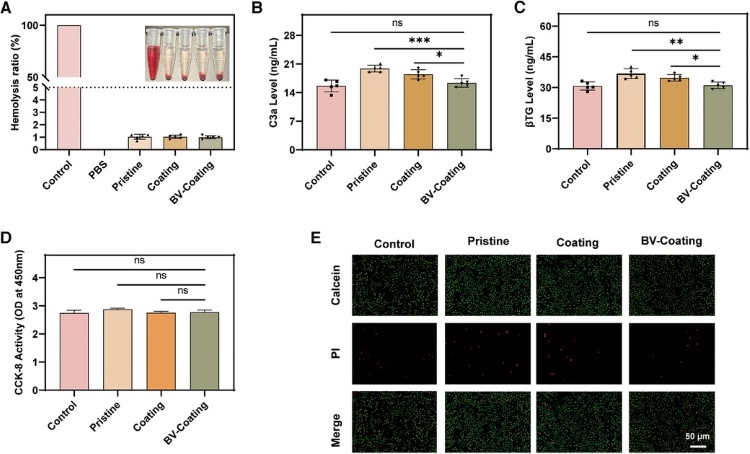 Fig.2 In vitro biocompatibility assessment of C3a, encompassing hemolysis and ELISA tests.2, 3
Fig.2 In vitro biocompatibility assessment of C3a, encompassing hemolysis and ELISA tests.2, 3
Evaluating C3a functionality generally involves examining its role within the alternative pathway of the complement system, using products such as anti-C3a antibodies for applications like WB, ELISA, and IP to measure C3a expression levels. For instance, these methodologies can quantify C3a from minimal samples in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. ELISA kits are employed to determine C3a protein concentrations across various biological samples, facilitating insights into the operational mechanisms of C3a. The recombinant C3a protein aids in elucidating its receptor binding structure. Functional hemolytic assays assess the effects of C3a inhibitors or genetic variants on complement activation, while C3a inhibitors are investigated for therapeutic potential in complement-associated diseases.
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive range of functional services focused on C3a, such as C3a binding assays, enzymatic activity evaluations, and hemolysis testing. These meticulously designed services are intended to support researchers in progressing their scientific investigations and clinical projects.
References
-
Gao, Shuang, Zhao Cui, and Ming-hui Zhao. "The complement C3a and C3a receptor pathway in kidney diseases." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 1875.
-
Gao, Wenqing, et al. "Bivalirudin-hydrogel coatings of polyvinyl chloride on extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for anticoagulation." Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine 10 (2023): 1301507.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 The dual role of C3a and its receptor C3aR.1, 3
Fig.1 The dual role of C3a and its receptor C3aR.1, 3
 Fig.2 In vitro biocompatibility assessment of C3a, encompassing hemolysis and ELISA tests.2, 3
Fig.2 In vitro biocompatibility assessment of C3a, encompassing hemolysis and ELISA tests.2, 3
