Introduction Published Data What We Can Offer? Workflow Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in developing effective therapeutics for complement-mediated diseases, such as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) or C3 glomerulopathy? Creative Biolabs' Soluble Complement Regulator Development services can help you accelerate drug discovery by providing high-quality, custom-engineered soluble complement regulators. We leverage advanced protein engineering and high-throughput screening to deliver potent and specific Factor H constructs, helping you navigate the complexities of complement-related drug development.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system is a sophisticated proteolytic cascade that forms a crucial part of the innate immune response, safeguarding the host from pathogens and clearing cellular debris. However, uncontrolled complement activation can lead to significant tissue damage and is a major contributor to a number of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders. The alternative pathway (AP) is particularly prone to dysregulation, making its control a key therapeutic strategy.
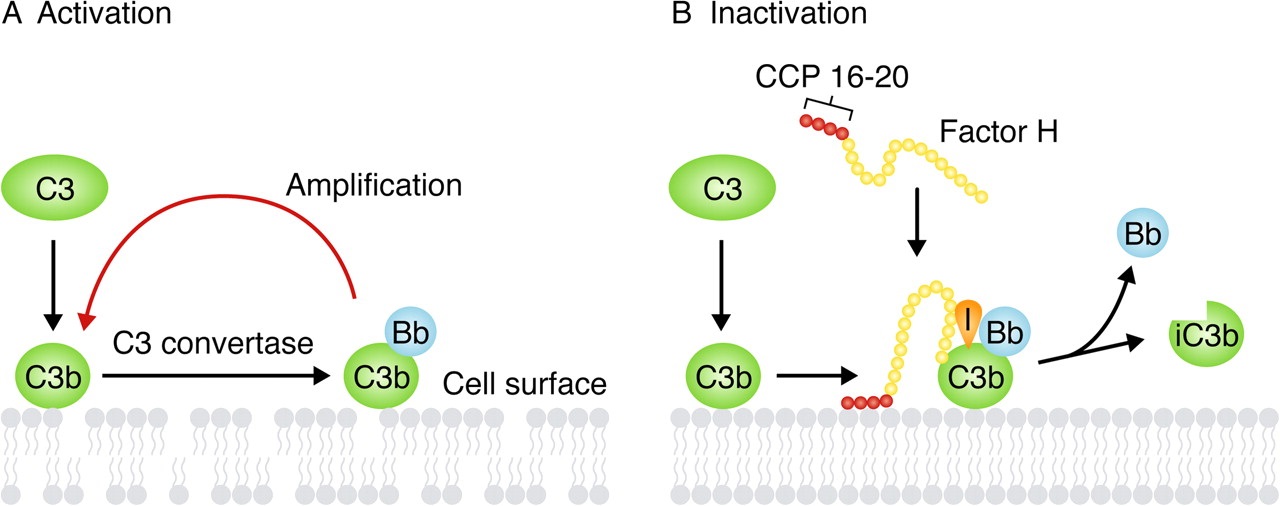 Fig.1 Function of FH in the alternative complement pathway.1,3
Fig.1 Function of FH in the alternative complement pathway.1,3
Factor H (FH) is the principal soluble negative regulator of the AP, circulating in human blood plasma. FH is a 155 kDa glycoprotein composed of 20 complement control protein (CCP) domains. Its key functions include acting as a cofactor for the Factor I-mediated cleavage of C3b and accelerating the decay of the AP C3-convertase (C3bBb). A study in Frontiers in Immunology (2020) highlights that genetic variations or autoantibodies targeting FH can lead to severe diseases, such as atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS) and C3 glomerulopathy (C3G), underscoring its critical role in health and disease. Another review (2021) describes how pathogens can hijack FH to evade the host immune response, further demonstrating its central importance in immune regulation.
Application
The development of soluble complement regulators like Factor H has wide-ranging applications in therapeutic and diagnostic fields.
Drug Discovery for Complement-Mediated Diseases
Therapeutic applications targeting Factor H are crucial for treating diseases characterized by complement overactivation, such as aHUS and C3G.
Ophthalmology
Factor H has a documented role in age-related macular degeneration (AMD), and its therapeutic manipulation can be a strategy for treating this debilitating eye disease.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disorders
Given the broad role of the complement system in inflammation, Factor H-based therapeutics are being explored for a wide range of autoimmune conditions.
Immunology Research
Recombinant Factor H and its variants are essential tools for studying the complement cascade, understanding disease mechanisms, and screening potential drug candidates.
Infectious Diseases
Understanding how pathogens exploit Factor H for immune evasion provides a basis for developing novel anti-infective therapies.
Published Data
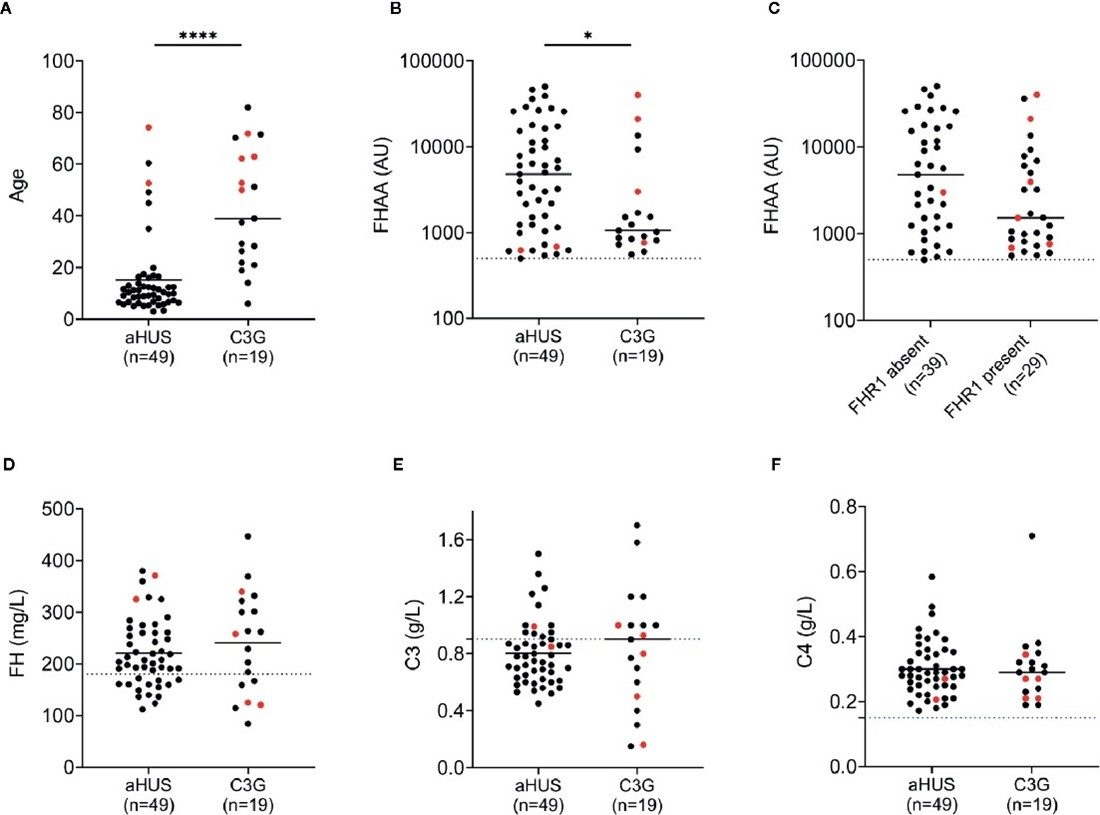 Fig.2 FH autoantibodies (FHAAs) and key biomarkers at the age-of-onset of disease in patients with aHUS and C3.2,3
Fig.2 FH autoantibodies (FHAAs) and key biomarkers at the age-of-onset of disease in patients with aHUS and C3.2,3
Recently published research highlights a strong link between the levels of soluble complement regulators and disease severity in patients with COVID-19. In a study, researchers used a shotgun proteomic approach to analyze the circulating levels of Factor H (FH), its variant Factor H-like 1 (FHL-1), and five Factor H-Related proteins (FHR1-5). The experiment revealed a significant elevation in FHR proteins, particularly FHR2 and FHR5, in patients with more severe disease compared to those with mild symptoms. This data supports the hypothesis that the elevation of FHR family proteins can predict disease severity. The study concludes that early, uncontrolled activation of the complement system, amplified through the alternative pathway, is a key feature of severe COVID-19, offering a crucial insight for targeted therapeutic strategies.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs offers a comprehensive suite of products and services to support your soluble complement regulator projects.
-
Recombinant Factor H & Variants: High-purity, validated recombinant Factor H protein, as well as engineered variants with altered binding, stability, or activity profiles.
-
Custom Protein Engineering Services: Design and development of novel Factor H constructs for specific therapeutic applications.
-
Antibody Development: Generation of high-specificity antibodies targeting Factor H or other complement components for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes.
-
Functional Assays: A full range of functional assays to measure complement activity, C3b deposition, and the regulatory efficacy of your proteins.
-
Expression Vectors: Custom expression vectors containing your desired Factor H gene sequence for your in-house expression needs.
Workflow
01
Target Analysis & Design: We begin with a detailed analysis of your project goals to design optimal Factor H constructs. This includes selecting appropriate domains and engineering constructs for specific therapeutic applications.
02
Gene Synthesis & Cloning: Our team synthesizes the designed gene sequences and clones them into proprietary high-expression vectors.
03
Protein Expression & Purification: We utilize state-of-the-art expression systems to produce the recombinant Factor H protein, followed by multi-step chromatography to ensure high purity and quality.
04
Structural & Functional Characterization: We perform a suite of assays to confirm the protein's identity, purity, and most importantly, its functional activity, including C3b binding and cofactor activity assays.
05
Deliverables Preparation: The final product is prepared according to your specifications, ready for your downstream applications.
Why Choose Us?
At Creative Biolabs, our expertise in developing soluble complement regulators offers you significant advantages in your research and therapeutic development.
-
Advanced Platforms: We utilize proprietary platforms for protein design and expression, minimizing production risks.
-
Comprehensive Characterization: Our analytical capabilities ensure high-quality products, with rigorous structural and functional validation. Published Data demonstrate high efficacy and specificity.
-
Proven Success: We have successfully assisted numerous clients, providing custom solutions that have accelerated their projects.
-
Customization: Our services are fully customizable. We work closely with you to tailor our approach to your specific scientific requirements.
-
Dedicated Support: Our team of experienced scientists is available to provide expert consultation and support throughout your project.
Obtain the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Seek a Quote Today
FAQs
Q: What is a soluble complement regulator, and why is it important in medicine?
A: Soluble complement regulators are proteins that circulate in the bloodstream and help prevent the complement system from attacking healthy host cells. In medicine, they are crucial because they can be used as therapeutics to inhibit uncontrolled complement activation, which is a key driver of many inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
Q: How can I determine which Factor H construct is best for my specific research or therapeutic goal?
A: The optimal construct depends on your specific application, such as whether you need to target a particular disease-related surface or a fluid-phase mechanism. We recommend a collaborative consultation to discuss your project in detail. Based on your needs, we can design and develop a custom construct that provides the most effective solution.
Q: Can these proteins be used in preclinical models, and what kind of data can I expect?
A: Yes, the proteins are suitable for use in preclinical models. You can expect to receive a comprehensive report with detailed data on protein purity, structural integrity, and functional validation, including its ability to inhibit complement activation in relevant assays.
Q: Are there any specific handling or storage precautions for these proteins?
A: Recombinant proteins are sensitive and require specific handling. They are typically shipped as a lyophilized powder or in a buffered solution and should be stored at −20°C or below. We provide detailed product information sheets with specific handling instructions to ensure protein stability and activity.
Q: How do these services compare to purchasing off-the-shelf proteins?
A: While off-the-shelf proteins can be useful for general research, our services offer the advantage of full customization. We can engineer proteins with specific mutations, expression tags, or other modifications that are not commercially available, giving you a distinct advantage in your unique research project.
Creative Biolabs is your partner in advancing complement therapeutics. Our Soluble Complement Regulators Development- Factor H Development Service is designed to accelerate your projects with high-quality, expertly engineered proteins and unparalleled scientific support.
Featured Services
Feature Products
References
-
Atkinson, John P, and Timothy H J Goodship. "Complement factor H and the hemolytic uremic syndrome." The Journal of Experimental Medicine vol. 204,6 (2007): 1245-8. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20070664
-
Zhang, Yuzhou et al. "Factor H Autoantibodies and Complement-Mediated Diseases." Frontiers in Immunology vol. 11 607211. 15 Dec. 2020, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.607211
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Function of FH in the alternative complement pathway.1,3
Fig.1 Function of FH in the alternative complement pathway.1,3
 Fig.2 FH autoantibodies (FHAAs) and key biomarkers at the age-of-onset of disease in patients with aHUS and C3.2,3
Fig.2 FH autoantibodies (FHAAs) and key biomarkers at the age-of-onset of disease in patients with aHUS and C3.2,3