Introduction Published Data What We Can Offer? Workflow Why Choose Us? FAQs Featured Services Featured Products
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in developing effective therapies for inflammation, ischemia-reperfusion injury, or other complement-mediated diseases? Creative Biolabs' Soluble Complement Regulators Development Service helps you accelerate drug discovery and obtain high-quality, targeted complement inhibitors through our advanced protein engineering and expression platforms. We provide a streamlined process from concept to final product, enabling you to confidently advance your project.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system is a critical component of the innate immune response, designed to clear pathogens and damaged cells. However, its dysregulation can lead to uncontrolled inflammation and tissue damage, contributing to a wide range of diseases, including autoimmune disorders, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and neurodegenerative conditions. Soluble complement regulators, such as sCR1, are naturally occurring proteins that play a vital role in preventing this self-inflicted damage by inhibiting complement activation in the fluid phase.
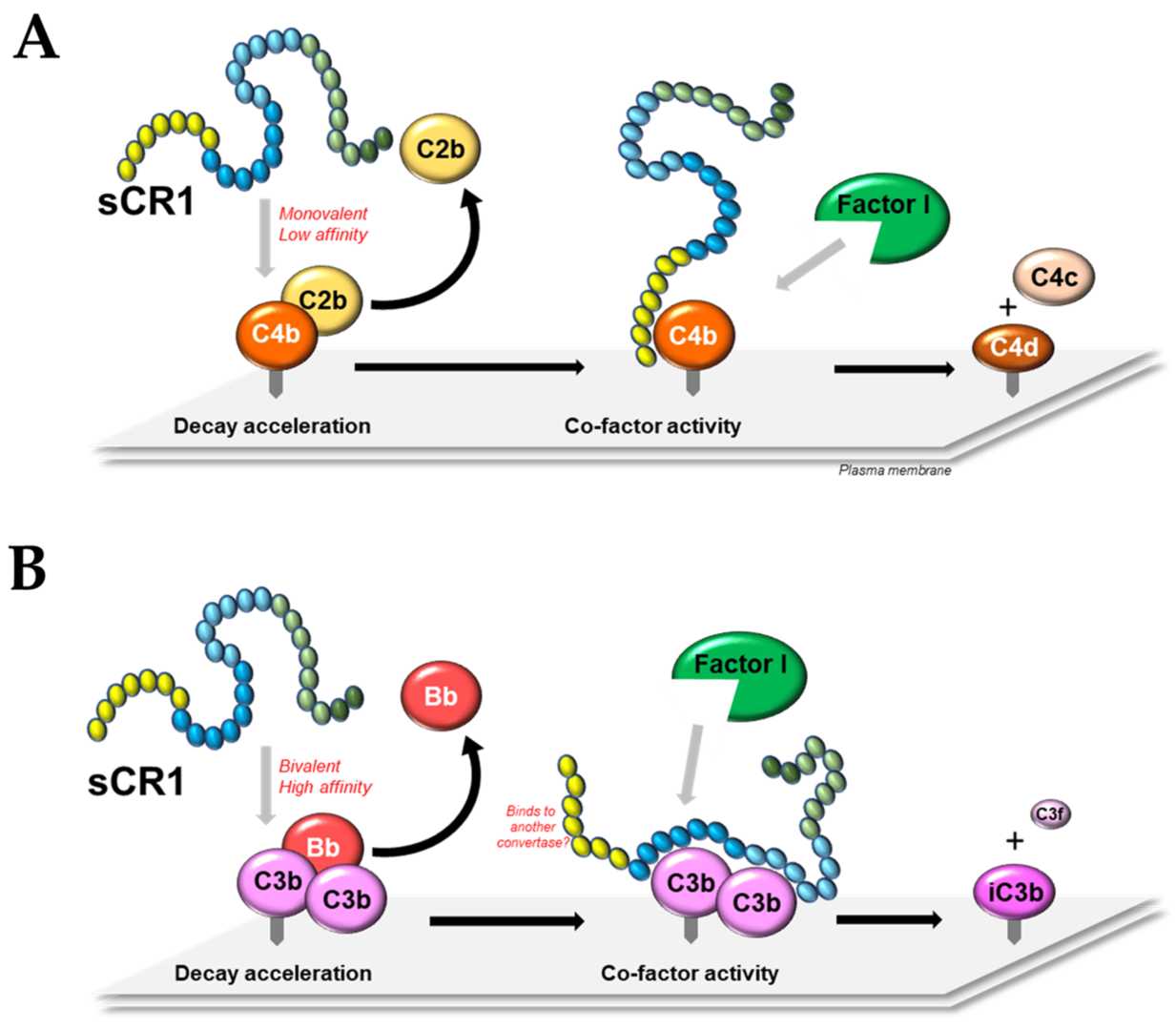 Fig.1 The sCR1 molecular mechanisms.1,3
Fig.1 The sCR1 molecular mechanisms.1,3
Complement Receptor 1 (CR1, CD35) is a large glycoprotein found on the surface of various immune cells. Its soluble form, sCR1, is a potent inhibitor of both the classical and alternative complement pathways. TP10 is a recombinant version of sCR1 that has been studied extensively for its therapeutic potential. It functions by acting as a cofactor for the inactivation of C3b and C4b and by accelerating the decay of the C3 and C5 convertases, effectively shutting down the complement cascade at a central point. Preclinical and clinical studies have demonstrated its safety and efficacy in conditions like cardiopulmonary bypass and organ transplantation.
CR1 vs. sCR1: Key Differences
To better understand the therapeutic role of sCR1, it's important to distinguish it from its membrane-bound counterpart, CR1. The table below outlines the key differences in their location, function, and therapeutic potential.
|
Feature
|
CR1 (Membrane-Bound)
|
sCR1 (Soluble Form)
|
|
Location
|
Integrated into the cell membranes of hematopoietic cells (e.g., erythrocytes).
|
Released into the plasma through a proteolytic process.
|
|
Function
|
Helps clear immune complexes and serves as a cofactor for Factor I to degrade C3b and C4b.
|
Retains the cofactor activity of CR1, helping to control the complement system in the fluid phase.
|
|
Therapeutic Potential
|
/
|
Can be used to prevent complement-mediated tissue damage.
|
|
Molecular Structure
|
Consists of 30 short consensus repeats (SCRs).
|
Composed of the first three SCRs of CR1, a truncated form of the native protein.
|
|
Clinical Use
|
Not used directly as a therapeutic
|
It has been studied in clinical trials for various diseases.
|
Application
Soluble complement regulators have a wide range of therapeutic applications due to their ability to precisely control the complement cascade.
-
Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: Used to prevent tissue damage that occurs when blood supply is restored to an organ after a period of ischemia.
-
Autoimmune Diseases: Applicable in conditions where chronic complement activation contributes to disease pathology, such as systemic lupus erythematosus.
-
Organ Transplantation: Reduces hyperacute rejection by preventing complement-mediated attack on the transplanted organ.
-
Cardiac Surgery: Attenuates systemic inflammatory responses and reduces complications in patients undergoing procedures like cardiopulmonary bypass.
-
Inflammatory Disorders: Potential treatment for various inflammatory conditions where the complement system plays a pathogenic role.
Published Data
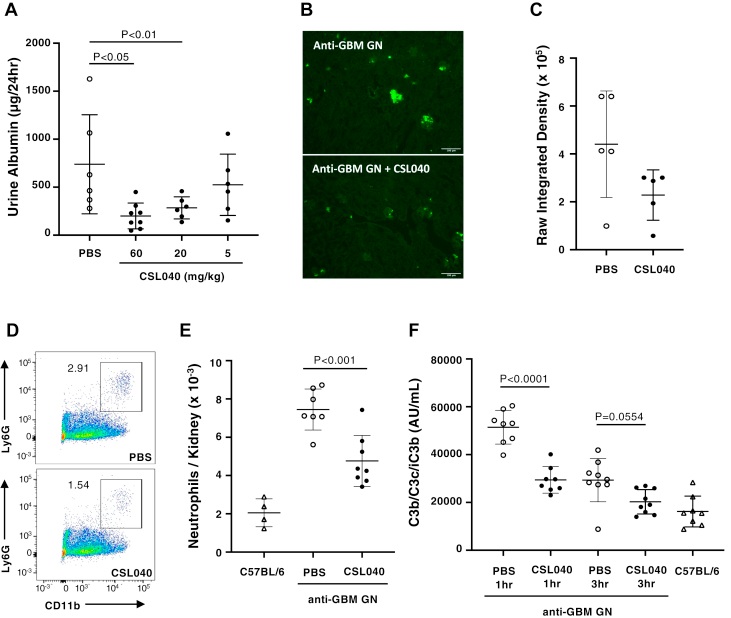 Fig.2 The effect of the specific sCR1 fragment in an attenuated-passive anti-GBM glomerulonephritis mouse model.2,3
Fig.2 The effect of the specific sCR1 fragment in an attenuated-passive anti-GBM glomerulonephritis mouse model.2,3
The study aimed to identify a minimal soluble fragment of human CR1 that could retain the full complement regulatory activity of the wild-type protein. They generated recombinant, soluble, and truncated versions of human CR1 and compared their ability to inhibit complement activation in vitro using multiple assays. The results confirmed that a specific sCR1 fragment maintained robust inhibitory activity. Further in vivo experiments using a murine model of kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury showed that this variant significantly attenuated kidney damage and reduced cellular infiltrates, providing strong evidence of its therapeutic potential. This data highlights the viability and efficacy of designing optimized sCR1 variants for therapeutic use.
What We Can Offer?
Our service portfolio is designed to support your project at every stage, from discovery to preclinical development.
-
Custom Soluble Regulator Design: Tailored design and engineering of novel soluble complement regulators to meet your specific project requirements.
-
Gene Synthesis and Recombinant Protein Expression: High-yield production of sCR1, TP10, or other custom constructs in our state-of-the-art mammalian expression systems.
-
Protein Purification and Characterization: Comprehensive purification services followed by extensive characterization to ensure product quality and integrity.
-
Functional Validation Assays: In-depth biological testing to confirm the protein's efficacy in inhibiting complement activation.
-
Preclinical Material Production: Scalable production of high-quality proteins suitable for in vivo studies.
Workflow
01
Target Design and Engineering: We design and engineer a soluble complement regulator construct based on your project goals.
02
Gene Synthesis and Cloning: The construct is synthesized and cloned into high-yield expression vectors.
03
High-Throughput Expression and Screening: Proteins are expressed in mammalian systems and screened for optimal expression and activity.
04
Protein Purification and Quality Control: We purify the protein to high purity and perform comprehensive quality control checks.
05
Functional Validation: The purified protein is rigorously tested in functional assays to confirm its ability to inhibit complement activation.
Why Choose Us?
At Creative Biolabs, we combine deep scientific knowledge with cutting-edge technology to deliver superior soluble complement regulator development services.
-
Exceptional Scientific Expertise: Our team consists of highly experienced protein engineers and immunologists with a profound understanding of the complement system.
-
Advanced Protein Engineering: We use innovative techniques to design and optimize soluble regulators for enhanced stability, affinity, and pharmacokinetic properties.
-
Robust Quality Control: Every product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure high purity, confirmed activity, and safety.
-
Proven Success: Our capabilities are supported by extensive internal research and published data demonstrating the efficacy of our protein development platforms.
Obtain the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Seek a Quote Today
FAQs
Q: How can I determine if a soluble complement regulator is the right approach for my project?
A: Soluble complement regulators are highly effective for diseases where uncontrolled complement activation is a primary cause of inflammation or tissue damage. We recommend starting with a small-scale in vitro study to assess the involvement of the complement system in your disease model.
Q: Are there any known side effects or safety concerns with these types of therapeutics?
A: Soluble complement regulators are designed to mimic natural inhibitors and are generally well-tolerated. However, as with any therapeutic, there is a risk of a general increase in susceptibility to infections due to complement inhibition. This risk is managed through careful dosing and patient monitoring.
Q: How do soluble complement regulators compare to antibody-based complement inhibitors?
A: While both are effective, soluble regulators offer distinct advantages, such as a broad-spectrum inhibitory effect on multiple complement pathways. Their natural origin can also lead to a different safety profile and potential for specific applications where systemic pathway-wide inhibition is desirable.
Q: What is the typical turnaround time for a project from start to finish?
A: The timeframe can vary depending on the complexity of the project, including the specific protein design, the expression system, and the extent of required quality control. We work closely with our clients to provide a realistic project timeline.
Q: Can I request modifications to a standard soluble complement regulator, such as a longer half-life?
A: Yes, protein engineering is one of our core strengths. We can incorporate various modifications, such as fusion to an Fc domain or PEGylation, to enhance the stability and pharmacokinetic properties of the final product.
Creative Biolabs is your trusted partner for the development of cutting-edge soluble complement regulator therapeutics. We are committed to providing high-quality, reliable, and scientifically sound solutions to accelerate your research and development efforts.
Featured Services
Feature Products
References
-
Hardy, Matthew P et al. "The Molecular Mechanisms of Complement Receptor 1-It Is Complicated." Biomolecules vol. 13,10 1522. 13 Oct. 2023, https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13101522
-
Wymann, Sandra et al. "A novel soluble complement receptor 1 fragment with enhanced therapeutic potential." The Journal of Biological Chemistry vol. 296 (2021): 100200. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA120.016127
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 The sCR1 molecular mechanisms.1,3
Fig.1 The sCR1 molecular mechanisms.1,3
 Fig.2 The effect of the specific sCR1 fragment in an attenuated-passive anti-GBM glomerulonephritis mouse model.2,3
Fig.2 The effect of the specific sCR1 fragment in an attenuated-passive anti-GBM glomerulonephritis mouse model.2,3