GTOnco™ MHC-associated Peptide Proteomics Assay Service
Immunogenicity is a key factor influencing the safety and efficacy of gene-therapy-based I-O products, such as peptide vaccines or T-cell vaccines for immunotherapy. MHC associated peptide proteomics (MAPPs) assay uses liquid chromatography / mass spectrometry (LC/MS) to identify peptide sequences which are presented by MHC on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and therefore may induce the immunogenicity. MAPPs assay can be also used for determining epitopes that can be deimmunized. As a leading service provider in the field of I-O drugs development, Creative Biolabs provides top-quality MAPPs assay services for our customers to directly identify the peptides presented by APCs to T cells.
Introduction of MHC-associated Peptide Proteomics Assay
The adaptive immune response is key to host defense against pathogens and malignancies and is closely associated with the human major histocompatibility complex (MHC), or human leukocyte antigens (HLA). MHC molecules function to capture the cellular proteome, bind to small peptide fragments (i.e., the immunopeptidome), and present them on the cell surface for surveillance by T lymphocytes. The precise molecular composition of these presented peptidomes ultimately determines T cell recognition and activation. Therefore, MHC-associated peptide proteomics (MAP-proteomics) assays are key enabling technologies in modern immunology and translational medicine. These assays combine immunoaffinity purification (IAP) of MHC-peptide complexes from biological samples with highly sensitive and accurate mass spectrometry (MS) analysis. Their goal is to comprehensively and objectively characterize the naturally presented immunopeptidome, thereby providing the molecular targets necessary for:
- Identifying novel T cell epitopes for personalized cancer vaccines
- Understanding the mechanisms of T cell tolerance in autoimmunity
- Characterizing viral and bacterial antigen presentation for infectious disease vaccine design
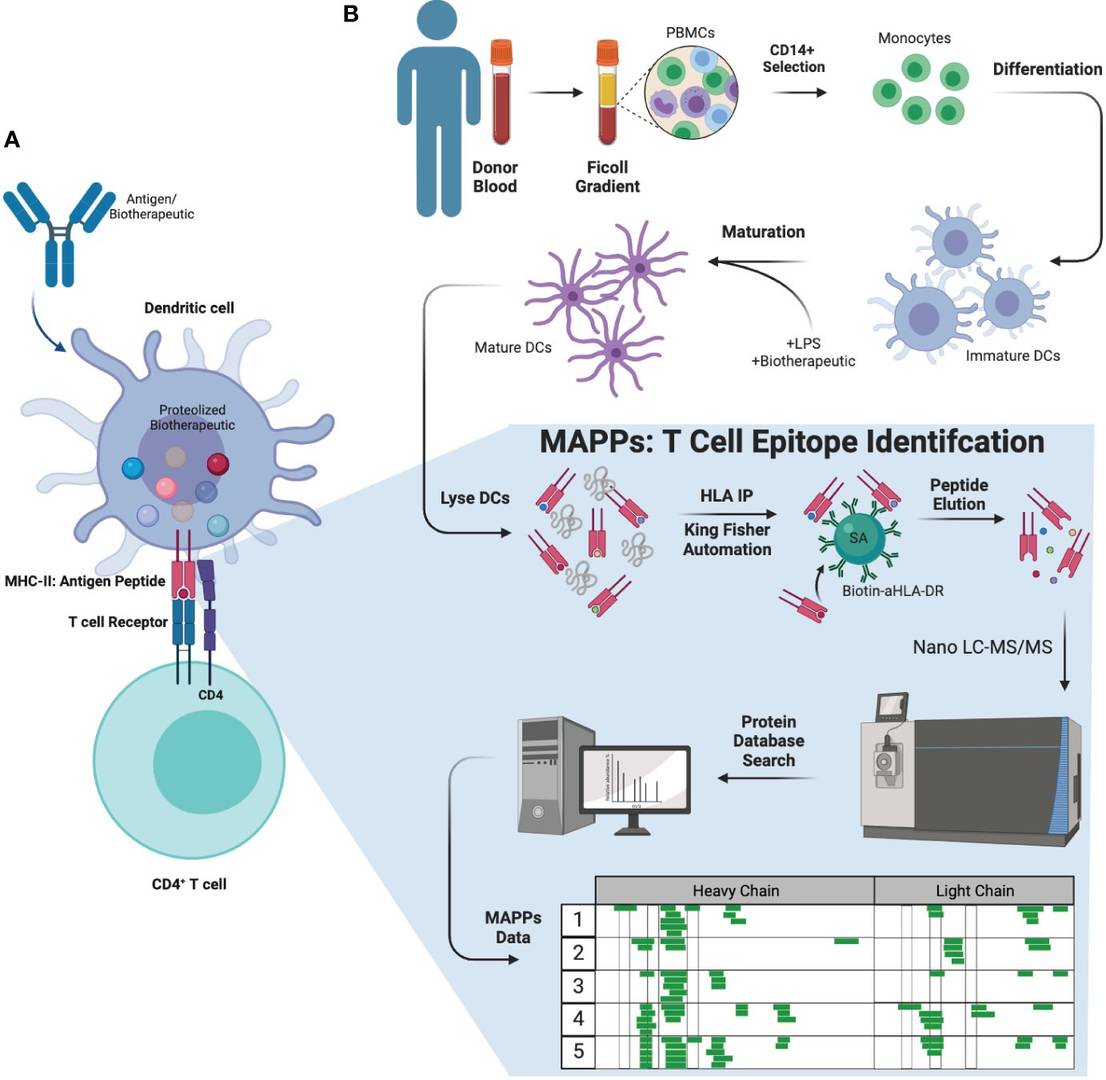 Figure 1 Biology of ADA formation, MAPPs workflow, and therapeutic molecules tested.1
Figure 1 Biology of ADA formation, MAPPs workflow, and therapeutic molecules tested.1
MHC Class I and Class II Peptides
The Structure and Function of MHC Class I and Class II Peptides: MHC molecules are divided into two major classes, each targeting different T cell subsets:
MHC Class I (MHC I): Presents peptides (typically 8-11 amino acids) derived from intracellular proteins to CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Their primary role is in surveillance for viral infection and malignant transformation.
MHC Class II (MHC II): Presents longer peptides (typically 12-25 amino acids) derived from extracellular or endosomal/lysosomal proteins to CD4+ helper T cells. These are crucial for coordinating the overall immune response.
Significant Advantages Over Traditional Methods
MAPPs are the gold standard because they directly measure naturally presented antigens, thus overcoming the limitations of predictive models:
| Method | Strength | Limitation | MAPPs Superiority |
|---|---|---|---|
| In Silico Prediction | Fast and cost-effective. | Ignores antigen processing (proteasomal cleavage, transport) and presentation efficiency. High false-positive rate. | Identifies peptides that have truly survived the entire processing and presentation pathway. |
| In Vitro Binding Assays | Measures peptide-MHC affinity. | Does not account for cellular processing (e.g., TAP transport, endosomal loading). | Confirms the biological relevance by identifying peptides presented on the cell surface ex vivo. |
Key MAPPs Technology Workflows
Creative Biolabs' proprietary MAPPs platform ensures maximum peptide recovery and fidelity:
Sample Preparation and Lysis
High-quality input material (cells or tissue) is required. A gentle lysis buffer is used to maintain the integrity of MHC-peptide complexes on the cell membrane.
Immunoaffinity Purification (IP)
MHC-peptide complexes are enriched using highly specific pan-MHC I and/or pan-MHC II antibodies coupled to magnetic beads (e.g., anti-HLA-A, -B, and -C antibodies for class I, and anti-HLA-DR, -DP, and -DQ antibodies for class II). This critical step requires high-purity reagents and an optimized protocol.
Peptide Elution and Cleanup
Peptides are released from the MHC channel by gentle acidic elution, followed by desalting and concentration to prepare low-concentration samples for MS. High-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis: Eluted peptides are analyzed using state-of-the-art nano-LC-tandem mass spectrometry (e.g., Orbitrap-based instruments), generating high-quality spectral data.
Bioinformatics Analysis
Raw mass spectrometry data is processed to match peptide fragment spectra to sequences in relevant databases (e.g., patient-specific mutation databases for neoantigens). Advanced algorithms are used for MHC motif deconvolution and presentation scoring.
Core Services at Creative Biolabs
At Creative Biolabs, we have successfully established an MHC associated peptide proteomics system to predict and assess T cell epitopes in amino acid sequences. In GTOnco™ MAPPs assay, the therapeutic I-O agent is co-incubated with APCs and the peptide fragments are further presented on MHC molecules. Then, the cells will be lysed and MHC-associated peptides are then extracted and purified. Finally, the amino acid sequences of the peptide will be analyzed by LC-MS/MS. A series of stringent criteria are applied to implement quality control of our assay process in order to guarantee reliability and identify true positive peptides.
| Service Category | Key Offerings | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Neoantigen Discovery | MAPPs for Patient Samples (Tumor/PBMCs) | High-resolution MHC I and II profiling to identify and validate true neoantigens for personalized vaccines. |
| Immunogenicity Assessment | Biologic Drug Epitope Mapping (MHC II) | Identify drug-derived peptides naturally presented on APCs to assess and mitigate immunogenicity risk in drug development. |
| Target Validation | TCR/CAR-T Target Identification | Comprehensive analysis of pMHC complexes on target cells to identify novel, highly specific targets for cellular therapies. |
| Custom pMHC Synthesis | Validated Peptide/MHC Complex Production | Synthesis of identified MHC-peptide complexes for downstream functional assays (e.g., TCR screening, T-cell activation assays). |
Applications of Our Services
Our MAPPs services play a key role across the biomedical research and drug development landscape:
- Personalized medicine: Designing specific cancer vaccines.
- Drug safety: Reducing the immunogenicity risk of therapeutic proteins and antibodies.
- Immunology research: Uncovering antigen presentation pathways in infectious diseases and autoimmunity.
- Biomarker discovery: Identifying pMHC patterns as potential biomarkers of therapeutic response (e.g., to checkpoint inhibitors).
Why Choose Our Services?
- Sensitivity and Depth: Our optimized protocols enable deep peptidomic coverage from minimal starting material (as low as 10^6 cells), critical for scarce clinical samples.
- Comprehensive Coverage: We offer both MHC I and MHC II peptidomic profiling, essential for a comprehensive understanding of CD8+ and CD4+ T cell responses.
- Proprietary Bioinformatics: Our advanced data processing and MHC motif analysis technologies ensure high-confidence peptide identification and accurate neoantigen prioritization.
- End-to-End Solutions: We offer a seamlessly integrated workflow from sample processing and liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to downstream T cell functional validation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the minimum sample amount required for MHC peptidome analysis?
A: For comprehensive MHC peptidome analysis using our standard bottom-up proteomics workflow, we typically recommend using 10 to 100 million cells, depending on MHC expression levels. However, we have optimized low-input protocols, and for particularly promising samples, only 1 to 5 million cells may be required to generate meaningful data. Specific requirements vary depending on factors such as MHC expression density, sample type (cell line vs. primary cells), and species.
Q: How many peptides can typically be identified from a single MHC peptidome analysis?
A: The number of peptides identified varies depending on sample type, MHC allotype, and analysis depth. In a typical experiment using 50 million human cells expressing common HLA allotypes, our high-sensitivity workflow typically identifies 2,000 to 5,000 unique MHC-associated peptides with high confidence.
Q: Can your service process both MHC class I and class II peptides?
A: Of course. Our platform is optimized for analyzing both MHC class I and MHC class II peptidomes. Due to significant differences in peptide length distribution, binding groove properties, and cellular processing pathways, the methods for analyzing these two classes of peptidomes differ significantly. For MHC class I peptides (typically 8-11 amino acids), we isolate them using antibodies (e.g., W6/32) that recognize folded HLA-A, -B, and -C complexes. For MHC class II peptides (typically 12-25 amino acids), we use antibodies against the invariant chain or specific HLA-DR, -DP, and -DQ molecules. We also offer specialized protocols for nonclassical MHC molecules (e.g., HLA-E, HLA-G, and MR1).
Q: How does your pMHC multimer technology differ from standard products?
A: Our pMHC multimer technology incorporates several innovative features that enhance performance and reliability. First, we implement rigorous quality control measures, using surface plasmon resonance to confirm binding affinity and specificity before reagent release. Second, we offer exceptional flexibility in multimer configurations, including tetramers, pentamers, and dextromorphs, along with a variety of fluorophore options to support complex experimental designs. Third, we have developed proprietary stabilization methods to extend the shelf life of our reagents without compromising biological activity. Most importantly, our extensive experience with rare HLA allotypes and modified peptides enables us to tackle challenging projects that other suppliers cannot support.
Q: How do we ensure the biological relevance of identified MHC-associated peptides?
A: We employ a multi-layered strategy to prioritize biologically relevant MHC-associated peptides. Our bioinformatics pipeline incorporates MHC binding prediction algorithms to assess whether identified peptides are likely binders or potential contaminants. We integrate available gene expression data to determine whether the target protein is expressed in the target sample. For cancer neoantigen discovery, we incorporate mutation information to identify mutant peptides.
Connect with Us Anytime!
The field of MHC-associated peptide proteomics has become an indispensable tool for immunology research and therapeutic development. At Creative Biolabs, we build on foundational technologies described in the scientific literature to create robust, sensitive, and reproducible platforms that provide actionable insights to our clients. Whether your goal is to discover novel antigens for cancer immunotherapy, monitor T cell responses in vaccine trials, or understand the fundamental principles of antigen presentation, our comprehensive service portfolio provides the expertise and technical capabilities to advance your research projects. For more detail information, please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- Lee M V, Saad O M, Wong S, et al. Development of a semi-automated MHC-associated peptide proteomics (MAPPs) method using streptavidin bead-based immunoaffinity capture and nano LC-MS/MS to support immunogenicity risk assessment in drug development. Frontiers in Immunology, 2023, 14: 1295285. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1295285 (Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.)
