Product List Background CR2 Functional Service
Background
CR2 (complement receptor 2), also known as complement C3d receptor or CD21 (cluster of differentiation 21), is a 140 kDa receptor encoded by the CR2 gene. The common CR2 ligands include complement C3 fragments iC3b, C3dg and C3d, Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein 350/220, and the immunoregulatory protein CD23. This receptor is found on B cells, thymocytes, follicular dendritic cells, T cells (subset), astrocytes, and pharyngeal epithelial cells and plays a major role in the immune responses through bridging innate and adaptive immunity against foreign pathogens and proteins. Acting as a B cell co-receptor, binding of CR2 to CD19 increases BCR-dependent cell activation. Besides, ligation of CR2 alone has been revealed to lead to BCR-independent phenotypes, including induction of homotypic adhesion, IL-6 generation, and antigen uptake and presentation to T cells. Furthermore, CR2 also plays a crucial role in increasing humoral immunity to T-dependent and T-independent foreign antigens and in mediating T-cell immunity to both autoantigens and non-autoantigens. In addition to the above, CR2 may be involved in innate immunity. It can bind to activators of innate immunity such as IFN-α, an anti-viral cytokine, causing B cell activation. During the development of autoimmunity, CR2 participants in maintaining tolerance to self-antigens. Deficiencies of CR2 are associated with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
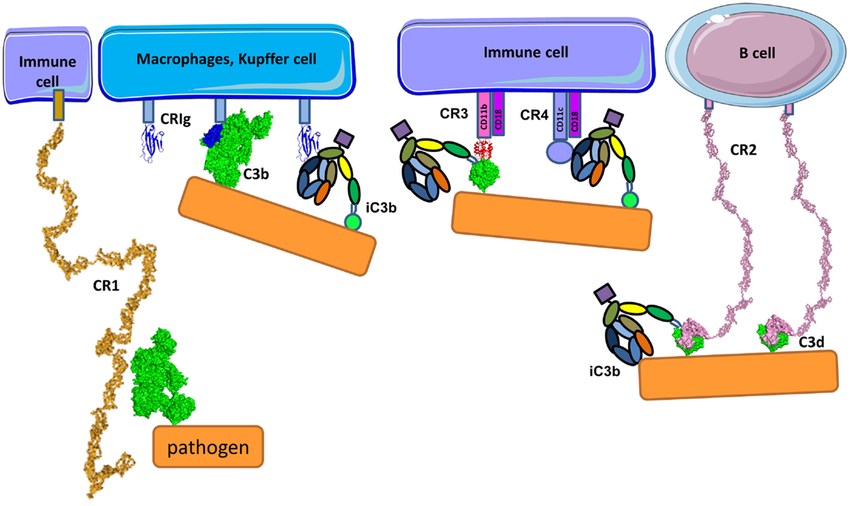 Fig.1 Schematic diagram of complement receptors.1, 3
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of complement receptors.1, 3
CR2 Functional Service
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive array of CR2-related products, encompassing anti-CR2 antibodies, ELISA kits and recombinant complement CR2 proteins. These carefully crafted resources are vital for progressing research efforts focused on developing therapeutic strategies for numerous diseases.
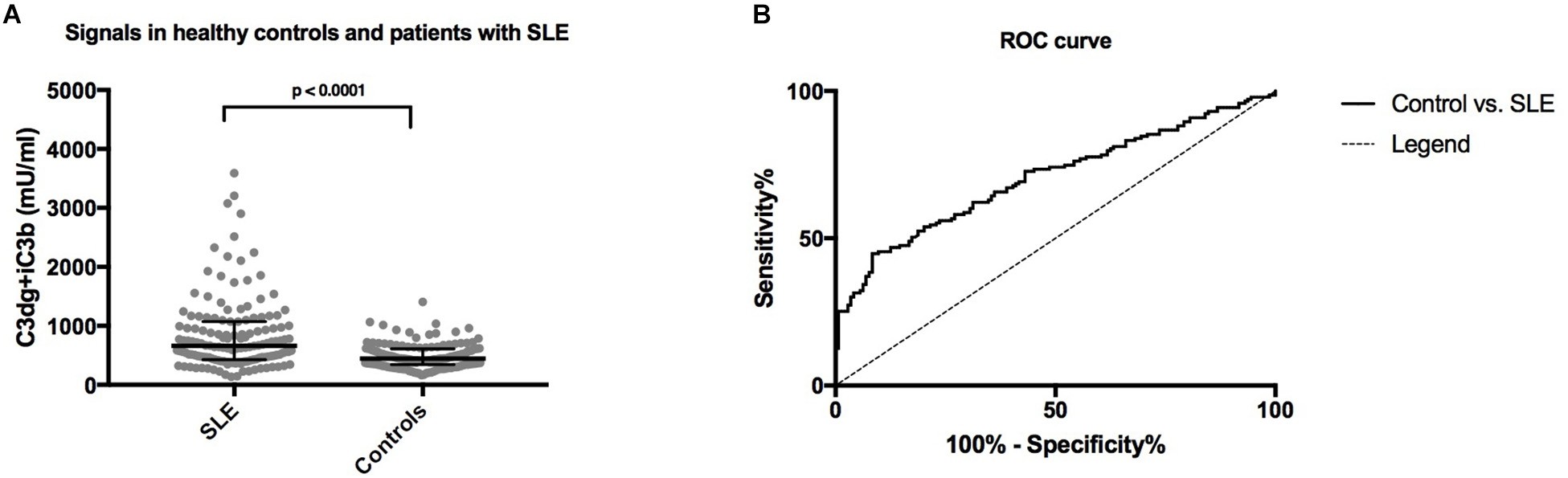 Fig.2 Assessment of plasma C3dg+iC3b levels in SLE: human CR2 assay vs. healthy controls.2, 3
Fig.2 Assessment of plasma C3dg+iC3b levels in SLE: human CR2 assay vs. healthy controls.2, 3
Researchers set out to develop a sensitive and robust assay for estimating systemic complement activation at the C3 level in both mouse and human plasma samples. To ensure specific and physiologically relevant capture of activation products iC3b and C3dg, they employed a construct comprising the iC3b/C3dg-binding site of human CR2 fused to the Fc portion of mouse IgG. This construct, derived from mouse myeloma cell line, was purified using protein G affinity chromatography and utilized in microtiter wells to capture C3 fragments. Anti-mouse or anti-human C3 antibodies facilitated detection. In assays, activated mouse serum exhibited up to three-fold higher signals than non-activated samples, with no signal in C3 knock-out serum. These assays represent the inaugural tools for complement activation utilizing a physiologically pertinent capture construct like CR2. They will serve as valuable resources for exploring complement system-related mouse models and human pathologies.
Creative Biolabs offers a range of CR2 services, including CR2 interaction analyses and supplementary functional solutions, tailored to aid our valued clients in scientific inquiry and clinical practice.
References
-
Merle, Nicolas S., et al. "Complement system part I–molecular mechanisms of activation and regulation." Frontiers in immunology 6 (2015): 262.
-
Halkjær, Lene, et al. "Complement receptor 2 based immunoassay measuring activation of the complement system at C3-level in plasma samples from mice and humans." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 774.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Schematic diagram of complement receptors.1, 3
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of complement receptors.1, 3
 Fig.2 Assessment of plasma C3dg+iC3b levels in SLE: human CR2 assay vs. healthy controls.2, 3
Fig.2 Assessment of plasma C3dg+iC3b levels in SLE: human CR2 assay vs. healthy controls.2, 3
