Antibody-expressing Oncolytic Virus Production Service
Introduction
Monoclonal antibody (mAb) is produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. With high specificity, mAb plays a role in recognition and targeting in tumor therapy. The high cost of mAb production can be well addressed by administering to patients the nucleotide sequence encoding the mAb, rather than the mAb protein. Oncolytic virus is a good method for antibody gene transfer, which can lyse tumor cells to release antigens, which provides more targets for monoclonal antibodies. Monoclonal antibodies can enhance immune activation and cooperate with oncolytic viruses to activate the immune system in all directions to overcome the immune escape of tumors. The combination of the two is expected to become a new strategy for more efficient and precise cancer treatment.
As a first-class biotech CRO, Creative Biolabs produces high-quality oncolytic virus products that express monoclonal antibodies with a full range of customized solutions tailored to client needs.
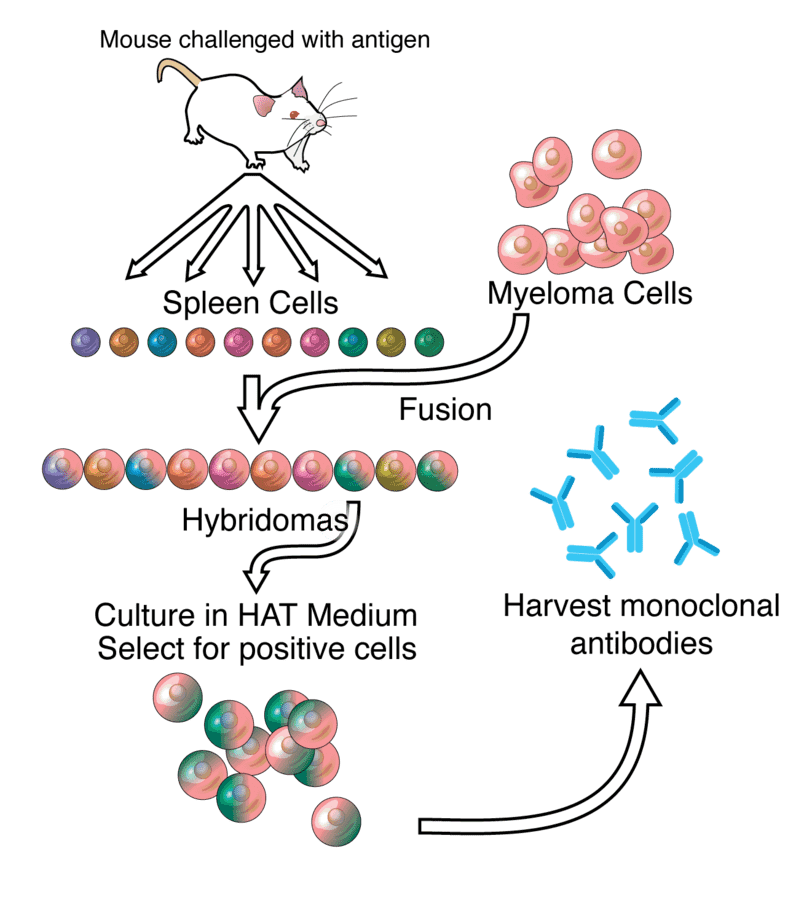 Fig.1 Monoclonal antibodiesDistributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Monoclonal antibodiesDistributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Tumor-targeting mAbs
Oncolytic viruses enhance selective tumor-cell killing by utilizing tumor-targeting mAbs. Researchers engineered an oncolytic vaccinia virus armed with scFv targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in humans and mice. After intravenous administration, tumor-specific delivery and sustained scFv production are observed in a tumor model, and the anti-tumor effect of the virus is enhanced. In addition, similar findings are reported after intratumor injection of oncolytic adenovirus equipped with αHER2 mAb, which can replicate efficiently in HER2+ breast cancer cells and express αHER2 antibodies, significantly enhancing the killing effect on breast cancer cells.
Immunomodulatory mAbs
In oncolytic virotherapy, immune checkpoint inhibition is required. Armed oAds with αCTLA-4 mAb exhibit better anti-tumor effects compared to unarmed virus despite its lack of immune function in the mouse model. After one week of intratumor injection, mAb levels in the tumor and plasma are significantly increased1. Other researchers demonstrate that vaccinia virus (VV) engineered with αTIGIT mAb is an effective oncolytic immunotherapy strategy. The results show that the anti-tumor efficacy of αTIGIT-armed VV is improved in several mouse tumor models, which significantly increases the recruitment and activation of CD8+ T cells and establishes long-term tumor-specific immune memory2.
In addition to antibodies directed against immune checkpoints, a focus on immune-cell function can be pursued. CD47 is a transmembrane protein that is overexpressed in a variety of tumor cell types, including breast cancer. CD47-SIRPα axis promotes tumor cells to escape macrophage-mediated phagocytosis. The use of HSV-1 expressing αCD47 mAb can effectively enhance the phagocytosis of breast cancer tumor cells by macrophages while activating the cytotoxicity of NK cells, and survival in an immunocompetent model of mice3. Therefore, αCD47 mAb therapy may provide a promising anti-tumor strategy.
Bispecific Antibodies
Bispecific antibodies (BsAbs) are therapeutic monoclonal antibodies that target tumor antigens or immune-related molecules. One type of BsAbs molecule consists of two single-chain variable fragments (scFv), each with a serine-glycine linker sequence connecting the heavy and light chains. The use of OV as a platform for intratumor BsAbs delivery takes advantage of the advantages of both drugs, showing higher tumor-targeting efficacy and improved treatment outcomes.
Tab.1 Clinical studies of Bispecific antibodies in hematological malignancie4
| OVs | Platform | Targets | In/ex vivo studies | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oncolytic vaccinia virus | vvDD | EphA2/CD3 | Lung cancer | Increased survival, greater anti-tumor activity |
| FAP/CD3 | Melanoma | T cell activation and anti-tumor activity | ||
| Oncolytic adenovirus | ICOVIR-15K | EGFR/CD3 | Lung cancer and Colorectal cancer | Tumor progression delay, T cell infiltration and expansion |
| EnAd | EpCAM/CD3ε | Ex vivo: malignant peritoneal ascites and pleural effusions | Kill endogenous tumor cells and activate T cells | |
| CD206/ CD3ε | Ex vivo: malignant ascites fluids | Depletion of M2-like macrophage | ||
| Measles Virus | —— | CEA/CD3 | Colorectal cancer | Delayed tumor progression and prolonged survival, T cells are increased in tumor site |
| CD20/CD3 | Melanoma | T cell accumulation and proliferation and increased effector-to-regulatory T cell ratio | ||
| Oncolytic herpes simplex virus | G207 | PD-L1/CD3ε | Ex vivo: malignant peritoneal ascites | T cell activation and cytotoxicity in immunosuppressive ascites fluids cytotoxicity to M2- like macrophages a lower level of PD-L1 expression of surviving cells |
Other Services on Oncolytic Virus Engineering Platform
- Pathogenicity Manipulation (Attenuation)
- Immunogenicity Manipulation
- Cytokine/Chemokine-expressing Oncolytic Virus
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-expressing Oncolytic Virus
Based on our well-established OVs engineering platform, the experienced scientists here at Creative Biolabs are dedicated to helping you develop a unique oncolytic virus. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References
- Dias, J. D., et al. "Targeted cancer immunotherapy with oncolytic adenovirus coding for a fully human monoclonal antibody specific for CTLA-4." Gene therapy 19.10 (2012): 988-998.
- Zuo, Shuguang, et al. "Enhanced antitumor efficacy of a novel oncolytic vaccinia virus encoding a fully monoclonal antibody against T-cell immunoglobulin and ITIM domain (TIGIT)." EBioMedicine 64 (2021).
- Wang, Jing, et al. "Enhanced treatment of breast cancer brain metastases with oncolytic virus expressing anti-CD47 antibody and temozolomide." Molecular Therapy Oncology 32.3 (2024).
- Wang, Yunmeng, and Ping Cheng. "Arming oncolytic viruses with bispecific T cell engagers: The evolution and current status." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Basis of Disease 1870.2 (2024): 166962.
