Cytokine/Chemokine-expressing Oncolytic Virus Production Service
Introduction
Oncolytic virotherapy, as an emerging tumor treatment method in recent years, has been widely discussed. Both cytokines and chemokines are small proteins secreted by cells with biological activity. Cytokines are mainly involved in immune response and immune regulation, promote the proliferation, differentiation, and activation of immune cells, and have anti-infection and anti-tumor effects. Chemokines attract the directed migration of immune cells to sites of inflammation, tumor sites, or other regions that require immune cells to function. The advantages of expressing chemokines or cytokines in oncolytic viruses are remarkable. On the one hand, chemokines can recruit immune cells to the vicinity of the tumor, and cytokines can activate the functions of immune cells. Together, they regulate the immune microenvironment. On the other hand, cytokines can enhance the oncolytic effect and promote the spread of the virus within the tumor tissue.
Based on the mature oncolytic virus engineering platform, Creative Biolabs provides a full range of customized solutions according to customer needs to produce high-quality oncolytic virus products expressing cytokines/chemokines.
Oncolytic adenovirus expressing CCL5 and IL-12
Chemokine C-C motif ligand 5 (CCL5) is mainly secreted by activated T lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and other cells. The main function is to attract a variety of immune cells to migrate to the site of inflammation or specific tissue sites. CCL5 is positively correlated with CD8+ T cell infiltration in solid tumors. The researchers use an oncolytic adenovirus (oAd) armed with CCL5 and IL12 (Ad5-ZD55-CCL5-IL12) in combination with CAR-T cells to treat kidney cancer. Ad5-ZD55-CCL5-IL12 promotes the proliferation of CAR-T cells and enhances the cytotoxic effect on renal cells1.
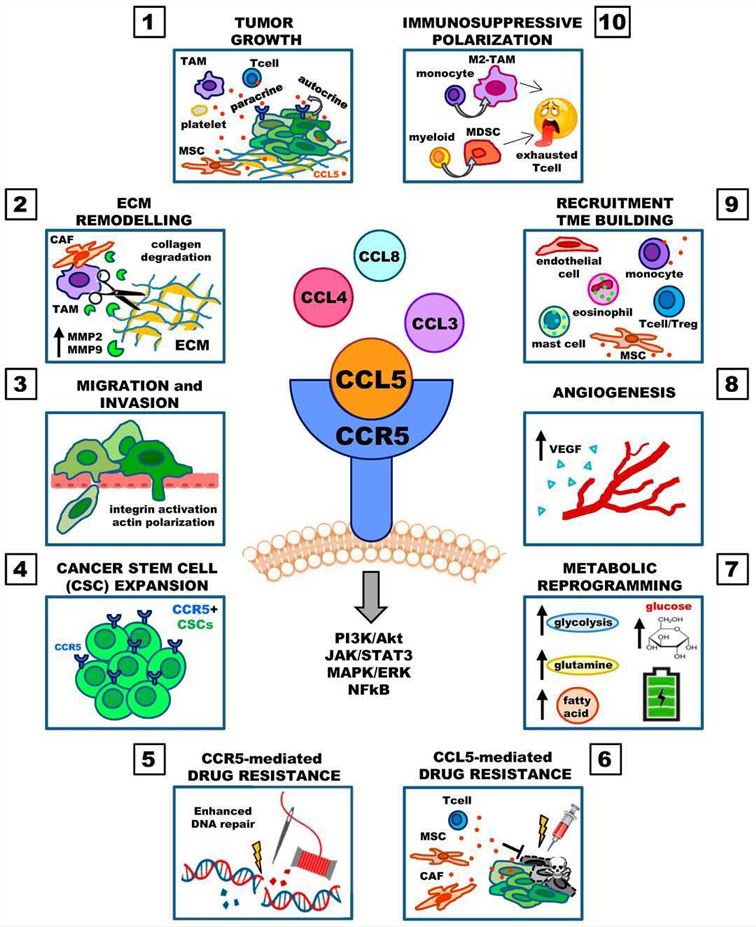 Fig.1 Involvement of the CCL5 in cancer progression2,9
Fig.1 Involvement of the CCL5 in cancer progression2,9
Oncolytic VACV expressing IL-15
IL-15, which is mainly produced by monocytes and macrophages, induces the differentiation and proliferation of T cells, B cells, and NK cells, and maintains memory T cell function. The researchers develop a recombinant variant of the VACV variant LIVP that expresses IL-15 or its receptor IL-15Rα to stimulate IL-15-dependent immune cells3. The in vivo results show that LIVP-IL15-RFP and LIVP-IL15Ra-RFP treating mice with breast cancer significantly prolongs survival time, marks tumor regression, leads to lymphocyte accumulation at the tumor site, and activates cytotoxic T cells and macrophages.
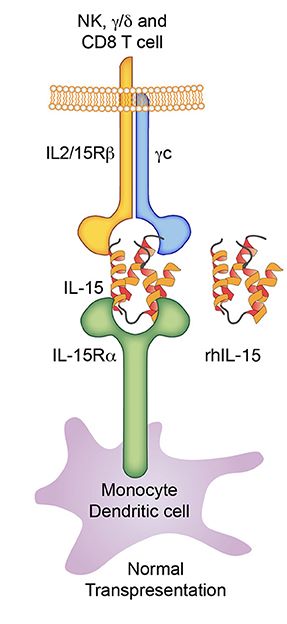 Fig.2 IL-15 agonists used in immunotherapy4
Fig.2 IL-15 agonists used in immunotherapy4
Oncolytic VACV expressing IL-12
IL-12 is mainly secreted by antigen-presenting cells (macrophages and dendritic cells) and exerts its biological functions by binding to its high-affinity receptors (IL-12Rβ1/IL-12Rβ2), which can induce T lymphocytes and NK cells to produce IFN-γ. The researchers design a novel oncolytic vaccinia virus expressing a human IL-12 cytokine transgene, IL-12 induces the production of IFN-γ and enhances the oncolytic activity of VACV. Combined treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors can trigger anti-tumor T cell immune response5.
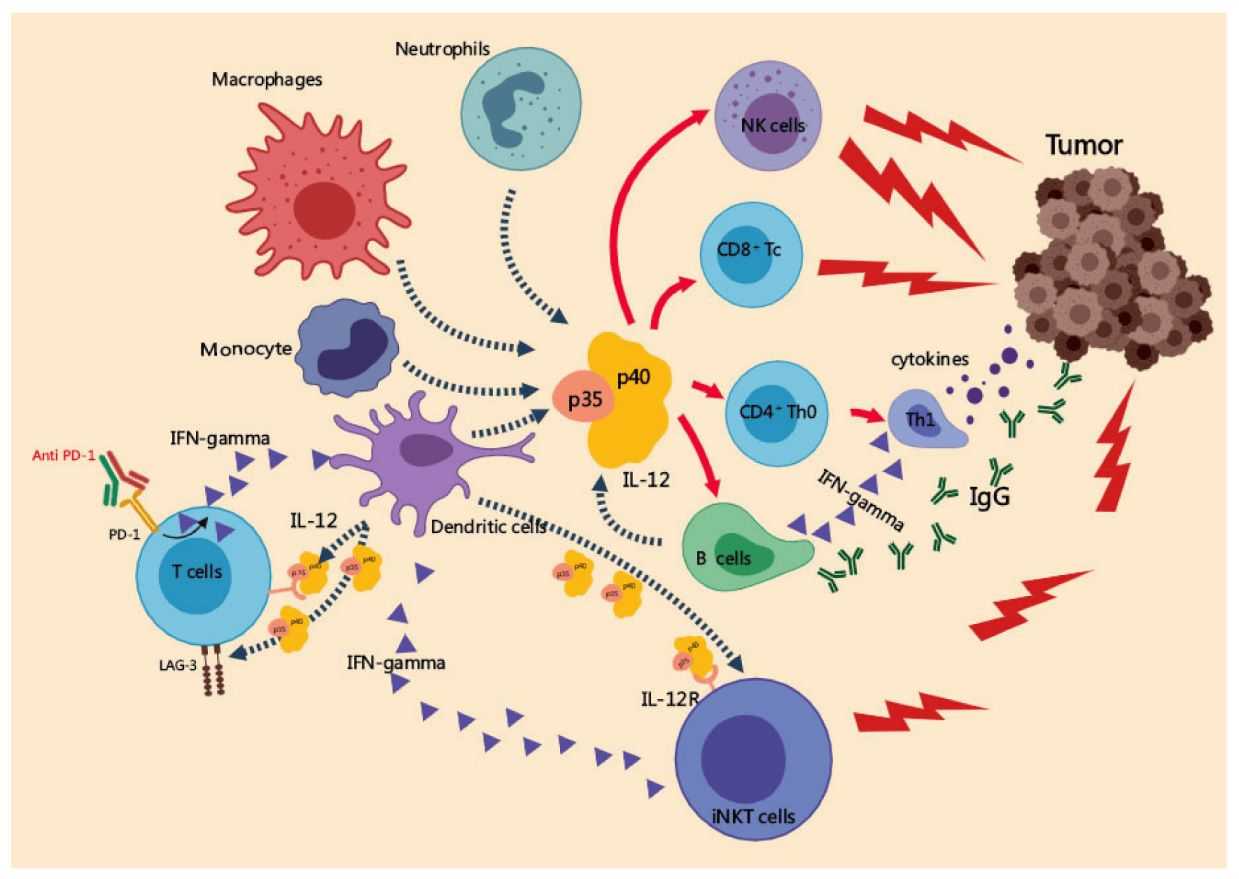 Fig.3 Anti-tumor mechanisms of IL-126,9
Fig.3 Anti-tumor mechanisms of IL-126,9
Oncolytic VACV expressing IL-21
IL-21 can effectively induce T cell activation in vivo, enhance antigen affinity of specific CD8+T cells, and induce NK and NKT cell maturation, activation, and oncolytic potential. Researchers use a new generation of oncolytic vaccinia virus armed with IL-21, combine with immune checkpoint inhibitors, to effectively inhibit tumor growth in glioma model mice, eliminate subcutaneous tumors, and enhance the effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors7.
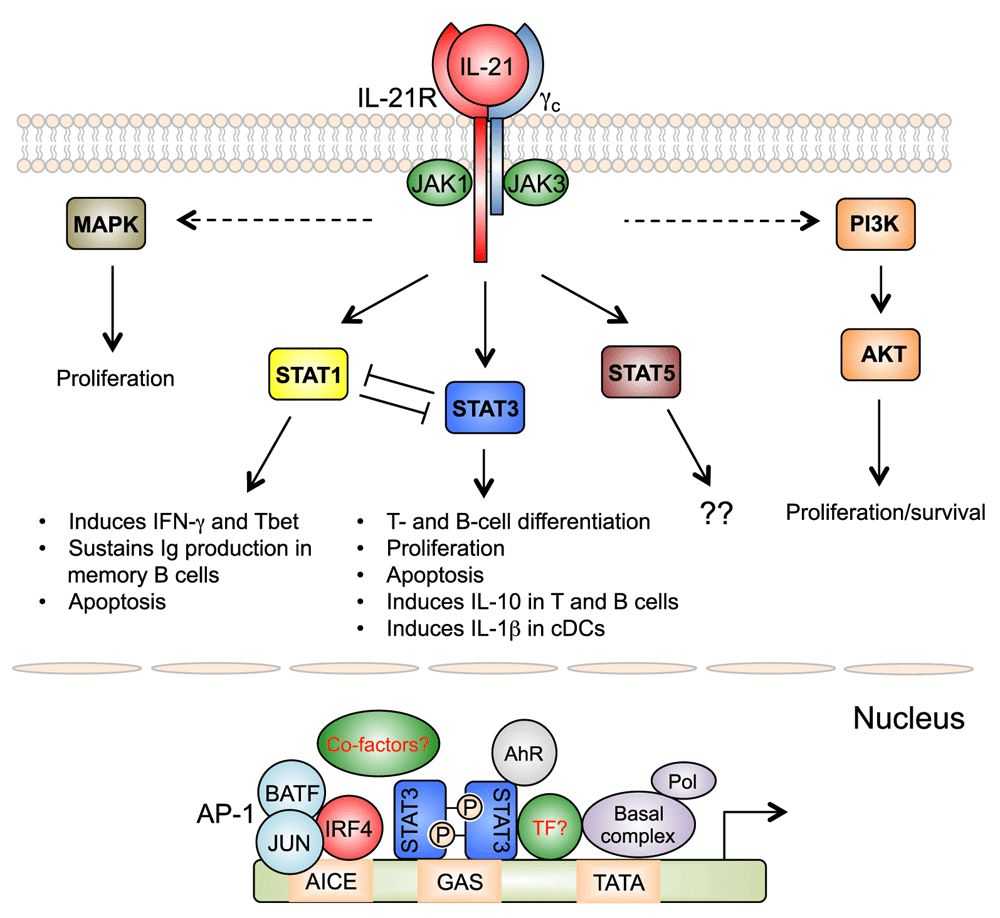 Fig.4 Signaling pathways activated by IL-218,9
Fig.4 Signaling pathways activated by IL-218,9
Other Services on Oncolytic Virus Engineering Platform
- Pathogenicity Manipulation (Attenuation)
- Immunogenicity Manipulation
- Antibody-expressing Oncolytic Virus
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-expressing Oncolytic Virus
Based on our well-established OVs engineering platform, the experienced scientists here at Creative Biolabs are dedicated to helping you develop a unique oncolytic virus. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote.
References
- Fang, Lin, et al. "Oncolytic adenovirus-mediated expression of CCL5 and IL12 facilitates CA9-targeting CAR-T therapy against renal cell carcinoma." Pharmacological Research 189 (2023): 106701.
- Aldinucci, Donatella, Cinzia Borghese, and Naike Casagrande. "The CCL5/CCR5 axis in cancer progression." Cancers 12.7 (2020): 1765.
- Shakiba, Yasmin, et al. "Oncolytic therapy with recombinant vaccinia viruses targeting the interleukin-15 pathway elicits a synergistic response." Molecular Therapy-Oncolytics 29 (2023): 158-168.
- Waldmann, Thomas A., et al. "IL-15 in the combination immunotherapy of cancer." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 868. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by extracting and using only Part "normal transpresentation" of the original image.
- Kurokawa, Cheyne, et al. "Mediation of antitumor activity by AZD4820 oncolytic vaccinia virus encoding IL-12." Molecular Therapy Oncology 32.1 (2024).
- Gao, Wei, Jun Pan, and Jianping Pan. "Antitumor activities of interleukin-12 in melanoma." Cancers 14.22 (2022): 5592.
- Sun, Yijie, et al. "An effective therapeutic regime for treatment of glioma using oncolytic vaccinia virus expressing IL-21 in combination with immune checkpoint inhibition." Molecular Therapy-Oncolytics 26 (2022): 105-119.
- Leonard, Warren J., and Chi-Keung Wan. "IL-21 signaling in immunity." F1000Research 5 (2016).
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification
