Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus Construction Service
As an oncolytic virus with distinct biological features, Vaccinia Virus (VV) has demonstrated substantial application potential and unparalleled allure within the realm of cancer therapeutics. Creative Biolabs with years of specialized experience, has established the OncoVirapy™ platform, which offers customized VV design schemes and efficiently produces oncolytic VV particles, facilitating research in oncolytic virus-based cancer treatment.
Introduction of Vaccinia Virus
VV belongs to the family Poxviridae and is a double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) virus with a genome approximately 190 kb in size. It has a large virion with a complex structure. The virion comprises a core, lateral bodies, and an envelope. VV enters target cells not by relying on specific cell-surface receptors but through a membrane-fusion pathway. Consequently, it can infect a wide range of cell lines.
The Western Reverse strain, Lister strain, Wyeth strain, and Copenhagen strain of VV possess oncolytic characteristics, with the Western Reverse strain demonstrating the most potent oncolytic properties in terms of efficient tumor cell lysis and disruption of tumor-related biological processes.
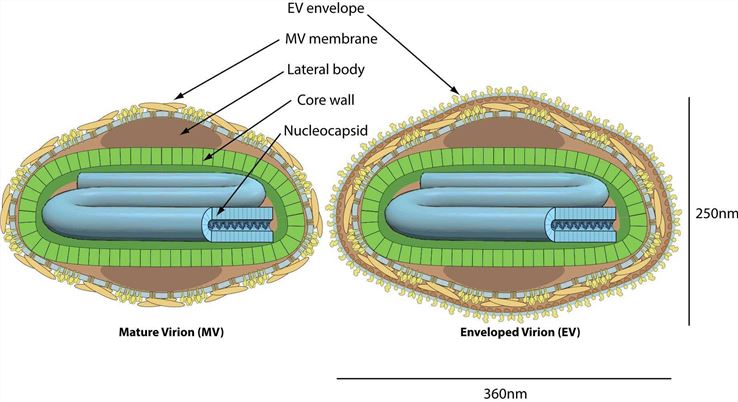 Fig.1 Structures of mature virion and enveloped virion.Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Structures of mature virion and enveloped virion.Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
There are two main forms of vaccinia virus: intracellular mature virion (IMV) and extracellular envelope virion (EEV). IMV exhibits a rapid replication rate and can efficiently attack and lyse tumor cells, thereby serving as a potent anti-tumor agent. EEV is equipped with a protective envelope, which can effectively neutralize antibody-mediated attacks. This enables EEV to travel long distances within the body and infect distant tumor tissues, expanding the scope of its anti-tumor action.
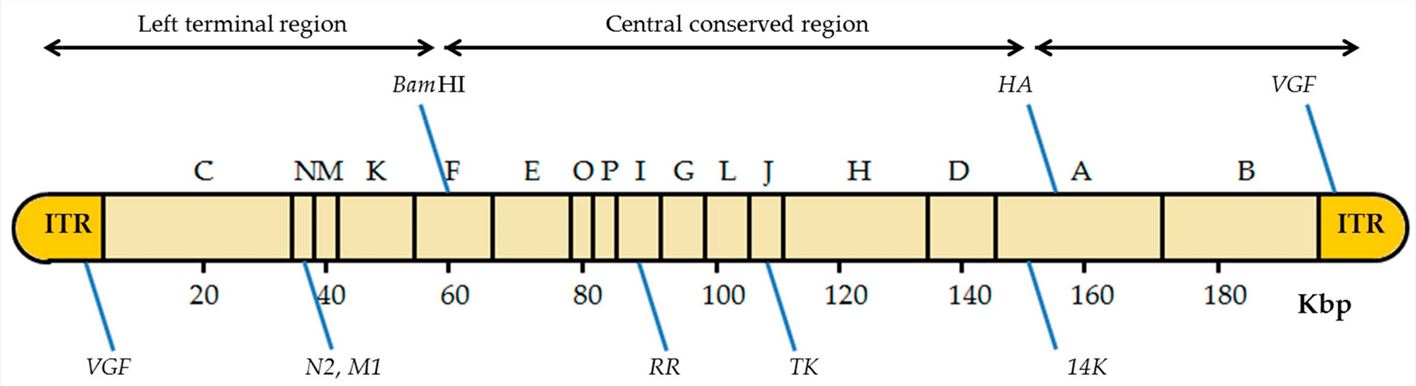 Fig.2 Genome structure of oncolytic vaccinia virus.1,3
Fig.2 Genome structure of oncolytic vaccinia virus.1,3
The vaccinia virus genome is composed of linear dsDNA, and the size varies slightly across different VV species. Terminal reverse repeats (ITRs), positioned at both termini of the genome, are sequences of reverse-complementary DNA. These sequences can fold into specific secondary structures, such as hairpin-like structures, which play crucial roles in facilitating the initiation and termination of viral DNA replication. The central coding region, situated between the two terminal inverted repeats, contains a large number of coding genes. The genes are densely packed, enabling the virus to efficiently utilize its genomic space and regulate a diverse array of biological functions, including viral replication, assembly, and interactions with the host cell.
Genetic Modifications of Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus Vectors
-
Vaccinia Virus Virulence Genes
- Thymidine Kinase (TK): TK deletion is aimed at preventing VV replication in normal cells. Tumor cells themselves can provide an ample amount of TK for the use of VV, ensuring its normal replication, and enabling it to attack and lyse tumor cells.
- The absence of VGF-mediated activation of the Ras pathway and associated cellular processes crucial for viral replication in normal cellular environments. Deletion of the gene encoding vaccinia growth factor (VGF) in the VV genome ensures VV replicates specifically in tumor cells.
- The deletion of the B18R gene helps shield the virus from the antiviral effects of type Ⅰ IFN and maintain viral virulence.
- The A48R gene encodes thymidylate kinase, which participates in nucleotide metabolism. The knockout of the A48R gene contributes to restricting the virus from replicating solely in tumor cells.
-
Strategies and Approaches to Enhance the Anti-Tumor Capacity of VV
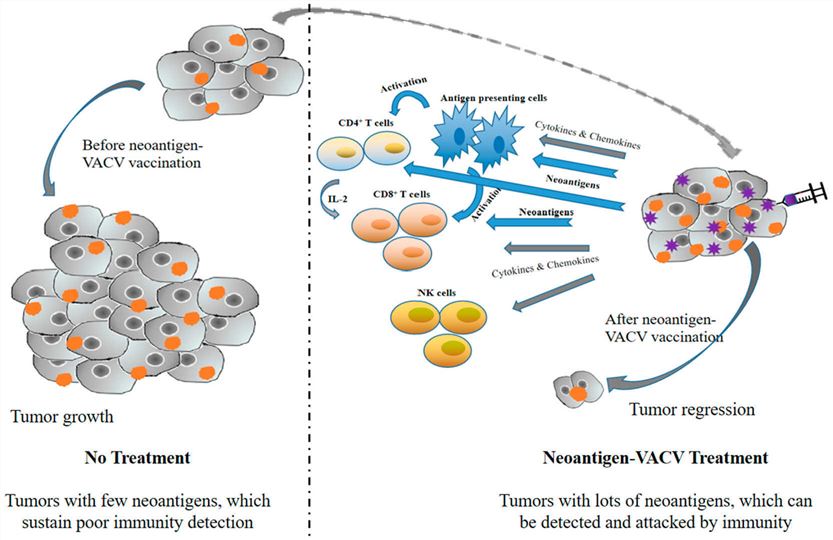 Fig.3 Simplified mechanism of neoantigen-VV in tumor cells treatment.2,3
Fig.3 Simplified mechanism of neoantigen-VV in tumor cells treatment.2,3
- Cytokines: Recombinant VVs expressing GM-CSF, such as JX-594 and JX-963, have demonstrated potentially safe therapeutic effects and enhanced antitumor efficacy by disrupting tumor blood vessels. Moreover, IFNs and ILs have also shown promising outcomes in oncolytic virotherapy.
- Chemokines: VV expressing CXCL11 increased CXCL11 expression levels in virus-infected cells and stimulated T cell trafficking to malignant tissues. vvDD-CCL5 enhanced immune cell infiltration into colorectal tumors in mice. The antitumor effect was further enhanced when vvCCL5 was used in combination with DC1 vaccination.
- Costimulators: B7-1 (CD80) and B7-2 (CD86) are two important costimulatory molecules present on the surface of specialized APCs. Proliferation of resting CD4+ T cells is enhanced with recombinant VV encoding B7-1 or/and B7-2.
- Tumor Antigens: The oncolytic VV recombinant engineered to express a combination of HER2 and GM-CSF has augmented effectiveness in modulating a tumor microenvironment abundant in MDSCs.
- Reporter-Expressing Viruses
Tab.1 Reporter genes commonly used in the generation of recombinant VV.1
| Report Gene | Origin | Product | Detection |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAT | Escherichia coli | Chloramphenicol acetyltransferase | ELISA |
| lacZ | Escherichia coli | β-galactosidase | Colorimetry |
| GUS | Escherichia coli | β-glucuronidase | Colorimetry or fluorescence |
| GFP | Aequorea victoria (jellyfish) | GFP | Fluorescence |
| LUC or luxCDABE | Photinus pyralis (firefly) and bacteria | Luciferase | Luminescence |
In vitro, reporter assays can help study the location, structure, and function of VV proteins during the infection cycle, as well as their interactions with host cell proteins. Fluorescent markers such as GFP, YFP, or luciferase can be used to label VV replication strains. The most common uses of recombinant VV in vivo are in the production of preventive vaccines and cancer therapy.
Featured Services and Construction Workflow
We provide a comprehensive range of VV services based on our advanced OncoVirapy™ platform.
- Select the GOI (encoding antibodies, cytokines, chemokines or immune checkpoint inhibitors, etc.) or the genes plan to be deleted for restriction mapping and sequencing verification
- Functional validation of transgenes
- Expression cassette design with the most appropriate promoter to guarantee the high-level expression
- Viral gene engineering (single gene or different genes combination)
- Different construction strategies (homologous recombination, BAC system, etc.)
- VV amplification, purification, titering services
- VV whole genome sequencing (WGS) service
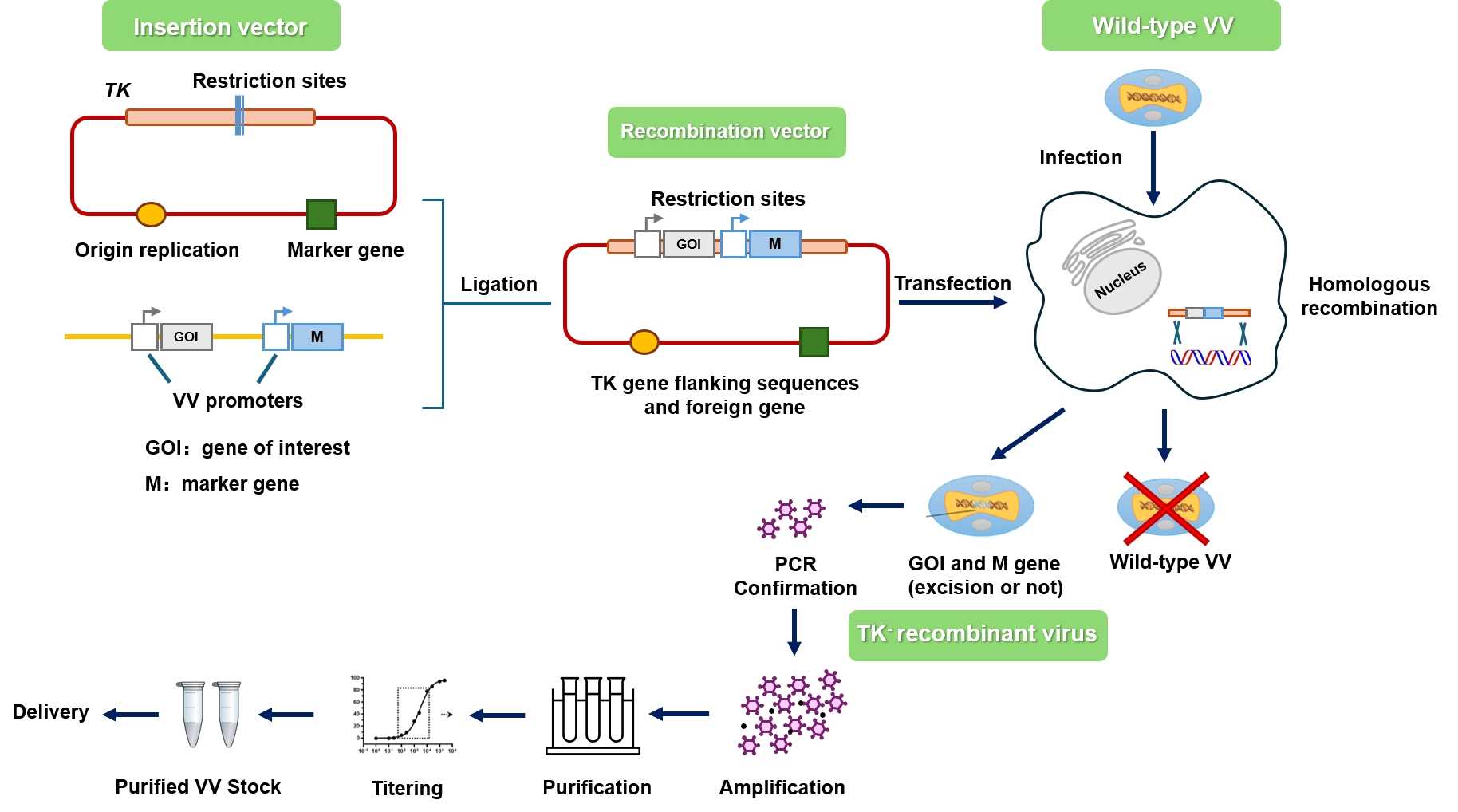 Fig.4 Workflow for Creative Biolabs construction of oncolytic vaccinia virus.
Fig.4 Workflow for Creative Biolabs construction of oncolytic vaccinia virus.
Cases of Vaccinia Virus Genetic Modifications
Tab.2 Representative clinical studies of oncolytic VV
| Name | Description | Delivery Route | Cancer | Phase | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Deletion | Transgene | ||||
| JX-594 | Wyeth Strain | TK |
GM-CSF β-galactosidase |
i.t. i.v. |
Hepatocellular caicinoma | 3 |
|
GL-ONC1 (GLV-1h68) |
Lister Strain |
TK F14.5L A45R |
GFP β-galactosidase β-glucuronidase |
i.v. i.p. |
Head and neck carcinoma | 1 |
| Vaccinia-CEA-TRICOM | Wyeth Strain | —— |
CEA TRICOM |
s.c. | Breast cancer | 2 |
| P53MVA | Ankara Strain | —— | Human p53 |
i.v. s.c. |
Ovarian cancer Colon cancer |
2 |
| TG6002 | Copenhagen Strain |
TK 14L |
FCU1 | i.v. |
Glioblastoma Colorectal cancer |
1/2 |
| TG4010 | Ankara Strain | —— |
MUC1 Human IL-2 |
s.c. | Non-small cell lung cancer | 2 |
| vvDD-CDSR | Western Reserve Strain |
TK VGF |
lacZ |
i.t. i.v. |
Melanoma Breast cancer |
1 |
| MVA-5T4 | Ankara Strain | —— | Tumor antigen 5T4 | i.m. | Ovarian cancer | 2 |
Creative Biolabs presents a range of custom oncolytic VV cloning and construction services which are characterized by reasonable cost and a rapid turnaround. In addition, we offer in vitro and in vivo validation services for the engineered oncolytic VV to facilitate the client's whole project.
References
- Al Ali, Sally, et al. "Use of reporter genes in the generation of vaccinia virus-derived vectors." Viruses 8.5 (2016): 134.
- Liu, Xinjun, et al. "Design strategies and precautions for using vaccinia virus in tumor virotherapy." Vaccines 10.9 (2022): 1552.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
