Oncolytic Virus Construction Services
Based on our well-established OVs engineering platform, the experienced scientists here at Creative Biolabs are dedicated to helping you develop a unique oncolytic virus. Please feel free to contact us for more information and a detailed quote. Oncolytic virus construction involves engineering viruses to specifically infect and replicate in tumor cells. By removing certain virulence-related genes in the virus, or by adjusting the virus's infection and replication mechanisms, the damage to normal cells is reduced. The expression of immunomodulatory factors, tumor antigens, and immune checkpoint inhibitors can enhance the anti-tumor immune response of the body. To construct an oncolytic virus with good genetic stability to reduce the risk of gene mutation or gene recombination and ensure safety. Creative Biolabs provides genetic engineering of commonly used oncolytic viruses, including but not limited to adenovirus (Ad), herpes simplex virus (HSV), measles virus (MV), vaccinia virus (VACV), vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) and adeno-associated virus (AAV).
Construction method of oncolytic virus
- Gene editing technique: Accurate editing and modification of the viral genome, selective deletion of non-essential genes, insertion of specific therapeutic genes, or site-directed mutation of genes are performed to achieve functional optimization of oncolytic viruses.
- Homologous recombination technique: Based on the homologous recombination mechanism of the virus itself, foreign genes are introduced into the viral genome. By co-transfecting the target gene and the viral genome into the host cell, the target gene is integrated into the viral genome.
- Synthetic biology technique: Design the viral genome sequence and synthesize the viral genome de novo by chemical synthesis. The gene sequences of viruses can be comprehensively designed and optimized to achieve precise regulation of viral functions.
Oncolytic Adenovirus
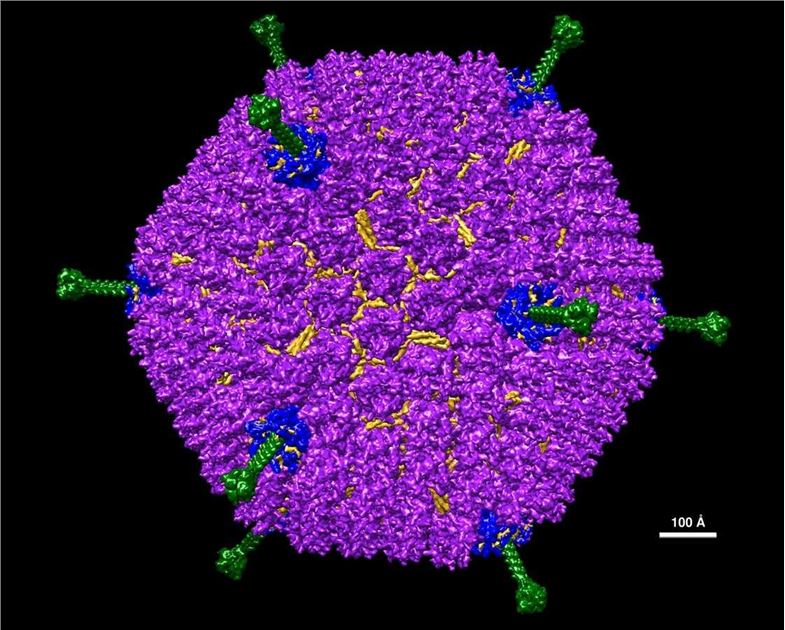
Adenovirus (Ad) is a non-enveloped dsDNA virus with an icosahedral structure and a genome size of 36 to 38 kb. Modifications to the adenovirus genome can attenuate virulence. The possible modifications include changing the structure of Ad capsid, replacing or incorporating promoter elements, and expressing target genes H101, the first commercialized oncolytic drug, is a recombinant Ad5 particle with deletion of E1B-55kD and E3 region gene fragments.
 Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Oncolytic Herpes Simplex Virus
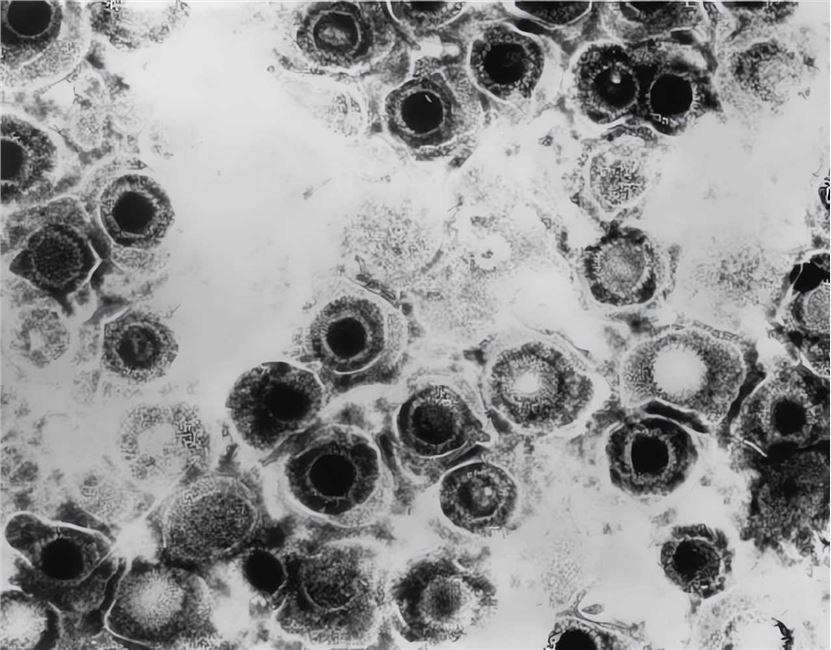 Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is an enveloped icosahedral dsDNA virus with a genome size ranging from 120 to 200 kb. At present, a series of attenuated HSVs have been successfully developed, including T-VEC, G207, HSV 1716, HF-10, G47Δ, etc. To avoid serious neurotoxic side effects, HSV needs to be engineered before being used as an oncolytic viral vector. The most commonly used approach involves partial or total deletion of the ICP34.5 gene while ensuring tumor-selective replication of HSV.
Oncolytic Vaccinia Virus
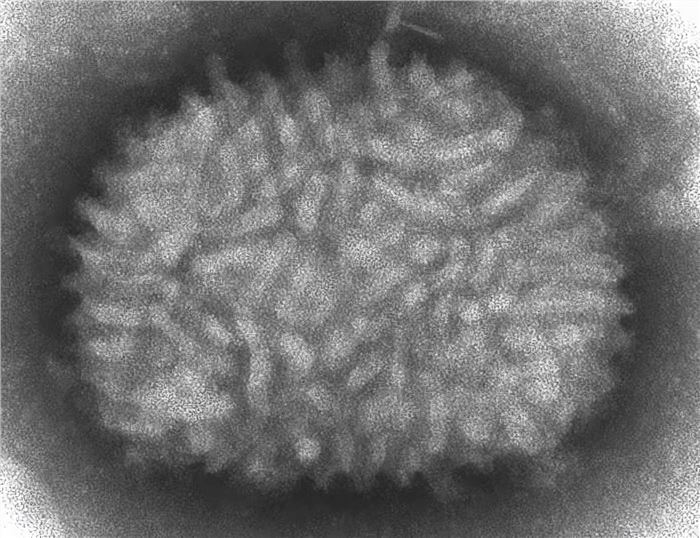 Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Vaccinia virus (VV) is an enveloped dsDNA virus with a size of 130-280 kb and a complex structure. VV has a natural selectivity for tumors and the potential for systemic delivery. VV function can be improved by knocking out VV growth factor (VGF) and thymus kinase (TK). Jx-594 is an engineered VV with endogenous TK inactivation, expression of GM-CSF and LacZ, and selective replication in tumors.
Oncolytic Vesicular Stomatitis Virus
Vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) is an enveloped Rhabdoviridae. The virus has a tightly coiled and symmetrical nucleocapsid, and its genome is a non-segmented, single-stranded negative-strand RNA (ssRNA), about 13-16 kb in length.
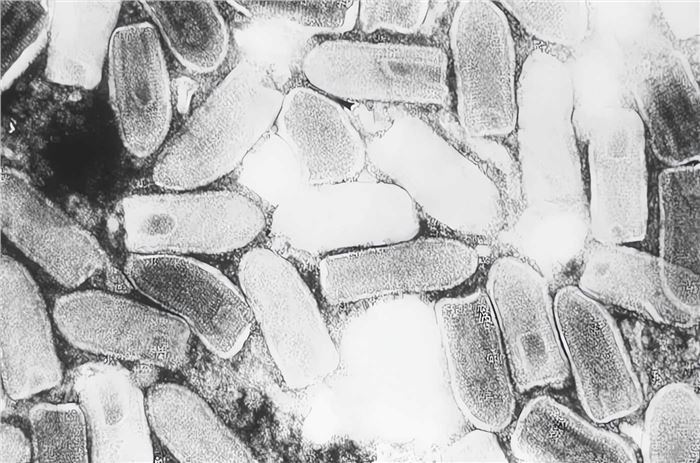 Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Oncolytic Measles Virus
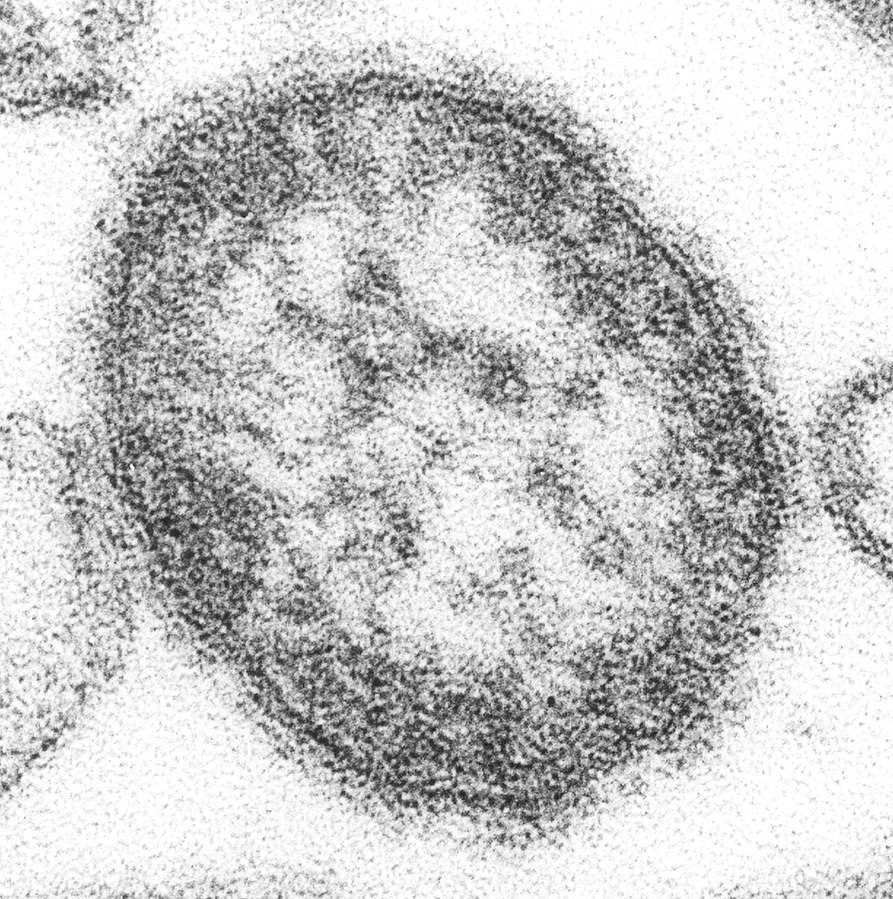 Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Measles virus (MV) is an enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus with a genome size of 16-20 kb. The receptors of wild-type MV are CD150/SLAM and Nectin-4 on lymphocytes, and the engineered MV infects cells through CD46.
Other Oncolytic Virus
- Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV)
NDV is an avian-enveloped virus of the paramyxovirus family with non-segmented negation-strand RNA. The hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) protein of NDV binds to sialic acid-containing receptors on host cells, and the F protein mediates virus entry into host cells through the fusion of the viral envelope and plasma membrane.
- Coxsackievirus (CV)
CV belongs to the picornaviridae family and is a non-enveloped virus with a single-stranded RNA genome. CV replicates in the cytoplasm of the host cell and the possibility of insertional mutations is greatly reduced. CVA21 is a widely studied CV, which uses ICAM-1 as the main receptor and DAF as a co-receptor to infect host cells.
- Reoviruses (ReV)
ReV is a non-enveloped dsRNA virus that can maintain replication, infection, and oncolytic capacity under hypoxia and down-regulate HIF-1α expression during infection of tumor cells.
- Protoparvoviruses (PV)
PV is a non-enveloped single-stranded DNA virus, and its natural host is rats. Among the currently known OVs, PV has the smallest genome size of about 5 kb, and the total diameter of the virion ranges from about 18 to 26 nm. H-1 PV is the only parvovirus that has successfully entered clinical trials.
 Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under Public domain, from Wiki, without modification.
 Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.