Hi-Affi™ In Vitro Cell based Lysophospholipid (LPA) Receptor Functional Assay Service
Lysophosphatidic (LPA) Receptors: Why They Matter
Lysophosphatidic (LPA) receptors are widely dispersed rhodopsin-like G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Upon endogenous ligands binding to LPA receptors, these receptors are activated and regulate a broad range of cellular functions such as cell proliferation and survival, Ca2+ homeostasis, etc. Studies have shown that LPA receptors have been implicated in many diseases involving inflammation, cancer, cardiovascular, nervous systems, etc. Accordingly, there is an urgent need to identify LPA receptors and explore the underlying mechanisms deeply.
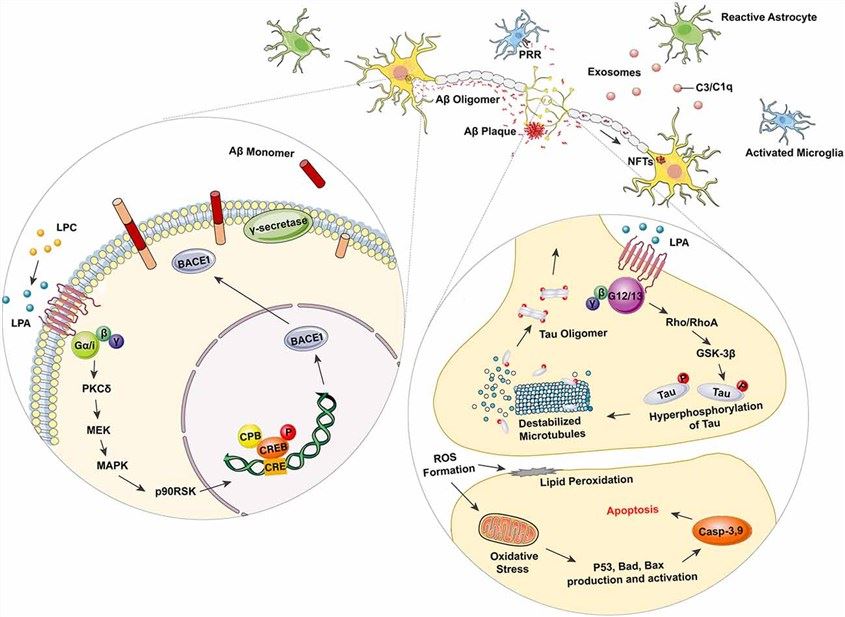 Fig.1 Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) related neurodegeneration.1
Fig.1 Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in Alzheimer's disease (AD) related neurodegeneration.1
Our Hi-Affi™ In Vitro Cell-based Lysophospholipid (LPA) Receptor Functional Assay Service
Leveraging our expertise and experience, Creative Biolabs innovatively developed a Hi-Affi™ in vitro cell-based lysophospholipid (LPA) receptor functional assay service and welcomes global customers to inquire and order.
In our Hi-Affi™ in vitro cell-based LPA receptor functional assay service, we integrate in vitro cell-based assay with LPA receptor functional assay. By measuring the accumulation of the second messenger and calcium flux triggered by the reaction of LPA receptors with ligands, we are capable of analyzing compounds and their ability to modify LPA receptors. Throughout this process, a full range of customized high-quality services will be offered by us to global customers.
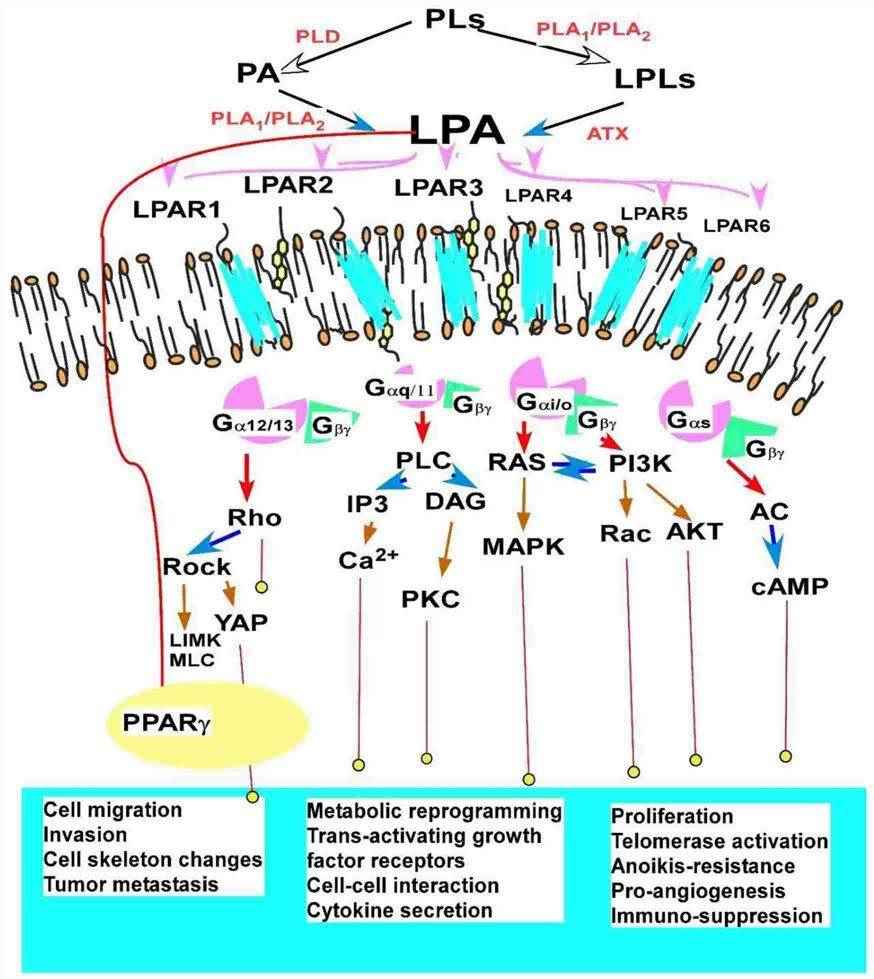 Fig.2 Signaling pathways and functions of lysophospholipid (LPA) receptors.2
Fig.2 Signaling pathways and functions of lysophospholipid (LPA) receptors.2
The benefit of Our Hi-Affi™ In Vitro Cell-Based Lysophospholipid (LPA) Receptor Functional Assay Service
Creative Biolabs is constantly developing and innovating the technical to satisfy customers' requirements, intending to provide the most advanced technology and high-quality services to global customers. Accordingly, our Hi-Affi™ in vitro cell-based LPA receptor functional assay service will benefit global customers with:

What the Data Say
DATA 1: To investigate whether these various Autotaxin (ATX) inhibitors function differently in a cellular setting.
The findings show that type I and type IV compounds were similarly effective at reducing ATX signaling in cell culture, while type I compounds were more effective than type IV compounds at decreasing ATX catalytic activity in vitro.
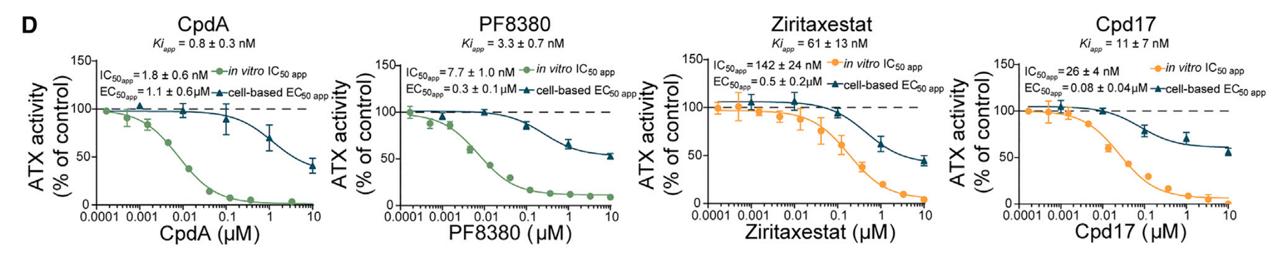 Fig.3 Inhibition of ATX activity in vitro and in BJeH cells.3
Fig.3 Inhibition of ATX activity in vitro and in BJeH cells.3
DATA 2: This study examines the possible antiviral applicability of the LPA1/3 inhibitor Ki16425. Ki16425 treatment increased Ifnb1 expression in macrophages and additionally raised the expression of Ifnb1, Cxcl10, and Ccl5 in fibroblast cells. In intestinal organoids, inhibiting LPA1 might significantly increase IFN-III or IFN-I expression. In accordance with this, treatment with Ki16425 enhanced virus clearance, as indicated by the decreased mean fluorescence of VSV-GFP.
Collectively, the findings demonstrated that inhibiting LPA1 with the inhibitor Ki16425 or using the preclinical drug may improve the generation of IFN-I and IFN-III in intestinal organoids and numerous cells against viral infection.
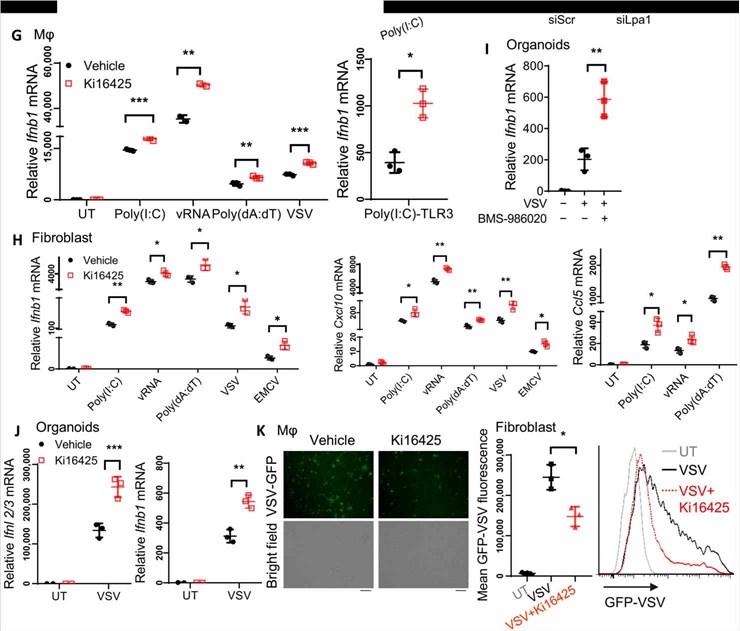 Fig.4 LPA1 receptor targeting against viral infections.4
Fig.4 LPA1 receptor targeting against viral infections.4
Work with Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs is constantly developing and innovating the technical to satisfy customers' requirements, intending to provide the most advanced technology and high-quality services to global customers. For more details about our Hi-Affi™ in vitro cell-based lysophospholipid (LPA) receptor functional assay service, please don't hesitate to contact us. Everyone here is eager to begin working with you right away.
References
-
Hao, Yining, et al. "Lysophospholipids and their G-coupled protein signaling in Alzheimer's disease: From physiological performance to pathological impairment." Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 13.58 (2020): 00058.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. -
Xu, Yan. "Lysophospholipid signaling in the epithelial ovarian cancer tumor microenvironment." Cancers 10.7 (2018): 227.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification. -
Salgado-Polo, Fernando, et al. "Autotaxin facilitates selective LPA receptor signaling." Cell Chemical Biology 30.1 (2023): 69-84.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0. The original image was modified by extracting and using part D, and the title was changed to "Inhibition of ATX activity in vitro and in BJeH cells". -
Zhang, Chi, et al. "Targeting lysophospholipid acid receptor 1 and ROCK kinases promotes antiviral innate immunity." Science Advances 7.38 (2021): eabb5933.
Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0. The original image was modified by extracting and using part G to part H, and the title was changed to "LPA1 receptor targeting against viral infections".
For Research Use Only.
