Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? Published Data FAQs Related Products Services
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in developing targeted therapies for complement-mediated diseases or seeking precise tools for complement pathway research? Creative Biolabs' advanced solutions for Complement Therapeutic Target-C1 Complex help you accelerate drug discovery, develop highly specific therapeutic antibodies, and gain deeper insights into complement-related pathologies through innovative antibody engineering and comprehensive assay platforms.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The C1 complex stands as the initial component of the classical complement pathway, a fundamental arm of the innate immune system crucial for host defense against pathogens and clearance of immune complexes and apoptotic cells. The C1 complex—composed of three distinct subunits: C1q, C1r, and C1s—constitutes a precisely controlled macromolecular structure.
Click the button to explore details.
C1q, the recognition subcomponent, binds to various activators such as antibody-antigen complexes (e.g., IgG or IgM bound to pathogens or altered self-surfaces), pentraxins, and apoptotic cells. Upon binding, C1q undergoes a conformational change that activates the associated C1r proteases, which then cleave and activate C1s. Activated C1s, in turn, acts as a serine protease, cleaving C4 and C2 to generate C4b and C2a, forming the classical pathway C3 convertase (C4bC2a). This convertase is central to amplifying the complement cascade, leading to opsonization, inflammation, and direct cell lysis.
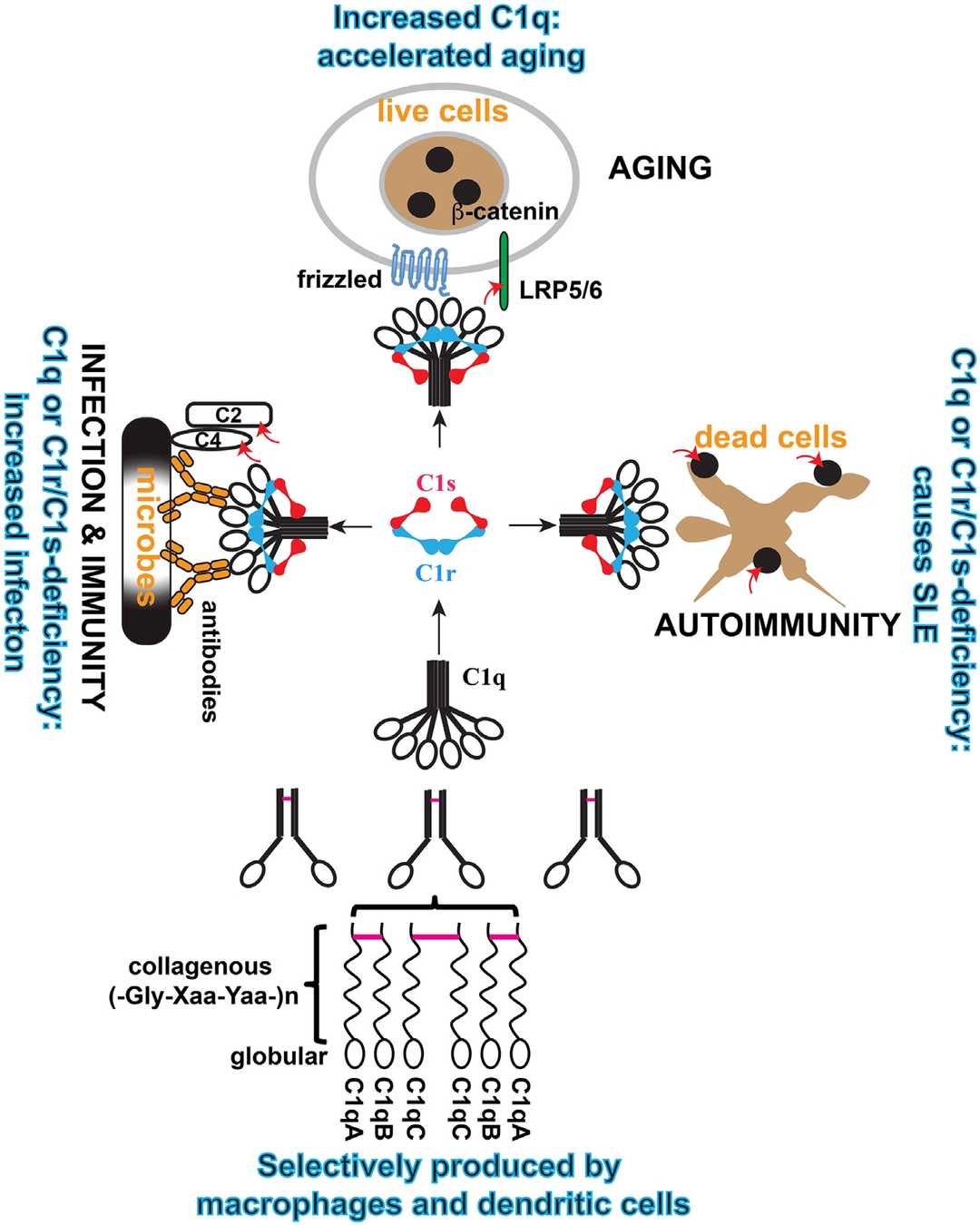 Fig.1 Structure of C1 complex..1
Fig.1 Structure of C1 complex..1
C1 Complex Related Disease
Dysregulation of the C1 complex and the classical pathway is implicated in a wide array of pathological conditions. Overactivation can lead to significant tissue damage in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), rheumatoid arthritis, and anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) disease. Furthermore, C1 complex involvement has been observed in various inflammatory disorders, ischemia-reperfusion injury, and certain neurological conditions like Alzheimer's disease and atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome (aHUS), where it contributes to neuronal damage and microvascular thrombosis, respectively. Given its central role in initiating the classical pathway, the C1 complex represents a highly attractive therapeutic target for modulating complement activity in these debilitating diseases. Targeting C1 offers a precise strategy to inhibit the classical pathway at its very beginning, thereby preventing downstream amplification and subsequent tissue injury while potentially preserving other complement pathways vital for host defense. This strategic targeting has garnered significant interest in developing novel therapeutics to control pathological complement activation.
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive array of complement therapeutics services targeting the C1 complex for multiple associated disorders, featuring:
-
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus-like Syndrome
-
Glomerulonephritis
-
Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
-
Hashimoto Disease
-
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
With professional knowledge and rich research experiences in drug discovery and the complement therapeutic field, Creative Biolabs' outstanding research groups are confident in providing high-quality biotherapeutics development services based on the complement C1 complex of the complement system. We deliver comprehensive or modular solutions tailored to client requirements. If you are interested in our platform or you are calling for our services, please contact us.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of products and services specifically designed to support research and therapeutic development targeting the C1 complex and the classical complement pathway. Our offerings are tailored to meet diverse client needs, from basic research to preclinical drug development.
C1 Complex-Targeting Antibodies:
-
Monoclonal antibodies against C1q, C1r, and C1s.
-
Antibody fragments (e.g., Fab, scFv) for specific applications.
-
Engineered antibodies for enhanced therapeutic properties (e.g., reduced immunogenicity, prolonged half-life).
-
Custom antibody development services for novel C1 complex epitopes.
Complement Pathway Assays:
-
Classical pathway activation assays.
-
C1 complex functional assays (e.g., C1 esterase activity, C4/C2 cleavage).
-
ELISA kits for quantitative detection of C1 complex components and activation products.
-
Custom assay development for specific research needs.
Recombinant Complement Proteins:
-
High-quality recombinant C1q, C1r, C1s, C4, and C2 proteins.
-
Mutant and truncated forms for structure-function studies.
Complement-Related Disease Models:
-
In vitro and in vivo models for studying complement-mediated diseases.
-
Assistance in evaluating the efficacy of C1 complex-targeting therapeutics in disease models.
Complement System Modulators:
-
Small molecule inhibitors and peptides targeting C1 complex activity.
-
Screening services for identifying novel complement modulators.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs leads in complement system research and therapeutic development, offering unparalleled expertise in targeting the C1 complex. Our commitment to scientific rigor and innovative solutions makes us the preferred partner for your critical projects.
-
Deep Scientific Expertise: Our team's two decades of experience provide a profound understanding of complement biology and C1 complex mechanisms, ensuring scientifically sound and effective solutions.
-
Cutting-Edge Antibody Engineering: We utilize advanced platforms to develop highly specific, high-affinity antibodies and fragments, generating novel therapeutic candidates with optimized properties.
-
Comprehensive Functional Validation: Rigorous in vitro and in vivo assays, including classical pathway and C1 complex binding tests, validate every antibody, ensuring expected performance in relevant biological contexts.
-
Customized Project Solutions: Creative Biolabs offers highly customizable services, from target validation to preclinical development, tailored to meet your unique research and therapeutic goals.
-
Proven Track Record: Our success stories, supported by Published Data, demonstrate our ability to deliver high-quality solutions and assist clients in advancing their complement-related therapeutic programs.
-
Quality and Reliability: Stringent quality control standards throughout development ensure the reliability and reproducibility of our products and services, providing confidence in your research outcomes.
Experience the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Get a Quote Today
Published Data
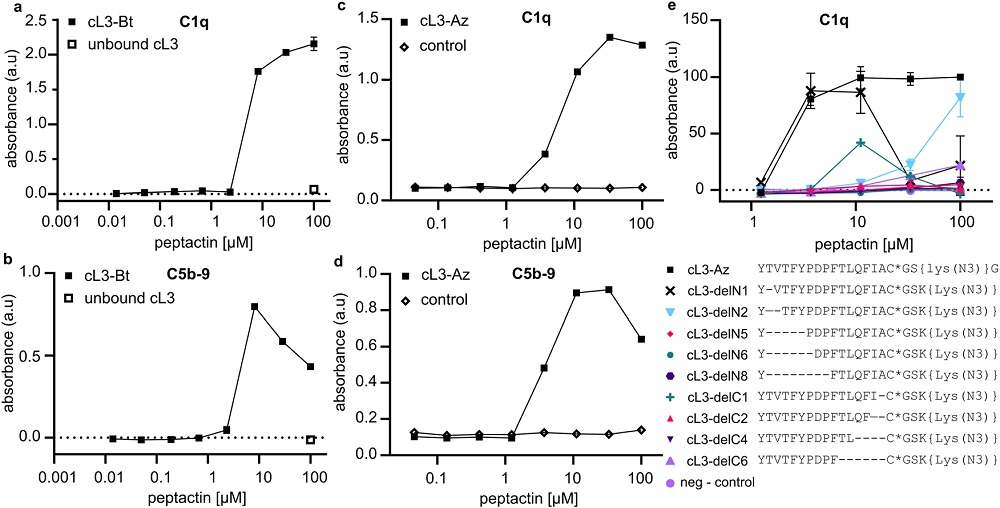 Fig.2 C1q-mediated triggering of complement cascade through cL3 engagement.2
Fig.2 C1q-mediated triggering of complement cascade through cL3 engagement.2
Complement system activation through the classical pathway, can be primarily initiated by the binding of the C1 complex to antibody hexamers. Structural insights have revealed that C1 engages with specific, compact interfaces on these antibodies. Leveraging this knowledge, a macrocyclic peptide, termed cL3, was engineered to replicate these interactions and targeting C1 complex. Selected through in vitro processes, cL3 binds to the C1 complex's globular domains. Remarkably, when cL3 is surface-immobilized, it recruits C1 from serum, activates associated proteases, and disrupts lipid membranes mimicking cellular structures. This innovative peptide not only activates complement upon immobilization but also uniquely inhibits complement-induced lysis, offering therapeutic avenues to modulate complement-related cytotoxicity.
FAQs
Q: How does targeting the C1 complex offer a distinct advantage over inhibiting downstream complement components?
A: Targeting the C1 complex, as the initial component of the classical pathway, provides a highly precise method to inhibit this specific pathway at its very beginning. This approach can prevent the entire cascade from activating, potentially minimizing off-target effects on other complement pathways (lectin and alternative pathways) that are crucial for host defense, thereby offering a more refined therapeutic intervention.
Q: What types of diseases or conditions are most likely to benefit from therapies that modulate the C1 complex?
A: Conditions characterized by pathological overactivation of the classical complement pathway are prime candidates. This includes various autoimmune diseases like lupus nephritis, certain inflammatory disorders, and some neurodegenerative diseases where complement-mediated damage contributes significantly to pathology.
Q: Are there any specific considerations or precautions when developing or utilizing agents that target this complex?
A: Yes, careful consideration of specificity and potential impact on beneficial complement functions is crucial. Ensuring that the therapeutic agent selectively modulates the classical pathway without broadly suppressing the entire complement system is important to maintain essential immune surveillance and prevent increased susceptibility to infections.
Q: How does the development process for a C1 complex-targeting therapeutic typically differ from other biological drug development?
A: The development process often requires specialized expertise in complement biochemistry and immunology. This includes specific functional assays to measure C1 activity, detailed characterization of binding to the complex subcomponents, and a thorough understanding of in vivo complement regulation to predict and assess therapeutic efficacy and safety.
Q: Can these targeting agents be used for diagnostic purposes in addition to therapeutic applications?
A: Absolutely. Highly specific agents that bind to components of the C1 complex can be invaluable tools for diagnostic assays. They can help detect complement activation, identify specific complement deficiencies, or monitor disease progression in conditions where classical pathway dysregulation is a hallmark.
Access the Creative Biolabs Edge – Request Your Quote Now
Related Hot Products
Explore Our Full Product Catalog:
-
C1q Related Products
-
C1r Related Products
-
C1s Related Products
Featured Services
References
-
Lu, Jinhua, and Uday Kishore. "C1 complex: an adaptable proteolytic module for complement and non-complement functions." Frontiers in Immunology 8 (2017): 592. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00592. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
-
Hamers, Sebastiaan MWR, et al. "Selection and characterization of a peptide-based complement modulator targeting C1 of the innate immune system." RSC Chemical Biology 5.8 (2024): 787-799. DOI: 10.1039/d4cb00081a. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 3.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig.1 Structure of C1 complex..1
Fig.1 Structure of C1 complex..1
 Fig.2 C1q-mediated triggering of complement cascade through cL3 engagement.2
Fig.2 C1q-mediated triggering of complement cascade through cL3 engagement.2