Introduction What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? Published Data FAQs Related Products Services
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in developing precise therapeutics for complement-mediated diseases, or struggling with off-target effects in your drug candidates? Creative Biolabs' expertise in Complement Therapeutic Target-C1r helps you accelerate drug discovery and obtain highly specific biologics by leveraging advanced protein engineering and high-throughput screening platforms. We offer innovative solutions to streamline your therapeutic development process.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The complement system constitutes a fundamental element of innate immunity, fulfilling critical functions in defending against pathogens and disposing of immune complexes and apoptotic cells. It consists of sequential plasma proteins that, when triggered, elicit inflammation—opsonization—and direct lysis of targeted cells. Classical complement activation is orchestrated by C1q binding to immunoglobulin-antigen complexes or specific pathogen surfaces.
Central to the classical pathway is the C1 complex, which consists of one C1q molecule, two C1r molecules, and two C1s molecules, held together in a calcium-dependent manner. C1r (Complement C1r subcomponent) is a serine protease that, upon C1q binding and conformational change, undergoes autoactivation. Once activated, C1r then cleaves and activates C1s, another serine protease within the complex. Activated C1s subsequently cleaves C4 and C2, leading to the formation of the classical pathway C3 convertase (C4b2a), which is responsible for the massive amplification of the complement cascade.
 Distributed under Open Access license CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki,
without modification.
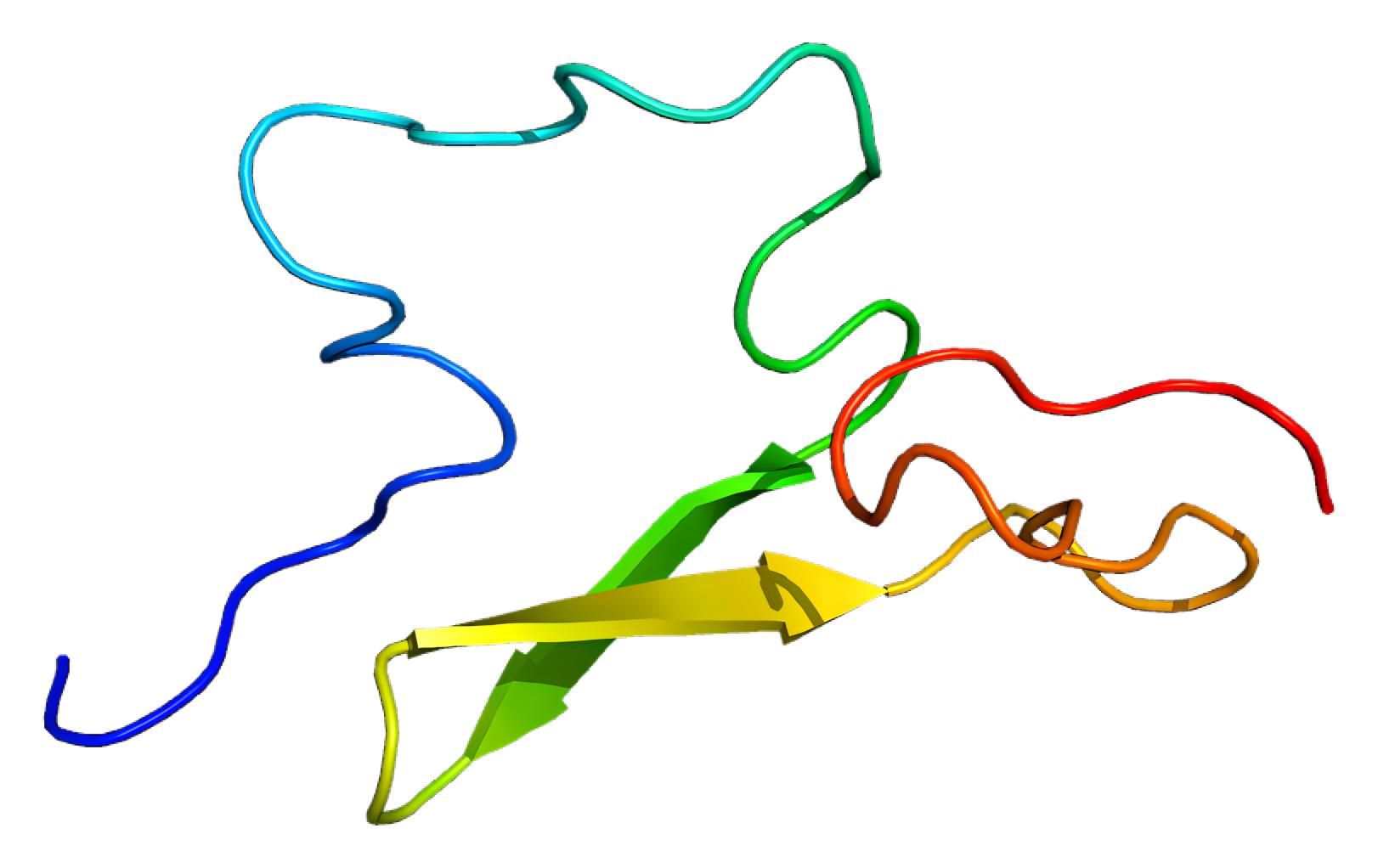
Fig.1 The 3D model of human C1r.
C1r Related Disease
Dysregulation or overactivation of the classical complement pathway, often driven by uncontrolled C1r activity, is implicated in the pathogenesis of numerous autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. These include, but are not limited to, lupus nephritis, myasthenia gravis, atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome, hereditary angioedema, and certain neurodegenerative conditions. In these diseases, excessive complement activation can lead to significant tissue damage and chronic inflammation. Therefore, C1r presents an attractive therapeutic target for selectively inhibiting the classical pathway, offering a precise intervention strategy that preserves the essential functions of the alternative and lectin pathways in host defense. Targeting C1r provides a refined approach to modulate complement activity for therapeutic benefit.
The C1r gene associates with periodontal Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and its mechanistic pathway involves generating C4/C2 activators alongside complement and coagulation cascades. Generally, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome constitutes a clinically and genetically diverse category of connective tissue disorders characterized by joint hypermobility and cutaneous abnormalities. Periodontal Ehlers-Danlos syndrome—previously categorized as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIII—constitutes an autosomal dominant variant. Its pathognomonic feature involves an Ehlers-Danlos phenotype exhibiting recurrent periodontal inflammatory events.
What We Can Offer?
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive suite of products and services designed to support your therapeutic development targeting C1r:
-
Recombinant C1r Proteins: High-purity, active recombinant human and animal C1r proteins for research and assay development.
-
C1r Activity Assay Kits: Ready-to-use kits for measuring C1r enzymatic activity and screening inhibitors.
-
Anti-C1r Monoclonal Antibodies: A diverse panel of highly specific antibodies for research, diagnostic, and therapeutic development purposes.
-
Custom Antibody Discovery & Engineering: Tailored services for the discovery, humanization, affinity maturation, and optimization of novel C1r-targeting antibodies.
-
Complement Pathway Functional Assays: Comprehensive in vitro assays to evaluate the impact of C1r inhibitors on classical pathway activation, including hemolytic assays and C3/C4 deposition assays.
-
Preclinical in vivo Efficacy Studies: Design and execution of animal models to assess the therapeutic potential of C1r inhibitors in relevant disease contexts.
-
Target Validation Services: Expertise in validating C1r as a therapeutic target for specific indications, including gene expression analysis and protein localization studies.
Why Choose Us?
Creative Biolabs stands at the forefront of complement therapeutics, offering unparalleled expertise in targeting C1r. Our dedication to scientific distinction and client achievement distinguishes us.
-
Deep Mechanistic Understanding: We possess an extensive understanding of C1r's intricate role in complement activation and its precise involvement in disease pathology, allowing for highly rational drug design.
-
Advanced Engineering Platforms: Our state-of-the-art protein engineering and antibody discovery platforms enable the rapid generation and optimization of C1r-specific therapeutic candidates with superior affinity and selectivity.
-
Comprehensive Functional Validation: We employ a rigorous suite of in vitro and in vivo assays to thoroughly characterize C1r inhibitors, ensuring their potency, specificity, and safety profiles.
-
Proven Track Record: Creative Biolabs has a history of successful collaborations, consistently delivering high-quality, validated therapeutic leads. (Published Data)
-
Customized Solutions: We offer flexible and tailored project designs, adapting to the unique requirements and objectives of each client's therapeutic development program.
-
Accelerated Development Timelines: Our optimized workflows and experienced team significantly reduce the time required from target validation to lead candidate identification.
Access the Creative Biolabs Edge - Request Your Proposal Now.
Published Data
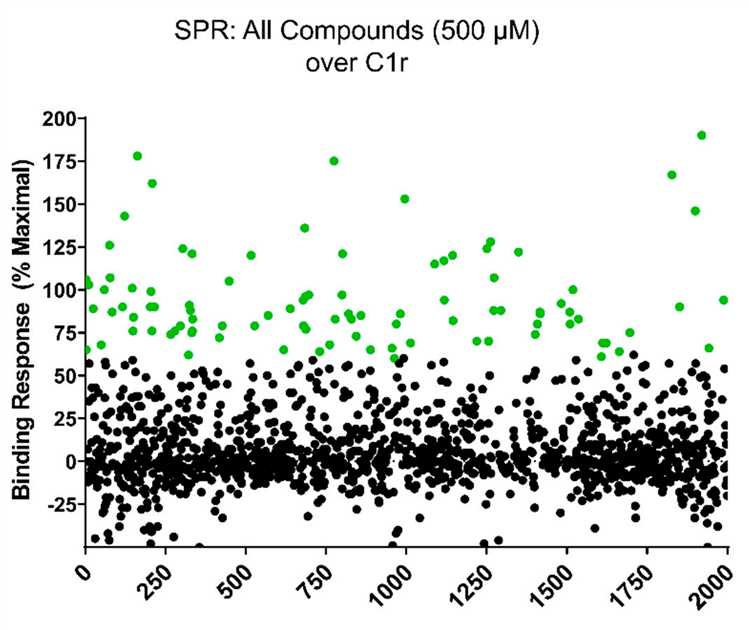 Fig.2 Surface plasmon resonance analysis of compound interactions with intact C1r.1
Fig.2 Surface plasmon resonance analysis of compound interactions with intact C1r.1
The protease C1r, which initiates the classical complement pathway, serves as a key intervention target for autoimmunity and inflammation treatments, yet it is less explored than other targets within the system. In this investigation, a fragment-based drug discovery method employing surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and molecular modeling was utilized to find novel small-molecule fragments that bind to C1r. A library of 2000 fragment compounds was screened via SPR for C1r affinity, resulting in 24 compounds with dissociation constants from 160 to 1700 µM. Among these, two fragments were found to hinder classical pathway activity in a dose-responsive manner, forming the groundwork for further high-affinity inhibitor development.
FAQs
Q: How does targeting C1r specifically benefit therapeutic development for complement-mediated diseases?
A: Targeting C1r offers a highly precise approach by selectively inhibiting the classical complement pathway. This specificity is crucial because it allows for the modulation of disease-driving complement activity while preserving the essential functions of other complement pathways, which are vital for general host defense. This can lead to therapeutics with improved safety profiles and reduced risk of broad immunosuppression.
Q: What types of diseases are most likely to benefit from C1r-targeted therapies?
A: Therapies focused on C1r are particularly promising for diseases where the classical complement pathway is a primary driver of pathology. This includes various autoimmune conditions such as lupus nephritis, myasthenia gravis, and certain forms of vasculitis, as well as inflammatory disorders where uncontrolled classical pathway activation contributes to tissue damage.
Q: What are the key considerations when developing an inhibitor against C1r?
A: Key considerations include ensuring high specificity for C1r to avoid off-target effects, achieving optimal potency to effectively block its enzymatic activity, and designing for favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. It's also important to consider the potential for immunogenicity if the inhibitor is a biologic, and to validate its efficacy in relevant disease models.
Q: How can the efficacy of a C1r inhibitor be evaluated?
A: Efficacy can be evaluated through a combination of in vitro and in vivo assays. In vitro, this might involve measuring the inhibition of C1r enzymatic activity, assessing the blockade of classical pathway-mediated hemolysis, or quantifying the reduction of downstream complement component activation (e.g., C4 and C3 deposition). In vivo, relevant animal models of complement-mediated diseases can be used to demonstrate therapeutic benefit, such as reduced inflammation, organ damage, or improved clinical symptoms.
Q: Are there any potential challenges or precautions associated with C1r inhibition?
A: While highly targeted, any modulation of the complement system requires careful consideration. Potential challenges include ensuring that the inhibition is sufficient to achieve therapeutic benefit without compromising essential immune functions. Precautions involve comprehensive safety profiling to identify any unforeseen side effects and careful patient selection to ensure the therapy is applied to individuals whose disease is clearly driven by classical pathway overactivation.
Access the Creative Biolabs Edge – Request Your Quote Now
Related Hot Products
Featured Services
Reference
-
Rushing, Blake R., et al. "Targeting the initiator protease of the classical pathway of complement using fragment-based drug discovery." Molecules 25.17 (2020): 4016. DOI:10.3390/molecules25174016. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:


 Fig.2 Surface plasmon resonance analysis of compound interactions with intact C1r.1
Fig.2 Surface plasmon resonance analysis of compound interactions with intact C1r.1