Product List Background C5b-9 Functional Service
Background
Overview of C5b-9 Complex
The C5b-9 complex is made up of various proteins, such as complement components C5b, C6, C7, C8, and C9. In response to external triggers, the host initiates the complement cascade, culminating in the creation of C5b-9 on the surfaces of pathogen cell membranes. Consequently, C5b-9 plays a crucial role as an effect factor of the immune system. Once formed, C5b-9 remaining on the infected cell surfaces forms pores that disrupt the cell membrane, enabling foreign substances to penetrate. This intrusion of foreign substances alters the osmotic pressure within the target cell, ultimately leading to cell lysis.
Formation of C5b-9 Complex
The complement system can be activated through three well-known pathways: the classical, alternative, as well as lectin pathways. Each pathway results in the creation of C3 convertase, which in turn triggers the terminal pathway by splitting C5 into C5a and C5b. C5b can then bind with C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 components on the membrane to produce C5b-9 or the membrane attack complex (MAC). C5b-9 situated on the cell membrane of microorganisms can facilitate cell lysis and eventual death.
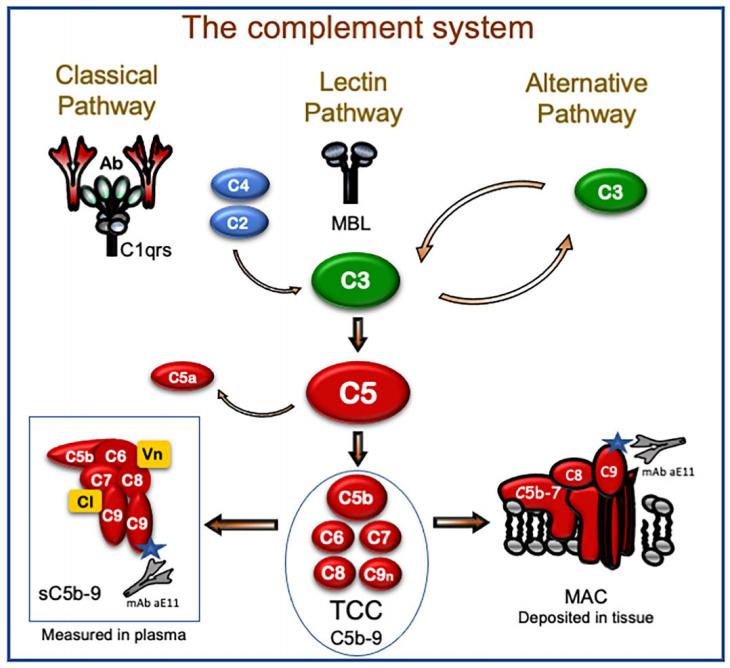 Fig.1 Focus on the terminal C5b-9 complex within the complement system.1
Fig.1 Focus on the terminal C5b-9 complex within the complement system.1
Relevant Signaling Pathways
The Gi protein pathway is closely linked to C5b-9-induced cell proliferation. In addition, C5b-9-mediated enhancement of cell survival is also associated with activation of the PI3-K/Akt pathway. Furthermore, evidence reveals that C5b-9 is involved in regulating JAK1 tyrosine phosphorylation. Importantly, C5b-9 also plays a critical role in the translocation of the cell cycle-related factor STAT3 into the nucleus.
C5b-9 and Diseases
The activation of complement and the creation of the C5b-9 complex result in cell lysis. Apart from eradicating intruders, the development of C5b-9 can also contribute to various immune-related illnesses like rejection of transplants and systemic lupus erythematosus. Moreover, C5b-9 is linked to the development of age-related macular degeneration. Furthermore, the formation of the C5b-9 complex may trigger specific inflammatory reactions due to viral infections, such as respiratory failure and systemic complement activation.
C5b-9 Assay
The SC5b-9 enzyme-linked immunoassay allows the measurement of SC5b-9 levels in a variety of samples, such as human serum, plasma, and other biological samples.
For more details on C5b-9 assays, please contact our complement experts.
C5b-9 Functional Service
Creative Biolabs provides an extensive selection of products associated with the C5b-9 complex, including anti-C5b-9 complex antibodies, ELISA kits and C5b-9 proteins. These meticulously crafted reagents are essential for advancing research focused on developing therapeutic strategies for a variety of diseases.
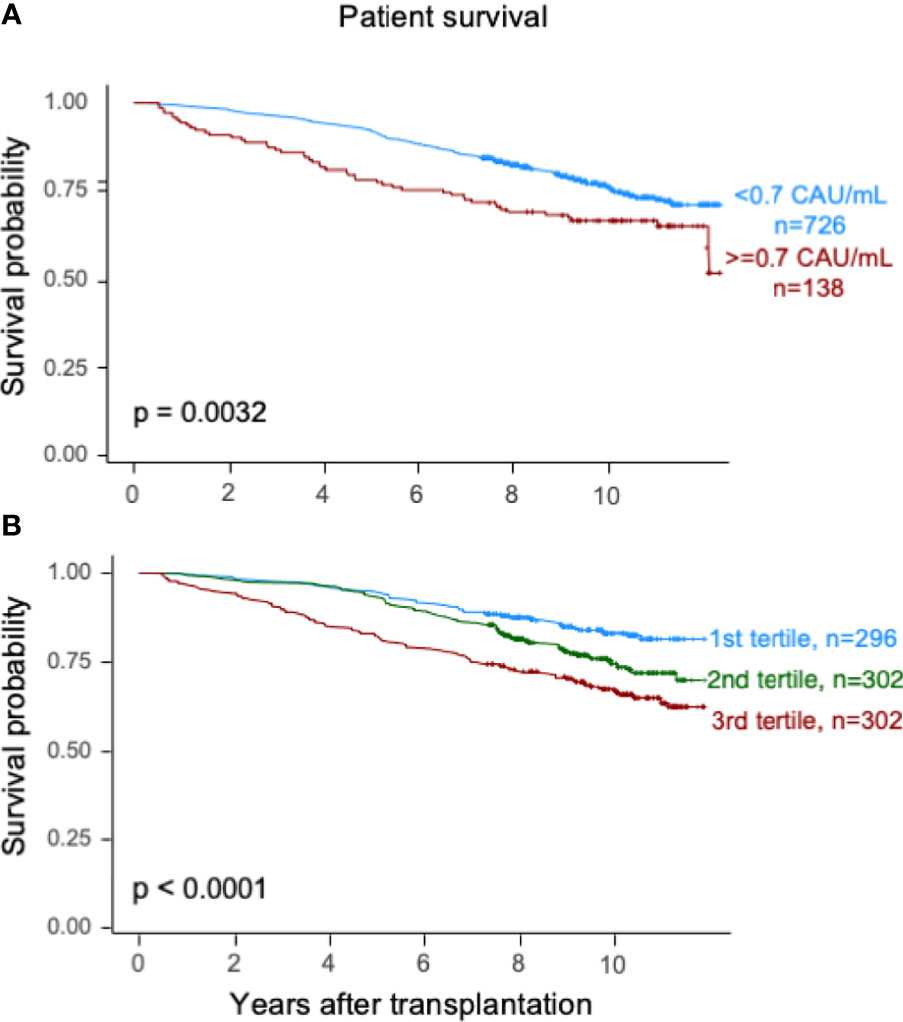 Fig.2 Survival analysis post-kidney transplantation based on plasma levels of terminal C5b-9 complex at 10 weeks.1
Fig.2 Survival analysis post-kidney transplantation based on plasma levels of terminal C5b-9 complex at 10 weeks.1
This study investigates the role of C5b-9 complement complex in long-term outcomes following kidney transplantation, with specific interest in its association with chronic tissue damage manifesting as interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy (IF/TA). Researchers analyzed C5b-9 complement complex plasma levels in 900 kidney transplant recipients 10 weeks post-transplantation and correlated these with clinical outcomes over a median observation period of 9.3 years. Elevated C5b-9 complement complex levels, observed in 138 patients, correlated with reduced 10-year patient and graft survival rates, including when censored for death. Multivariable Cox analyses revealed significant associations between high C5b-9 complement complex levels and decreased patient survival, graft loss, alongside factors such as recipient/donor demographics, smoking, diabetes, and prolonged pre-engraftment renal replacement therapy. Elevated C5b-9 complement complex was also linked to death-censored graft loss, alongside HLA-DR mismatches and elevated immunological risk.
Creative Biolabs delivers a broad spectrum of customized services related to the C5b-9 complex, including comprehensive interaction analyses and additional functional options. These carefully crafted services aim to assist clients in furthering their exceptional scientific investigations and clinical endeavors.
Reference
-
Witczak, Bartlomiej J., et al. "Elevated terminal C5b-9 complement complex 10 weeks post kidney transplantation was associated with reduced long-term patient and kidney graft survival." Frontiers in Immunology 12 (2021): 738927. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Focus on the terminal C5b-9 complex within the complement system.1
Fig.1 Focus on the terminal C5b-9 complex within the complement system.1
 Fig.2 Survival analysis post-kidney transplantation based on plasma levels of terminal C5b-9 complex at 10 weeks.1
Fig.2 Survival analysis post-kidney transplantation based on plasma levels of terminal C5b-9 complex at 10 weeks.1
