Labeling Proteins by 5-Hydroxytryptophan Residues
Introduction
Unnatural amino acid mutagenesis technology offers a breakthrough in chemoselective protein labeling by enabling the targeted introduction of unnatural chemical functional groups into recombinant proteins. This approach utilizes an engineered tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase-tRNA (TrpRS–tRNA) pair that specifically allows for the incorporation of unnatural amino acids (Uaas), such as 5-hydroxytryptophan (5HTP), in response to repurposed nonsense codons. 5HTP is easily obtained, which can be site-specific binding to proteins expressed in E. coli. Aryldiazonium species, which can be effectively utilized in various chemical conjugations, can be prepared from corresponding aromatic amines through a simple and efficient diazotization reaction.
The following describes a method for site-specific conjugation of 5HTP into αHer2 Fab fragment expressed in the ATMW1 strain, which is then labeled using a chemoselective rapid azo-coupling reaction (CRACR).
Disclaimer
The procedures outlined in this document are for reference only. Creative Biolabs makes no assurances or warranties regarding the outcomes that may result from the customer's implementation of this guideline.
Materials
Expression and Purification of 5HTP-containing Fab
- Electrocompetent ATMW1 cells.
- Plasmid 1 (inducing the expression of TrpRS-tRNA pair).
- Plasmid 2 (expressing αHer2 Fab induced by arabinose).
- LB medium (with 10 μg/mL casein peptone, 10 μg/mL NaCl, and μg/mL yeast extract).
- LB Agar plates (supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin, 50 μg/mL spectinomycin, and 35 μg/mL chloramphenicol).
- Stock solutions: Spectinomycin (50 mg/mL in water), ampicillin (100 mg/mL in water), kanamycin (50 mg/mL in water), gentamycin (10 mg/mL in water), chloramphenicol (35 mg/mL in ethanol).
- L-arabinose (20% in water).
- 5HTP (100 mM in water) .
- Protein G Agarose.
- Syringe (1 mL).
- Cotton wool.
- Periplasmic lysis buffer (30 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8), 1 mM EDTA, 20% sucrose, 0.2 mg/mL lysozyme, and 1X Halt Protease Inhibitor Cocktail).
- Buffer 1 (pH 5.2, 50 mM sodium acetate, for PGAC binding).
- Buffer 2 (pH 2 ~ 3, 100 mM glycine-HCl, for PGAC elution).
- Neutralization buffer (pH 8, 1 M Tris-HCl).
- Centrifugal filter (3 kDa MWCO).
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7, 100 mM Na2HPO4, and 150 mM NaCl).
- Dialysis device (3 kDa MWCO).
Protein Labeling by CRACR
- 6-Aminofluorescein.
- Sodium nitrite (NaNO2).
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl, 10 mM).
- 5HTP solution (6 mM in water).
- Centrifugal filter (10 kDa MWCO).
Methods
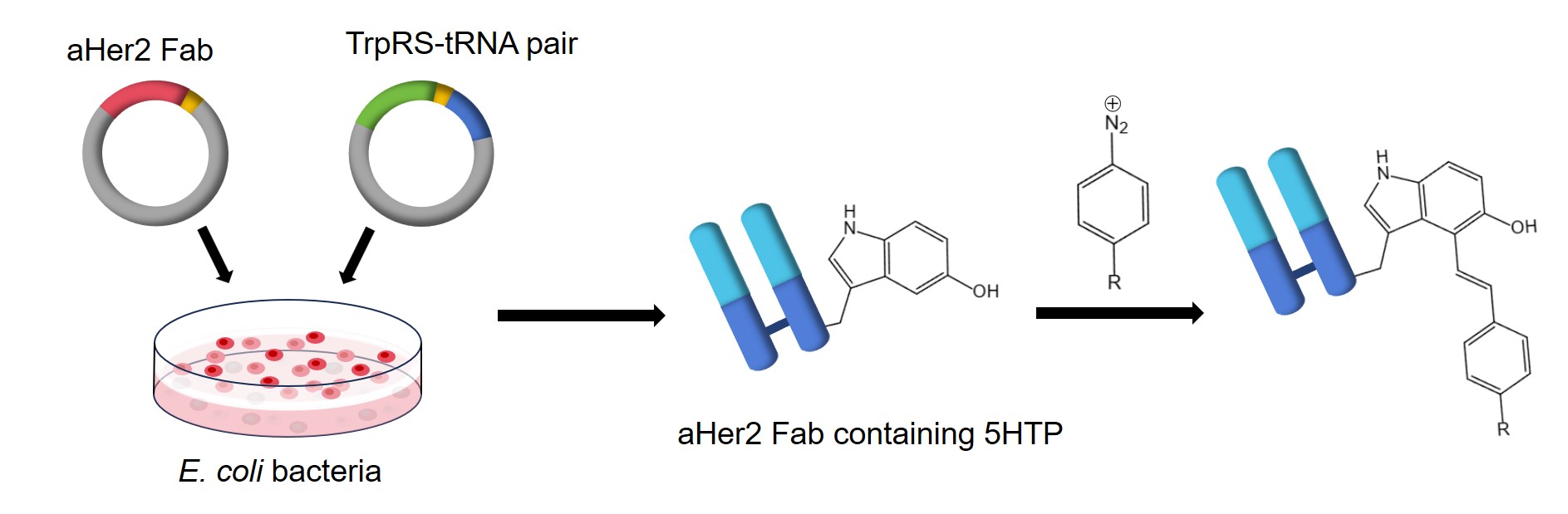
Expression and Purification of 5HTP-containing Fab
- Cotransform plasmid 1 (100 ng) and plasmid 2 (100 ng) into the electrocompetent ATMW1 strain (50 μL). Following electroporation, recover the cells in LB medium (1 mL), and then incubate them at 37°C for 1 hour with continuous shaking (250 rpm). Plate the transformed cells on LB Agar and incubate at 37°C overnight.
- Inoculate a single colony into LB medium (5 mL, supplemented with appropriate antibiotics). Then, incubate it at 37°C overnight with continuous shaking (250 rpm).
- Add the 5 mL starter culture into 500 mL LB (supplemented with appropriate antibiotics) and incubate it at 37°C with continuous shaking at 250 rpm until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reaches 0.6.
- To induce protein expression, add 0.02% L-arabinose and 1 mM 5HTP to the culture. Then, shake the culture at 250 rpm for 16 hours at 22°C.
- Centrifuge the culture at 5000 × g for 10 minutes. Separate the cell pellet and resuspend in 40 mL of periplasmic lysis buffer. Then, incubate it at 37°C for 30 minutes.
- Centrifuge the culture at 17,000 × g for 30 min at 4°C. Take the clarified lysate and dilute it with buffer 1 (pH 5.2) at a ratio of 1:1 and then place it on ice.
- Use cotton wool to fill the 1 mL syringe to the mark of 500 μL. Then, fill the column evenly with protein G agarose resin (50 μL). Finally, carefully equilibrate the column by rinsing it with 500 μL of buffer 1 (pH 5.2) to avoid disturbing the resin bed.
- Carefully load the lysate into the column and let it flow through by gravity. After the lysate has fully passed through the column, rinse with 1 mL of buffer 1 (pH 5.2).
- Elute the antibody 10 times with 50 μL of buffer 2 (pH 2 ~ 3) and then neutralize each eluate with 10 μL of neutralization buffer (pH 8).
- Collect the antibody-containing fractions by Bradford assay. Use a centrifugal filter (3 kDa MWCO) to concentrate them to 100 μL according to the product instructions.
- Dialyze against PBS (pH 7) by a dialysis device (3 kDa MWCO).
- Detect the concentration of the antibody by Bradford assay, and determine the purity by sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) analysis. The binding of 5HTP residues can also be confirmed using mass spectrometry (MS).
Protein Labeling by CRACR
- Prepare 100 μL of 6-aminofluorescein solution (10 mM in 10 mM HCl) and 100 μL of NaNO2 solution (60 mM in water), respectively, and place both on ice to cool down until use.
- To obtain a fluorescein-diazonium (8.33 mM), add 20 μL of NaNO2 solution (60 mM in water) into 100 μL of 6-aminofluorescein solution (10 mM in 10 mM HCl). Then, mix the solutions briefly using a vortex and incubate on ice for 5 minutes.
- Dilute the conjugate solution with 880 μL of ice water to a final concentration of 1 mM.
- After adding 1 μL of fluorescein-diazonium solution (1 mM) and 10 μL of αHer2-Fab-5HTP (ideal protein concentration of 4-10 μM) in PBS (pH 7), immediately mix the solutions and incubate on ice for 30 minutes.
- To effectively quench the free diazonium, add 2 μL 5-HTP (6 mM) into the reaction mixture and mix thoroughly with a pipette.
- Add 250 μL of PBS (pH 7) to dilute the reaction mixture, and then use centrifugal filters (10 kDa MWCO) to concentrate the solution to 25 μL.
- Assess the purity of modified protein using SDS-PAGE, verify successful labeling with fluorescence using an imager, and evaluate the extent of labeling by MS.
Notes
- To prepare a solution of 5HTP, first dissolve the compound in water. If complete dissolution is not achieved, incrementally add a small amount of NaOH (2 M) and shake vigorously until fully dissolved. Then, store the solution at -20°C.
- Higher yields can be achieved by flowing the lysate through the column a second time.
- The NaNO2 solution used in the procedure must be freshly prepared.
- Aromatic diazonium compounds exhibit instability, leading to their gradual hydrolysis over time. Due to this susceptibility, these compounds must be prepared freshly and utilized immediately.
