Immunopathology Complement Activation Complement Molecular Mechanisms Related Products Hot Services Q&A Resources
Are you facing challenges in understanding C3 glomerulopathy (C3G), which complicates the development of effective therapies? Creative Biolabs equips you with state-of-the-art tools and expertise essential for advancing research and development of complement-targeting therapeutics. We facilitate the exploration of the complex mechanisms underlying C3G and expedite the identification of novel intervention points through advanced protein analysis, antibody development services, and comprehensive biomarker profiling.
C3 Glomerulopathy Immunopathology
C3G represents a distinct category within membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, characterized by complement system dysregulation, particularly within the alternative pathway. This dysregulation results in excessive complement activation and deposition, primarily of C3 fragments, causing glomerular damage. Unchecked C3b amplification may be observed in circulation or along the glomerular basement membrane. C3G comprises two primary forms: C3 glomerulonephritis (C3GN) and dense deposit disease (DDD). These forms are distinguished by the presence and distribution of electron-dense deposits in the glomerular filter, with DDD's manifestations typically occurring earlier, often during adolescence, compared to C3GN.
Symptoms of Hemolytic C3 Glomerulopathy
The major features of C3G include blood in the urine (hematuria), high levels of protein in the urine (proteinuria), reduced glomerular filtration rate (reduced ability of the kidney to filter the blood and make urine), elevated creatinine, fatigue, swelling (edema) in many areas of the body. The morbidity of C3G is very rare, affecting 1 to 2 per million people worldwide and the frequency is equal in men and women.
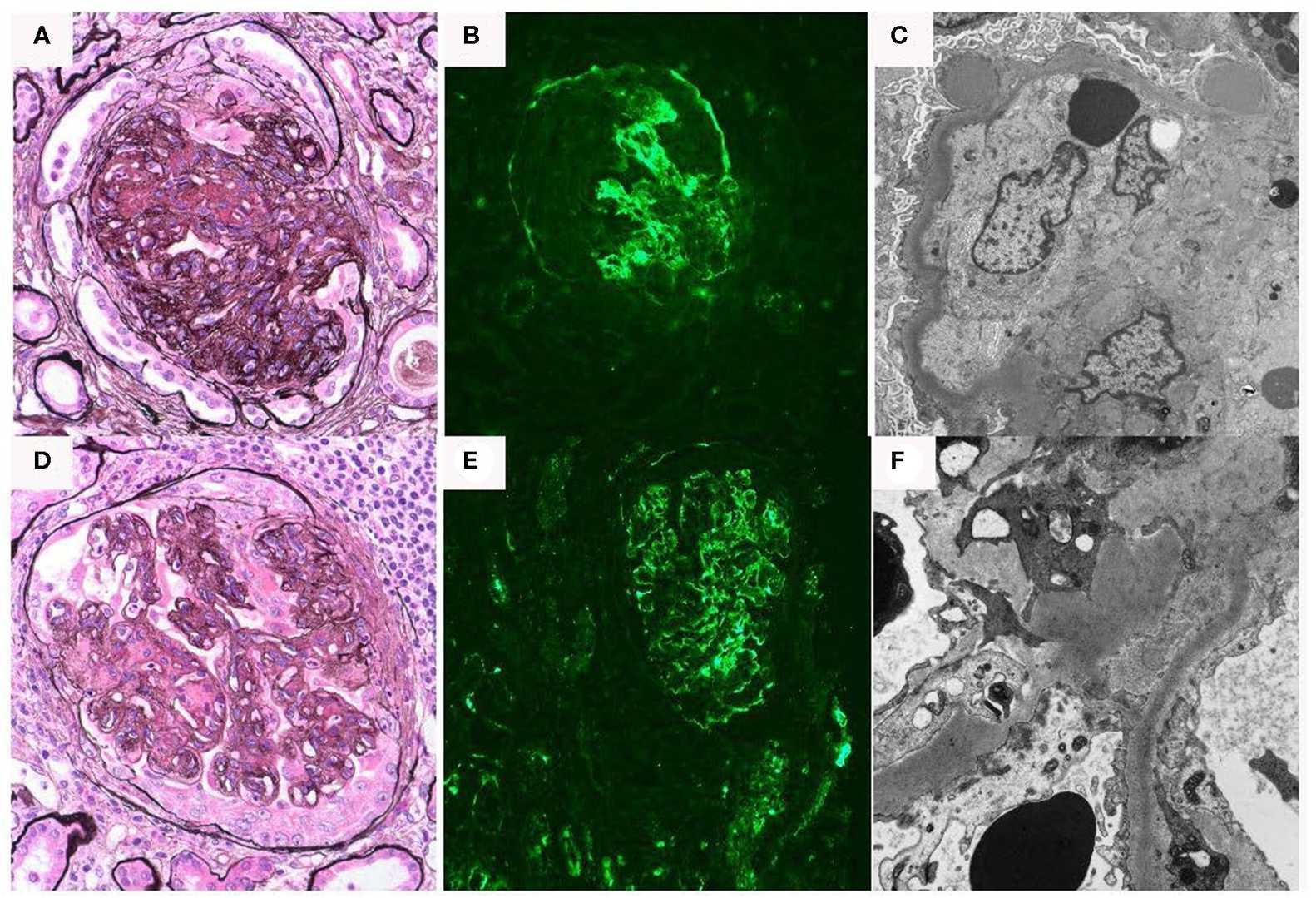
Fig. 1 Renal biopsy data for C3 glomerulopathy patient.1, 2
Pathophysiology of C3 Glomerulopathy
-
Autoantibodies
C3 nephritic factor (C3NeF) is an autoantibody that can bind to a neoepitope on the C3 convertase of alternative pathway, which is beneficial for the stability of the convertase against complement factor H-mediated decay. Meanwhile, the binding can potentiate C3 cleaving action, resulting in uncontrolled C3 activation and low serum C3 levels, but high levels in glomerulus.
-
Genetic Sequence Variation
C3G is associated with sequence changes in many genes. The patients suffering from DDD are seronegative for C3NeF, because of a homozygous missense mutation in the CFH gene. Moreover, deletion of a CFH codon results in circulating mutant CFH that is defective binding to C3b. In a later DDD pedigree, heterozygous deletion of two codons within the C3 gene was found to produce a hyper functional C3 molecule. The heterozygous mutations in CFH, CFI and MCP genes are associated with C3G.
-
Genetic Structure Variation
The structural changes of CFHR proteins are identified by multiplex-ligation probe amplification (MLPA), which are further associated with the presence of CFH autoantibodies in patients with C3G.
Complement Activation Pathways and C3G Pathogenesis
C3G is primarily driven by dysregulation of the complement system's alternative pathway. This dysregulation often results from genetic mutations affecting complement regulatory proteins or the presence of nephritic factors that stabilize the alternative pathway C3 convertase, leading to uncontrolled and excessive activation. Consequently, there is increased cleavage of C3 and dominant deposition of C3 fragments within the glomeruli, which causes inflammation and kidney damage. Although initial triggers may involve elements from other pathways, the sustained and pathogenic process in C3G fundamentally arises from unchecked activity and amplification within the alternative pathway.
Uncontrolled activation of the AP leads to a cascade of events: including excessive C3 cleavage, C3 fragment deposition, formation of C5 convertase, activation of the terminal pathway, and anaphylatoxin generation.
Complement Molecular Mechanisms in C3G
In aHUS, complement system dysregulation—especially within the alternative pathway—results in excessive activation that damages endothelial cells lining blood vessels, predominantly in the kidneys, leading to thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), a hallmark of HUS. Key complement proteins involved include:
Table 1 Molecular mechanisms of complement-mediated.
|
Key Complement Components
|
Functions
|
|
Complement Factor B (CFB) and C3
|
Gain-of-function variants can lead to increased formation or stability of the C3 convertase.
|
|
Complement Factor H (CFH)
|
Mutations can impair its ability to bind to host surfaces and inactivate C3b, leading to increased C3 convertase formation on glomeruli. Some mutations can also affect its cofactor activity for Factor I.
|
|
Complement Factor I (CFI)
|
Mutations can reduce its ability to cleave and inactivate C3b, resulting in the accumulation of C3b on glomerular surfaces.
|
|
Membrane Cofactor Protein (MCP or CD46)
|
Reduced expression or functional impairment on glomerular cells can lead to decreased C3b inactivation on these surfaces.
|
|
CFHR
|
Genetic rearrangements leading to hybrid CFHR proteins or deletions can disrupt Factor H function or lead to the production of competitive inhibitors of complement regulation.
|
Creative Biolabs has established advanced Complement Therapeutics platform including antibody engineering platform, protease inhibitor platform, and drug discovery platform, and is equipped to offer a full range of biotherapeutics development services regarding drug discovery and validation for C3G. Please contact us for detailed information.
Related Hot Products
Our extensive complement platform provides a wide and economical array of products related to complement. Please feel free to contact us.
Table 2 Featured products.
Related Hot Services
Table 3 Complement test services for SS-related complement studies.
Resources
References
-
Hanna, Ramy M., et al. "Diverse clinical presentations of C3 Dominant glomerulonephritis." Frontiers in Medicine 7 (2020): 293.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: