Introduction Activation of CP What We Can Offer? Why Choose Us? Published Data FAQs Related Products Protocols Resources
Accelerate Your Research and Development!
Are you currently facing challenges in deciphering complex complement-mediated disease mechanisms, developing targeted inhibitors, or accurately assessing drug efficacy in complement-related disorders? Creative Biolabs' Classical Pathway services help you accelerate research into complement-mediated diseases, obtain high-quality reagents, and develop novel therapeutics through our unparalleled expertise in complement biochemistry and advanced assay platforms.
Contact our team to get an inquiry now!
Introduction
The classical pathway is a crucial arm of the innate immune system, serving as a primary defense mechanism against pathogens and a critical link to adaptive immunity. This pathway is typically initiated by the binding of the C1 complex (composed of one C1q molecule and two molecules each of C1r and C1s) to the Fc regions of antibody-antigen complexes, primarily IgM or certain IgG subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3). C1q can also directly recognize and bind to pathogen surfaces, apoptotic cells, or aggregated proteins, bypassing the need for antibodies.
Creative Biolabs delivers a complete portfolio of therapeutic antibodies, inhibitors, soluble complement regulators, plus tailored services targeting classical pathway components, including:
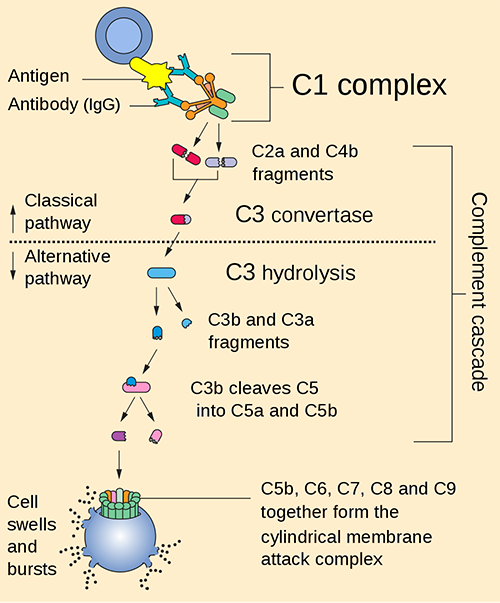 Fig. 1 Illustration of the classical and alternative pathway. Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig. 1 Illustration of the classical and alternative pathway. Distributed under Public Domain, from Wiki, without modification.
Activation of the Classical Pathway
The enzyme cascade can be delineated into three stages:
C1q recognition of IgM or hexameric IgG antibody complexes, microbial surface proteins, or apoptotic cellular material initiates the classical complement pathway. This phase involves three distinct steps:
-
First, zymogen C1 binds immediately to activators through C1q's globular domains.
-
Ligand attachment prompts C1q to undergo conformational alterations, which in turn facilitate the repositioning and self-activation of the C1r precursor dimer.
-
C1r then processes C1s, yielding a fully functional C1s enzyme with catalytic capabilities.
Activated C1s engages C4, enzymatically releasing C4a and C4b. This action subsequently drives the scission of C2 into C2a and C2b. Surface-bound C4b acts as a scaffold for the assembly of C3 convertase (C4bC2a). This C3 convertase subsequently cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b, a process critical for ensuing catalytic steps.
C3b combines with the C4b2a complex to form C5 convertase (C4b2a3b). Concurrently, C3a functions as an anaphylatoxin, attracting inflammatory cells. Subsequently, C5 convertase divides C5 into its C5a and C5b components. C5b then unites with the remaining terminal elements—C6, C7, C8, and C9—to assemble the Membrane Attack Complex (MAC). This complex facilitates the demise of invading bacteria by embedding itself within their cellular membranes, thereby generating permeable channels.
What We Can Offer?
Targeting the classical complement cascade is a primary focus in drug development, especially for autoimmune diseases and transplant rejection. Creative Biolabs' classical pathway services are designed for detailed mechanistic study, offering tools to explore each pathway step. A core service is complement activation assays, which detect and quantify classical pathway activation in various biological samples. This encompasses CH50 assays, C1q binding analyses, and other methodologies. Our expert scientific team supports tailored assay development, innovative protocol creation, and sophisticated data analysis regarding complement activation mechanisms.
We offer a full range of complement function or activity test services and use high-quality standards in all operations, including the testing procedures and delivery reports. Our specialized and dedicated team is available to support our clients with R&D, pre-clinical development programs.
The complement C1q-binding assay is mainly used for measuring the ability of antibody candidates to bind to the complement C1q. For the assay, antibody samples developed by clients with different concentration gradients will be tested, and proper positive and negative controls will be included.
C3b Deposition Assay enables precise and reliable quantification of C3b deposition on the cell surface. It may play an important role in solving the challenges in elucidating complement system activation, developing targeted therapeutics, and dissecting disease mechanisms.
Why Choose Us?
At Creative Biolabs, our commitment to scientific excellence and client success sets us apart in the field of classical pathway research and therapeutic development. Our unique advantages include:
-
Deep Scientific Expertise: Our team comprises seasoned immunologists and biochemists with extensive experience in complement biology, ensuring a profound understanding of the classical pathway's intricacies and its role in health and disease.
-
Advanced Platform Capabilities: We leverage state-of-the-art platforms for high-throughput screening, functional assays, and mechanistic studies, enabling rapid and precise analysis of complement activity and its modulation.
-
Comprehensive Reagent Portfolio: We provide a wide array of high-quality, validated complement proteins, antibodies, and assay kits, ensuring reliable and reproducible results for your experiments.
-
Project-Specific Strategies: We recognize every research initiative's distinct requirements. Our services are highly customizable, designed to meet your specific research objectives and accelerate your discovery timeline.
-
Proven Track Record: Our success stories, supported by Published Data, demonstrate our capability to deliver impactful results and contribute significantly to our clients' breakthroughs in complement therapeutics.
Leverage the Creative Biolabs Advantage – Submit a Proposal Request Today
Published Data
Presented are findings showcased within articles pertaining to classical pathway studies:
1. Classical Pathway Activation Assay
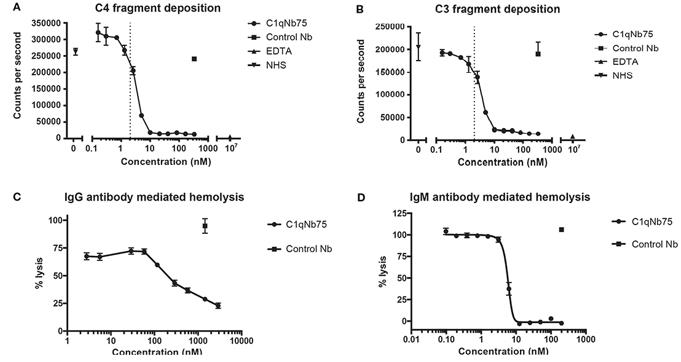 Fig. 2 C1qNb75 inhibits IgG and IgM mediated activation of the classical pathway and hemolysis.1
Fig. 2 C1qNb75 inhibits IgG and IgM mediated activation of the classical pathway and hemolysis.1
Nick S. Laursen et al. described the development and in vitro characterization of a C1q-specific
nanoantibody (C1qNb75) specifically targeting C1q. C1qNb75 binds to the globular head module of human C1q with
sub-nanomolar affinity and prevents classical pathway-mediated IgG and IgM hemolysis. Structural analysis showed
that C1qNb75 recognizes an epitope located predominantly in the C1q B chain that overlaps with the binding sites for
IgG and IgM. Thus, C1qNb75 competitively prevents C1q from binding to IgG and IgM, thereby blocking complement
activation by the classical pathway.
FAQs
Q: How can I accurately measure the activation of this specific immune pathway in my samples?
A: Measuring pathway activation typically involves specific assays that detect the cleavage products or activated forms of key components. Techniques often include ELISA-based assays, Western blotting, or functional assays that assess hemolytic activity or deposition of activated fragments. The choice of method depends on the sample type and the specific component you wish to analyze.
Q: What are the primary applications of studying this pathway in drug development?
A: Understanding this pathway is crucial for developing therapeutics for a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, as well as infectious diseases and certain cancers. It allows for the identification of novel drug targets, the screening of potential inhibitors or activators, and the assessment of drug efficacy and safety in modulating immune responses.
Q: Are there any specific precautions or considerations when working with complement components?
A: Complement components are often sensitive to temperature changes and repeated freeze-thaw cycles, which can affect their activity. Proper handling and storage are essential to maintain their functional integrity. Additionally, careful experimental design is needed to account for potential non-specific interactions or interference from other serum proteins.
Q: How does modulating this pathway compare to targeting other immune pathways for therapeutic intervention?
A: Modulating this pathway offers a highly specific approach to controlling immune responses, particularly those involving antibody-mediated inflammation or immune complex clearance. While other immune pathways might offer broader immunomodulation, targeting this specific pathway can provide more precise therapeutic effects with potentially fewer off-target side effects, especially in conditions where this pathway is a primary driver of pathology.
Q: Can this pathway be studied in various biological matrices, such as serum, plasma, or cell culture supernatants?
A: Yes, this pathway can be effectively studied in a variety of biological matrices. Serum and plasma are commonly used for assessing systemic pathway activity, while cell culture supernatants can be utilized to study pathway activation in response to specific cellular stimuli or in localized inflammatory environments. Specialized protocols are often required to ensure accurate and reliable measurements in each matrix.
Related Product
We understand that each research project is unique, and we are committed to providing personalized solutions to meet
your specific scientific goals. By leveraging our deep expertise and state-of-the-art products, we ensure that your
research is supported by the most reliable and precise tools available.
We offer proteins/peptides, antibodies, kits, inhibitors, sera and plasma used in the study of the classical pathway
of complement activation. You can find the products you need by target.
Browse Products based on target listing:
Protocols
Resources
Reference
-
Laursen, Nick S., et al. "Functional and structural characterization of a potent C1q inhibitor targeting the classical pathway of the complement system." Frontiers in Immunology 11 (2020): 1504. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01504. Distributed under an Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Illustration of the classical and alternative pathway.
Fig. 1 Illustration of the classical and alternative pathway.  Fig. 2 C1qNb75 inhibits IgG and IgM mediated activation of the classical pathway and hemolysis.1
Fig. 2 C1qNb75 inhibits IgG and IgM mediated activation of the classical pathway and hemolysis.1