Nephropathy Disorders Types Complement Regulatory Proteins Therapeutic Strategies Related Products Hot Services Q&A Resources
Are you grappling with the intricate challenges of complement-mediated nephropathies, facing hurdles in developing effective and targeted therapies? Creative Biolabs empowers your research and development with cutting-edge solutions to unravel the complexities of complement activation in kidney disease. Our advanced platforms and expert knowledge help you accelerate the discovery and development of novel complement therapeutics through comprehensive target identification, precise preclinical models, and robust biomarker analysis.
Nephropathy Disorders
The complement system serves as a crucial link between innate and adaptive immunity, essential for defending against pathogens and maintaining homeostasis. It is activated not only by pathogens but also by autoantibodies and damaged cells. This complex network involves leukocytes, platelets, and tissues in inflammation via three pathways: classical, lectin, and alternative, with over 40 components regulating its activity to prevent imbalance. Recently, its role in diseases like nephropathy has been highlighted, as improper activation of pathways is detrimental, and associated with disorders such as glomerulonephritis, C3 glomerulopathy, and ischemic injury after kidney transplantation.
-
Glomerulonephritis
Glomerulonephritis is one of the most common reasons of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal failure in the world. It is generally caused by the presence of autoantibodies and the autoantibody-mediated involvement of classical pathway. Lupus nephritis is one representative symptom of glomerulonephritis, which develops due to an impaired clearance of apoptotic cells, and thus leads to immune complex deposition in glomeruli. So the immune system is constantly exposed to autoantigens and subsequent development of autoimmunity. The complement component C1q is a key regulating factor in the clearance of immune complexes, and C3, C4 are associated with lupus development and activity. The MBL (initiator of lectin-pathway) deficiency may also be predisposed to lupus nephritis development.
-
Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome
The hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is characterized by the triad of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute renal failure. It is a heterogeneous disease of the microvasculature and the main cause in the pathogenesis is the deficiency in the regulation of the alternative complement pathway. In the HUS patients, multiple mutations of complement component have been identified, including regulatory proteins [factor H, factor I, MCP (CD46)] and complement activators (CFB and C3), which reveals the central role in the pathogenesis of HUS.
-
C3 Glomerulopathy
C3 glomerulopathy is demonstrated to be associated with the uncontrolled systemic activation of the alternative pathway. The disease-causing mutations in alternative pathway inhibitors, such as factor H and factor I, can lead to C3 glomerulopathy, additionally, some autoantibodies leading to the activation or blockage of alternative pathway proteins have also been identified as a pathogenic cause.
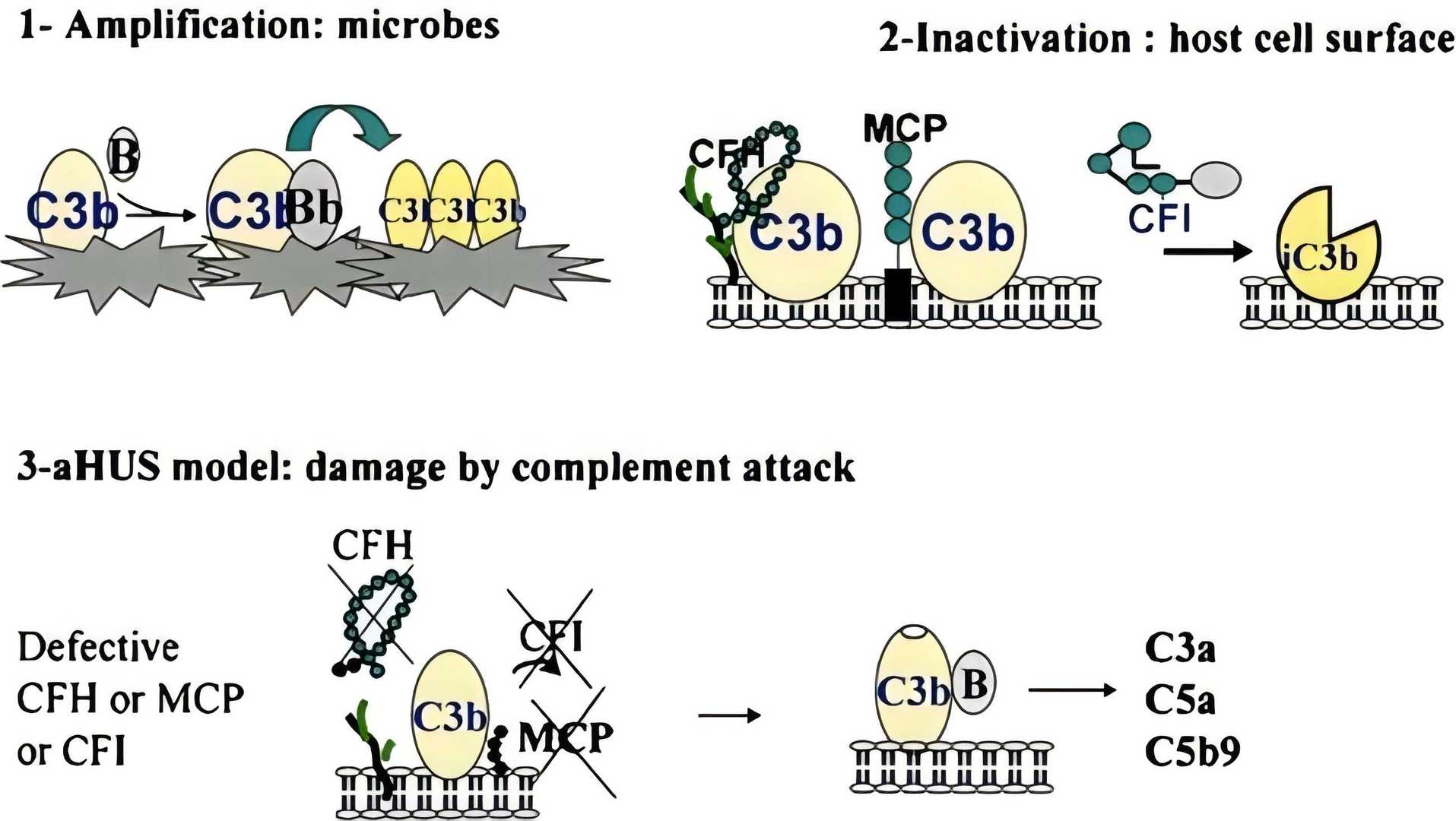
Fig. 1 Inefficient protection of endothelial cells in complement activation caused aHUS.1, 2
Complement Regulatory Proteins
Autoimmune diseases that involve the complement system emerge and progress through a series of complex interrelated molecular activities. The innate immune system mistakenly identifies self-antigens that activate complement pathways through classical, lectin, or alternative means. Targeted therapeutic interventions require comprehensive knowledge of intricate molecular mechanisms to effectively modulate specific points within the complement cascade.
Table 1 Regulatory complement proteins in nephropathy.
|
Complement Regulatory Proteins
|
Complement Pathway Regulated
|
Function
|
|
Factor H (FH)
|
Alternative
|
Deficiencies/dysfunction strongly linked to C3G and aHUS.
|
|
Factor I (FI)
|
All
|
Defects lead to uncontrolled complement activation, implicated in C3G and aHUS.
|
|
C4b-binding protein (C4BP)
|
Classical/Lectin
|
Dysregulation is implicated in some glomerulonephritides.
|
|
Properdin (Factor P)
|
Alternative
|
The amplified activity contributes to nephropathies with alternative pathway overactivation (e.g., IgAN, C3G).
|
|
DAF/CD55
|
All
|
Reduced expression/dysfunction can increase complement deposition in the kidney.
|
|
MCP/CD46
|
All
|
Mutations are a major cause of aHUS.
|
|
CR1/CD35
|
All
|
Reduced expression/dysfunction may impair immune complex clearance and contribute to glomerulonephritis.
|
|
Protectin/CD59
|
Terminal Pathway
|
Deficiency can lead to increased MAC deposition and cellular damage in the kidney.
|
Research Frontiers and Novel Therapeutic Strategies
|
|
Therapies
|
Mechanisms
|
|
Targeting the Alternative Pathway
|
factor B Inhibitor
|
Recently received accelerated approval by the FDA for the reduction of proteinuria in adults with primary IgA nephropathy (IgAN) at risk of rapid disease progression.
|
|
C3 inhibitor
|
Binds to C3 and inhibits its cleavage, thus blocking all three complement pathways at a proximal level. It is being investigated for various nephropathies, including C3G and IgAN.
|
|
factor D inhibitor
|
Currently in clinical development for IgAN and other complement-mediated diseases.
|
|
factor B mRNA targeting LICA
|
Reduced factor B production. It is being evaluated in clinical trials for IgAN.
|
|
Targeting the Terminal Pathway
|
C5 protein mAb
|
Binds to the C5 protein, inhibiting its cleavage into C5a and C5b, thus blocking the formation of the MAC. It is approved for aHUS and is used off-label in some other complement-mediated nephropathies.
|
|
C5 siRNA
|
Reducing its production. It is being investigated for IgAN.
|
|
Targeting the Lectin Pathway
|
MASP-2 mAb
|
Targeting MSAP-2, under investigation for various nephropathies, including IgAN and thrombotic microangiopathies.
|
|
Other Complement-Targeting Strategies
|
Recombinant Complement Regulatory Proteins
|
Development of recombinant forms of endogenous complement inhibitors like CFH or soluble CR1 to restore complement regulation.
|
|
Gene Therapy
|
Approaches aimed at correcting genetic deficiencies in complement regulatory proteins are particularly relevant for diseases like aHUS caused by mutations in CFH, CFI, or MCP.
|
Related Hot Products
Our extensive complement platform delivers a wide array of complement-associated products efficiently and economically. Should you have any interest, please do not hesitate to reach out for further information.
Table 2 Featured products.
Related Hot Services
At Creative Biolabs, we provide a comprehensive suite of services and innovative technologies to support your journey in developing complement-targeted therapies for nephropathy:
Table 3 Complement test services for nephropathy-related complement studies.
Creative Biolabs offers a range of therapeutic antibodies, inhibitors, and soluble complement regulators, along with specialized services targeting complement-related nephropathy. Our comprehensive complement platform ensures the rapid and cost-effective delivery of various complement-related products. If you are interested, please contact our team for more detailed information.
Resources
References
-
Loirat, Chantal, Marina Noris, and Véronique Fremeaux-Bacchi. "Complement and the atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in children." Pediatric nephrology 23 (2008): 1957-1972.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections: