Complement C1QBP
Complement C1q binding protein (C1QBP), also known as ASF/SF2-associated protein p32 or mitochondrial matrix protein p32, is a multifunctional and multicompartmental protein involved in many functions. It was named C1QBP since it was originally discovered as the receptor of the globular head of complement component 1q (gC1qR).
Human C1QBP is a 33 kDa highly acidic cellular protein with 282 amino acids forming three homologous subunits. It is a widely distributed multicompartmental protein that can bind to multiple ligands, such as complement C1q, kininogen-1, coagulation factor, Protein kinase D1, and so forth. C1QBP on the cell surface is thought to act as an endothelial receptor for complement C1q, which specifically binds to the globular 'heads' of C1q thus inhibiting the activation of complement C1 and complement classical pathway. Additionally, C1QBP also has been indicated to implicate in a wide variety of biological processes, including inflammation, the immune response to pathogens, ribosome biogenesis, protein synthesis in mitochondria, regulation of apoptosis, transcriptional regulation, pre-mRNA splicing, and coagulation. Recently, C1QBP has been found that over-expressed in several different types of tumor cells, and selectively bound to a tumor homing peptide LyP-1 in tumor cells.
The abnormal expression of C1QBP can cause complement dysfunctions. When involved in interactions with other ligands, C1QBP abnormity is associated with combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 33, Rubella, infections, and coagulation dysfunction.
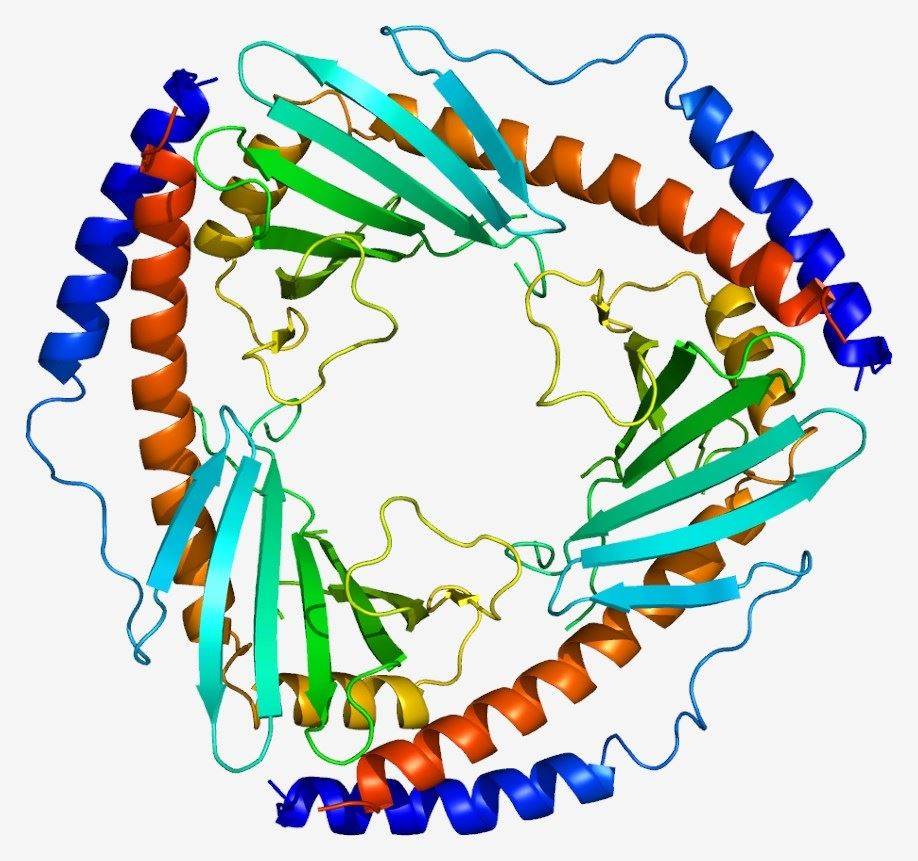 Fig. 1 Complement C1QBP structure.1
Fig. 1 Complement C1QBP structure.1
Reference
-
From Wikipedia: By Emw - Own work, CC BY-SA 3.0 https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Protein_C1QBP_PDB_1p32.png.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig. 1 Complement C1QBP structure.1
Fig. 1 Complement C1QBP structure.1