Complement C4BPB
Complement C4 binding protein beta chain (C4BPB) is one of the two polypeptides of complement C4 binding protein (C4BP), a regulatory protein presenting in the fluid phase of normal plasma that plays an important role in the complement cascade. Usually, each C4BP protein complex contains a C4BPB chain. Human C4BPB is a 252-amino acid peptide encoded by the C4BPB gene, weighing about 28 kDa.
Similar to C4BPA, C4BPB also contains two cysteine residues and an amphipathic a-helix at the C-terminal, which are involved in disulfide-linkage polymerization. There are 3 complement control protein (CCP) repeat domains in human and rat C4BPB, while 2 CCPs in cattle C4BPB. In the human C4BPB, CCP1 domain is a critical binding site for the vitamin K-dependent Protein S, an anticoagulant plasma protein serving as a cofactor to activated protein C in the degradation of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa. Once C4BPB is bound to Protein S with high affinity, the C4BP-Protein S complex will inhibit the activation of the complement pathways on the apoptotic cells, on the other hand, prevents Protein S from acting as a cofactor in coagulation. It has been indicated that the CCP2 domain may not act as a binding site but localizes and stabilizes CCP1. The diseases associated with C4BPB mainly include Patellar Tendinitis and Cone-Rod Dystrophy 2.
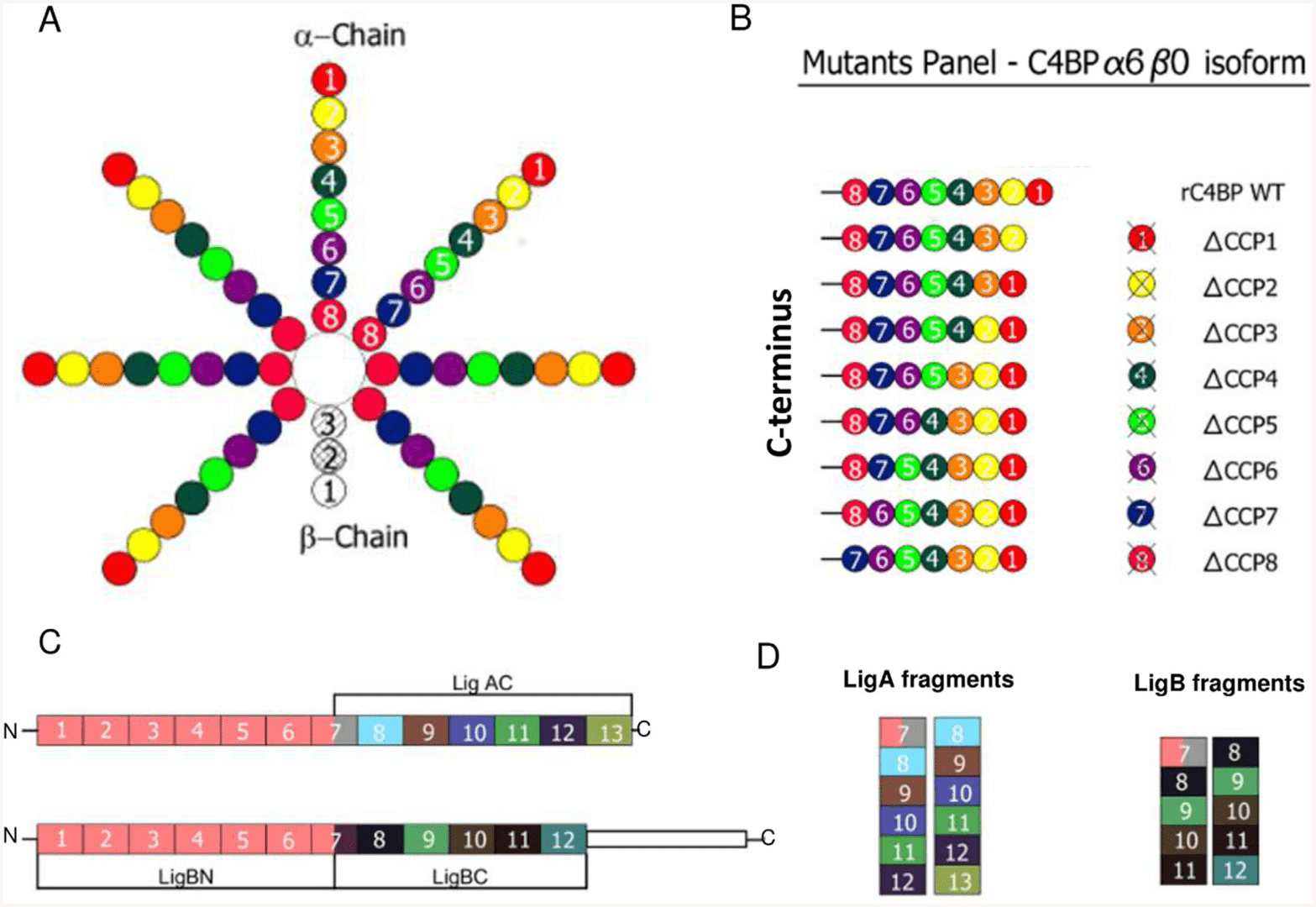 Fig.1 Protein S and the protein S-C4BP complex. (Dahlbäck, 2005)
Fig.1 Protein S and the protein S-C4BP complex. (Dahlbäck, 2005)
Reference
-
Dahlbäck, B.; Villoutreix, B.O. Regulation of blood coagulation by the protein C anticoagulant pathway: novel insights into structure-function relationships and molecular recognition. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2005, 25(7): 1311-1320.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig.1 Protein S and the protein S-C4BP complex. (Dahlbäck, 2005)
Fig.1 Protein S and the protein S-C4BP complex. (Dahlbäck, 2005)