Product List Background C5 Convertase Functional Service
Background
Complement C5 convertase is a kind of serine protease that cleaves the C5 into fragments C5a, an anaphylatoxin and a chemotactic factor, C5b, the first component of the membrane attack complex (MAC). C5 convertase is made up of three fragments, in the classical or lectin pathways is C4b, C2a, and C3b, while in the alternative pathway is one C3b and two Bb. C5 convertase is generated on activating surfaces after the deposition of C3b molecules on the target surface in the vicinity of C3 convertase complexes.
Normally, C5 convertase cleaves the C5 is the final enzymatic step in the complement activation cascade resulting in the generation of the cytolytic proteolytically activated form of C5b-9 complex. Besides, C3 convertase binding to the additional C3b molecules nearby was thought to be needed for forming C5 convertase activity. In addition, high C5 convertase activity is related to the generation of C3b-C3b or C3b-C4b dimers in which the additional C3b molecule was shown to be covalently attached to a specific site on the first C3b or C4b molecule.
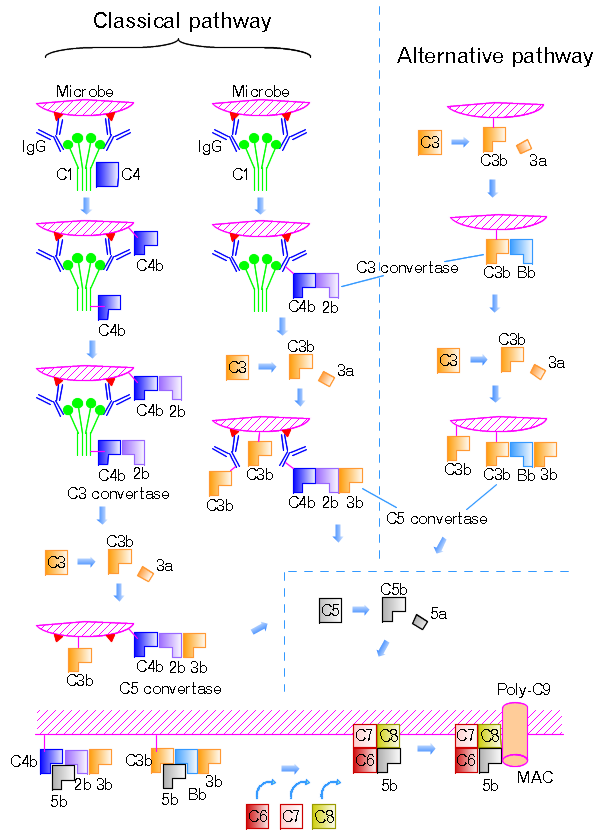 Fig.1 Involvement of C5 convertase in both classical and alternative pathways.Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Involvement of C5 convertase in both classical and alternative pathways.Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
C5 Convertase Functional Service
Creative Biolabs offers an extensive suite of C5 convertase-related products, including ELISA assay kits, which are proficient in detecting and monitoring the interaction between antibody regions and C5 Convertase. These reagents are crucial for advancing research dedicated to therapeutic developments for various diseases.
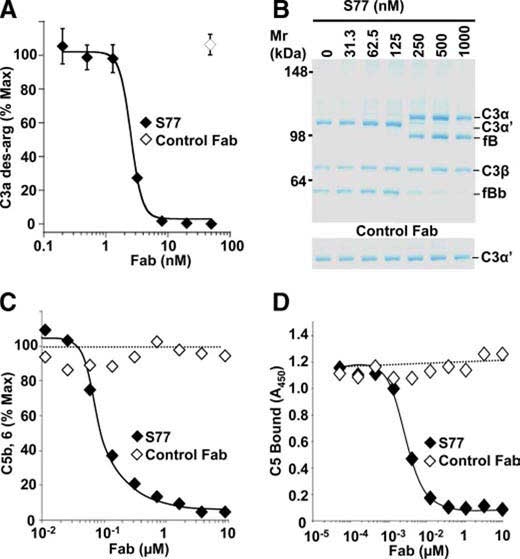 Fig.2 Inhibition of alternative pathway C3 and C5 convertase by anti-C3b Fab fragment.1
Fig.2 Inhibition of alternative pathway C3 and C5 convertase by anti-C3b Fab fragment.1
A key alternative pathway player C3b can suppress excessive inflammation by mitigating complement-mediated immune responses and tissue damage. Utilizing phage display technology, an antibody was developed that specifically binds to C3b, without recognizing the non-activated C3 molecule. The crystal structure of C3b complexed with the antibody’s Fab fragment unveils the mechanism behind this specificity. The assembly of C5 convertase was carried out on zymosan particle surfaces. Various concentrations of anti-C3b Fab fragment or a control Fab were combined with constant levels of C5 and convertase. The activity of the convertase was measured through a hemolytic assay with chicken erythrocytes, and results were reported as the percentage of hemolysis observed without the presence of an inhibitor. Results show that anti-C3b Fab fragment obstructs both factor B and C5 binding to C3b, thereby inhibiting C5 convertase activity. This inhibition curtails anaphylatoxin production and membrane-attack complex formation. This study sheds light on the molecular underpinnings of alternative pathway complement activation, showcasing a novel approach to complement inhibition.
Creative Biolabs delivers an extensive suite of customized C5 convertase-focused services, including comprehensive interaction assessments and a variety of specialized evaluations. These precisely crafted solutions are designed to assist clients in progressing their scientific investigations and clinical projects.
Reference
-
Katschke, Kenneth J., et al. "Structural and functional analysis of a C3b-specific antibody that selectively inhibits the alternative pathway of complement." Journal of Biological Chemistry 284.16 (2009): 10473-10479. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Involvement of C5 convertase in both classical and alternative pathways.
Fig.1 Involvement of C5 convertase in both classical and alternative pathways. Fig.2 Inhibition of alternative pathway C3 and C5 convertase by anti-C3b Fab fragment.1
Fig.2 Inhibition of alternative pathway C3 and C5 convertase by anti-C3b Fab fragment.1
