Product List Background C8G Functional Service
Background
Complement component 8 (C8), a heterotrimer protein composed of three different subunits, α chain, β chain, and γ chain, is one of the five complement components of the cytolytic membrane attack complex (MAC). The γ chain, also known as C8G, is a 202-amino acid 22 kDa polypeptide encoded by the C8G gene. Different from C8A and C8B, human C8G is a single domain polypeptide independent of any complement protein, which is a member of the lipocalin family capable of binding small hydrophobic ligands. Although the Cys 40 of C8G is attached to the Cys 164 of C8A through a disulfide bond, C8G is not essential for both the structure and function of MAC. As a lipocalin, C8G contains a typical lipocalin fold with a distinct binding site for small molecules, such as retinol, steroids, and fatty acids.
Different from the human C8A and C8B genes that are closely linked on chromosome 1p, the human C8G gene is located on chromosome 9q. Mutations in the C8G gene associates with immunodeficiency due to a late component of complement deficiency. Besides, C8G deficiency also has been reported to play important role in Acute Salpingo-Oophoritis, a reproductive disease related to salpingo-oophoritis and pyelonephritis.
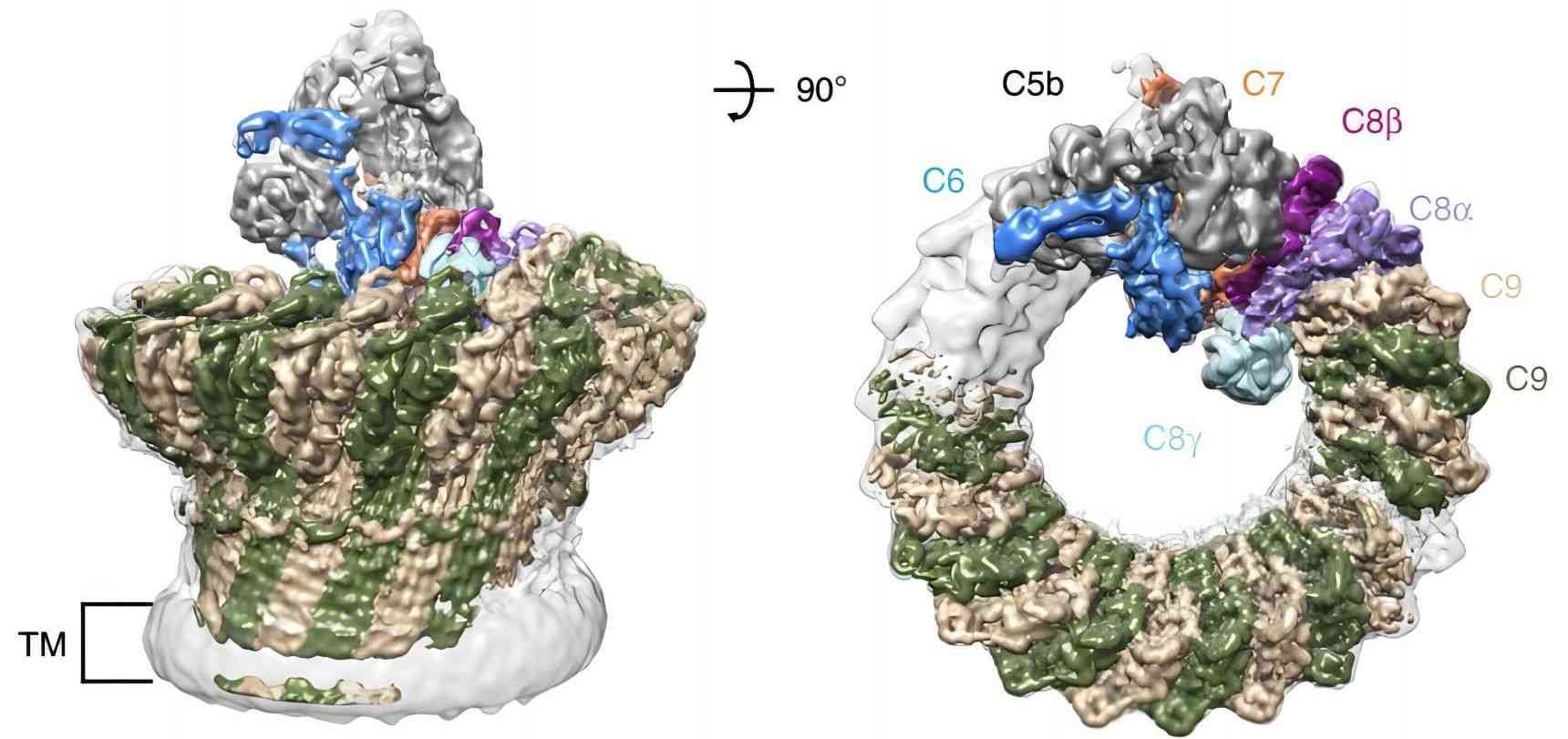 Fig.1 Structural role of C8G in the formation of the MAC pore.1, 3
Fig.1 Structural role of C8G in the formation of the MAC pore.1, 3
C8G Functional Service
Creative Biolabs offers a broad array of C8G-associated products, such as anti-C8G antibodies, ELISA kits for C8G detection, recombinant C8G proteins, and reporter vectors containing the C8G gene. These precisely engineered reagents are essential for promoting research aimed at devising therapeutic strategies for numerous diseases.
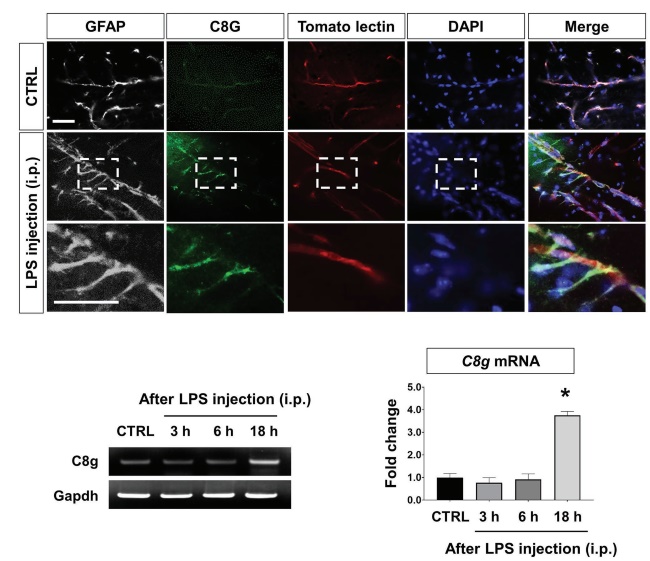 Fig.2 Expression of C8G in perivascular astrocytes within LPS-induced inflamed brain.2, 3
Fig.2 Expression of C8G in perivascular astrocytes within LPS-induced inflamed brain.2, 3
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is important for regulating the movement of molecules between the central nervous system and the circulatory system, ensuring the brain’s homeostasis. BBB impairment is linked to various neurological conditions and is associated with neuroinflammatory processes involving leukocyte infiltration and glial activation. Researchers investigated the role of C8G in BBB integrity. C8G has been found to inhibit neuroinflammation by modulating the sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P)-S1PR2 pathway. Immunofluorescence analysis revealed C8G localization in perivascular astrocytes, while S1PR2 is present in endothelial cells. Recombinant C8G administration preserved BBB integrity and reduced inflammation in a neuroinflammation model, indicating astrocytic C8G’s essential role in BBB protection.
Creative Biolabs offers an extensive suite of tailored C8G-functional services, encompassing comprehensive interaction analyses and other specialized assessments. These meticulously developed services are designed to support clients in advancing their scientific research and clinical endeavors.
References
-
Menny, Anaïs, et al. "CryoEM reveals how the complement membrane attack complex ruptures lipid bilayers." Nature communications 9.1 (2018): 5316.
-
Kim, Jong-Heon, Jin Han, and Kyoungho Suk. "Protective effects of complement component 8 gamma against blood-brain barrier breakdown." Frontiers in Physiology 12 (2021): 671250.
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Structural role of C8G in the formation of the MAC pore.1, 3
Fig.1 Structural role of C8G in the formation of the MAC pore.1, 3
 Fig.2 Expression of C8G in perivascular astrocytes within LPS-induced inflamed brain.2, 3
Fig.2 Expression of C8G in perivascular astrocytes within LPS-induced inflamed brain.2, 3
