Complement Factor H Related Protein 4
The human complement factor H (CFH) protein family is composed of glycoproteins encoded by six tandem genes in the regulation of complement activation (RCA) gene cluster. These functional proteins include CFH, CFH-like protein 1 (FHL-1), and complement factor H-related proteins (CFHR1-5), among which FHL-1 is a variant of CFH by alternative splicing, while CFHR1-5 are homologous to CFH in varying degrees.
Complement factor H-related protein 4 (CFHR4) is a plasma glycoprotein with two splice variants, CFHR4A and CFHR4B. CFHR4A contains 9 short consensus repeat (SCR) domains, in which SCR1-4 are highly identical to SCR5-8. CFHR4B consists of 5 SCRs, in which SCR2-5 share 100% amino acid homology to SCR6-9 of CFHR4A, and SCR1 is 98% identical to SCR1 of CFHR4A. Similar to CFHR3, both CFHR4A and CFHR4B lack the N-terminal dimerization domain. It is challenging to detect CFHR4B concentration in plasma or serum since that FHR4B domains are practically identical to that of CFHR4A, making it difficult to prepare FHR4B-specific antibodies.
CFHR4 functions as a cofactor for CFH to regulate complement activity. By binding to the complement C3b, CFHR4 serves as a platform for the assembly of C3 convertase to activate the complement alternative pathway. And, another novel ligand C-reactive protein (CRP) has been identified recently, by which CFHR4 recruited and facilitated the native CRP bind to necrotic cells, playing an opsonization role. CFHR4 abnormality is related to atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome and hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
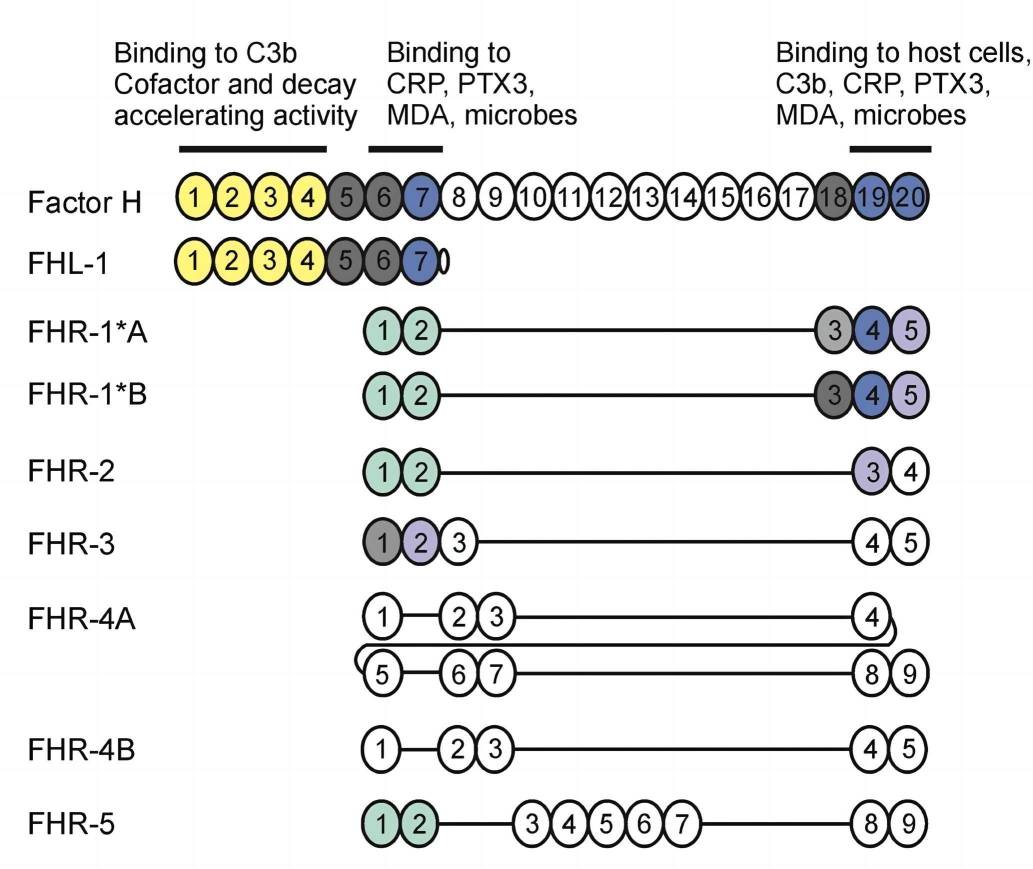 Fig. 1 The human factor H protein family.1
Fig. 1 The human factor H protein family.1
Reference
-
Józsi, Mihály. "Factor H family proteins in complement evasion of microorganisms." Frontiers in immunology 8 (2017): 571.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig. 1 The human factor H protein family.1
Fig. 1 The human factor H protein family.1