Complement Receptor 4 (CD11c+CD18)
Complement receptor 4 (CR4), also known as ITGAX/ITGB2 or p150/95, is a major adhesion-associated heterodimer protein that is composed of α (CD11c) and β (CD18) chains. CR4 is usually co-expressed on the myeloid subsets of leukocytes, also found on NK cells and activated T and B lymphocytes. CR4 is commonly employed as one of the markers of dendritic cells. CR4 is a member of the β2 integrin family which contains three other members, LFA-1 (CD11a/CD18), CR4 (CD11c/CD18), and CD11d/CD18. CR4 is closely related to CR3. The α chain of CR4 has about 87% homology with the α chain (CD11b) of CR3 in the sequence and can bind to similar ligands such as IC3b, fibrinogen, and ICAM-1. Although CR3 and CR4 share ligands, in some cases they are selective about their ligands. For example, CR3 inclines to bind positively charged species, while CR4 binds strongly negative-charged species.
Similar to CR3, CR4 is also involved in leucocyte adhesion, activation and recruitment, host defense responses, cytokine production, and phagocytosis. CR3 and CR4 have been revealed to interact with bacterial lipopolysaccharide and β-glucans and aid phagocytosis of unopsonized bacteria and yeast. Studies also reported CR3 and CR4 were highly expressed on NK cells which play a key role in complement-dependent cell cytotoxicity (CDCC). However, the role of this NK cell effector mechanism is unclear.
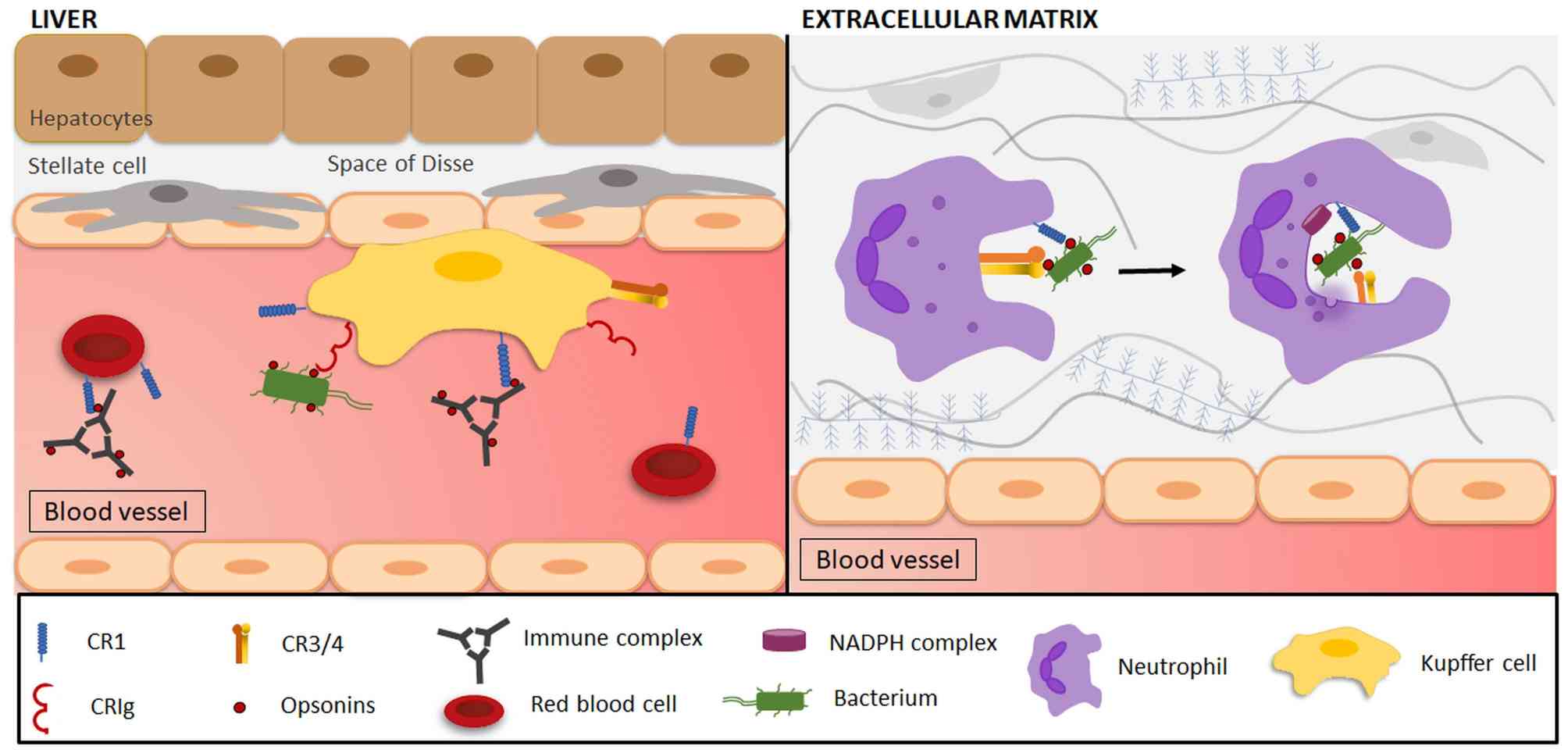 Fig. 1 Involvement of CR4 in immune complex clearance and phagocytosis for microorganism.1
Fig. 1 Involvement of CR4 in immune complex clearance and phagocytosis for microorganism.1
Reference
-
Vandendriessche, Sofie, et al. "Complement receptors and their role in leukocyte recruitment and phagocytosis." Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology 9 (2021): 624025.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig. 1 Involvement of CR4 in immune complex clearance and phagocytosis for microorganism.1
Fig. 1 Involvement of CR4 in immune complex clearance and phagocytosis for microorganism.1