Product List Background CR1 Functional Service
Background
Complement receptor type 1 (CR1), also known as CD35, is encoded by the CR1 gene and has a ~200 kDa molecular weight. The extracellular domain of the most common form of CR1 is made up of several 30 repeating units called short consensus repeats (SCRs). The SCRs are distributed in four long homologous repeats (LHRs A, B, C, and D), which is result from a seven-SCR unit. CR1 is mainly in neutrophils, monocytes, erythrocytes, B and T cells, and dendritic cells as well as in microglia, neurons, and the choroid plexus of the brain, in the membrane or insoluble form. The soluble CR1 (sCR1) form is derived from proteolytic cleavage in terminal secretory vesicles or the cell membrane.
Both CR1 forms play an important role in regulating complement activity which is achieved through binding cleaved C3b and C4b components and the complement cascade initiation molecules mannose-binding lectin (MBL-2), ficolins (FCN1, FCN2, and FCN3), and C1q. CR1 has the same binding site as serine proteases (MASPs) and competes with MASPs to prevent the initiation of the lectin pathway of complement. When the CR1 binding, the membrane-bound form of CR1 internalizes the opsonized elements or presents them to other immune cells, thus inhibiting the production of the C5 convertase and prevent the generation of the membrane attack complex (MAC). CR1 might also block excessive complement activation, playing as a cofactor for the Factor I-mediated cleavage of soluble/bound C3b and C4b.
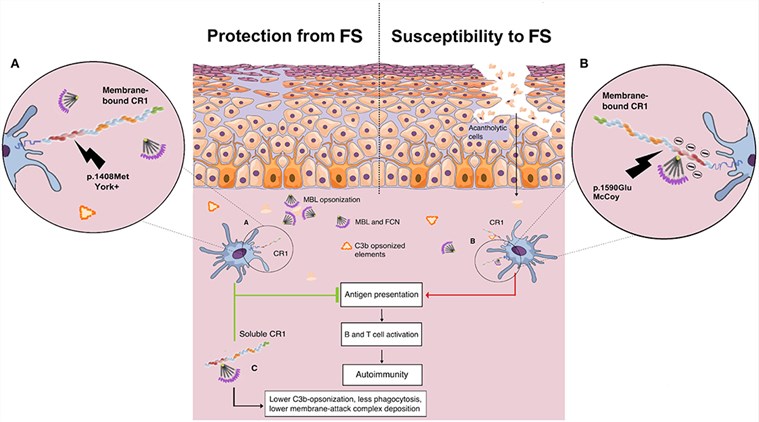 Fig.1 Illustrated potential influence of Knop blood group CR1 variations and circulating soluble CR1 in the susceptibility to endemic pemphigus foliaceus.1, 3
Fig.1 Illustrated potential influence of Knop blood group CR1 variations and circulating soluble CR1 in the susceptibility to endemic pemphigus foliaceus.1, 3
CR1 Functional Service
Creative Biolabs offers a wide array of CR1-targeted products, encompassing anti-CR1 antibodies, ELISA kits, and recombinant human complement CR1 proteins. These carefully crafted resources are vital in propelling research efforts focused on developing therapeutic strategies for numerous diseases.
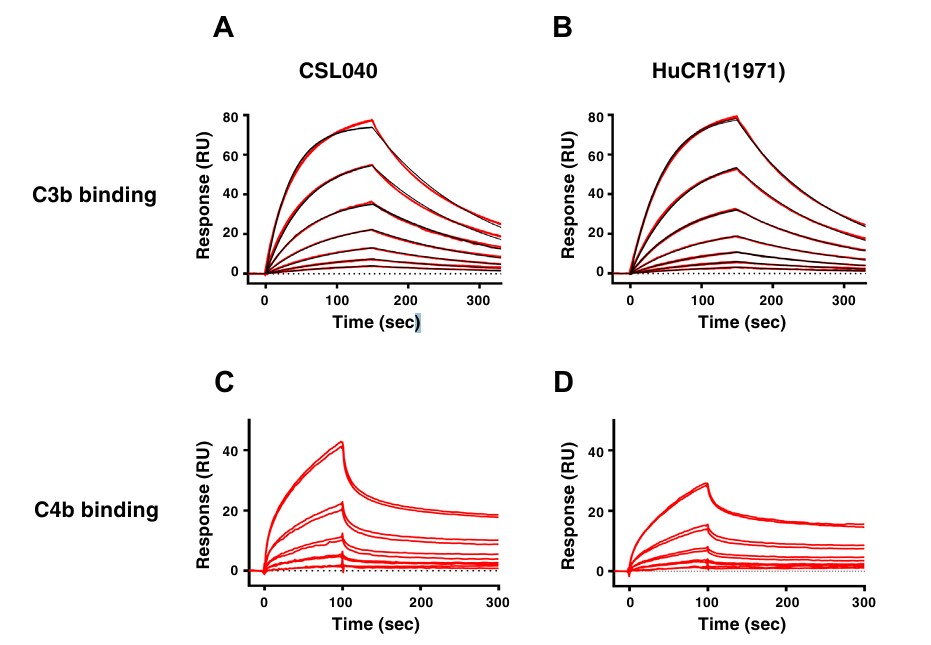 Fig.2 Affinity comparison of truncated human CR1 versus CR1 to human complement components C3b and C4b.2, 3
Fig.2 Affinity comparison of truncated human CR1 versus CR1 to human complement components C3b and C4b.2, 3
Human CR1 (HuCR1) plays an essential role in modulating complement system activity, affecting all three complement pathways. It serves as a binding site for C3b and C4b, aids in the destabilization of C3/C5 convertase, and facilitates factor I-mediated proteolysis of C3b and C4b. This research aimed to identify a minimal soluble HuCR1 fragment with preserved complement regulatory functions. Soluble HuCR1 truncations were created and assessed for their inhibitory effects on complement activation. The fragment truncated at amino acid 1392, emerged as the most effective inhibitor among variants. It retained binding affinity and regulatory activity, demonstrating stability and a favorable pharmacokinetic profile in mice. HuCR1 truncations significantly reduced kidney damage in a glomerulonephritis model, highlighting its therapeutic potential for complement-mediated diseases.
Creative Biolabs provides a suite of CR1-centric services, including CR1 interaction evaluations and functional assays, tailored to enhance the endeavors of our valued clients in research and clinical settings.
References
-
Oliveira, Luana Caroline, et al. "Complement receptor 1 (CR1, CD35) polymorphisms and soluble CR1: A proposed anti-inflammatory role to quench the fire of “fogo selvagem” pemphigus foliaceus." Frontiers in immunology 10 (2019): 2585.
-
Wymann, Sandra, et al. "A novel soluble complement receptor 1 fragment with enhanced therapeutic potential." Journal of Biological Chemistry 296 (2021).
-
Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Illustrated potential influence of Knop blood group CR1 variations and circulating soluble CR1 in the susceptibility to endemic pemphigus foliaceus.1, 3
Fig.1 Illustrated potential influence of Knop blood group CR1 variations and circulating soluble CR1 in the susceptibility to endemic pemphigus foliaceus.1, 3
 Fig.2 Affinity comparison of truncated human CR1 versus CR1 to human complement components C3b and C4b.2, 3
Fig.2 Affinity comparison of truncated human CR1 versus CR1 to human complement components C3b and C4b.2, 3
