Product List Background Factor B Functional Service
Background
Complement Factor B is a highly specific serine protease that is tightly regulated. The proenzyme factor B is made up of three N-terminal complement control protein (CCP) domains and connected via a 45-residue linker to a VWA domain and a C-terminal serine protease (SP) domain, which carries the catalytic center. Fragment Bb contains the VWA and SP domains, fragment Ba contains the CCP1 through CCP3 and the linker.
The activate process of Factor B has several steps: first, it binds to surface-bound C3b or its fluid-phase counterpart C3(H2O); second, it is cleaved into fragments Ba (residues 1-234) and Bb (residues 235-739) via factor D; third, fragment Ba dissociates from the complex, leaving behind the alternative pathway C3 convertase complex C3b-Bb, which cleaves C3 into C3a and C3b. The C3b-Bb complex is very unstable. Besides, a similar C3 convertase complex is generated upon activation of the classical (antibody-mediated) and lectin-binding pathways, made up of C4 and C2, which are homologous to C3 and factor B, respectively. After activated, Factor B catalyzes the central amplification step of complement activation to initiate inflammatory responses, cell lysis, phagocytosis, and B-cell stimulation.
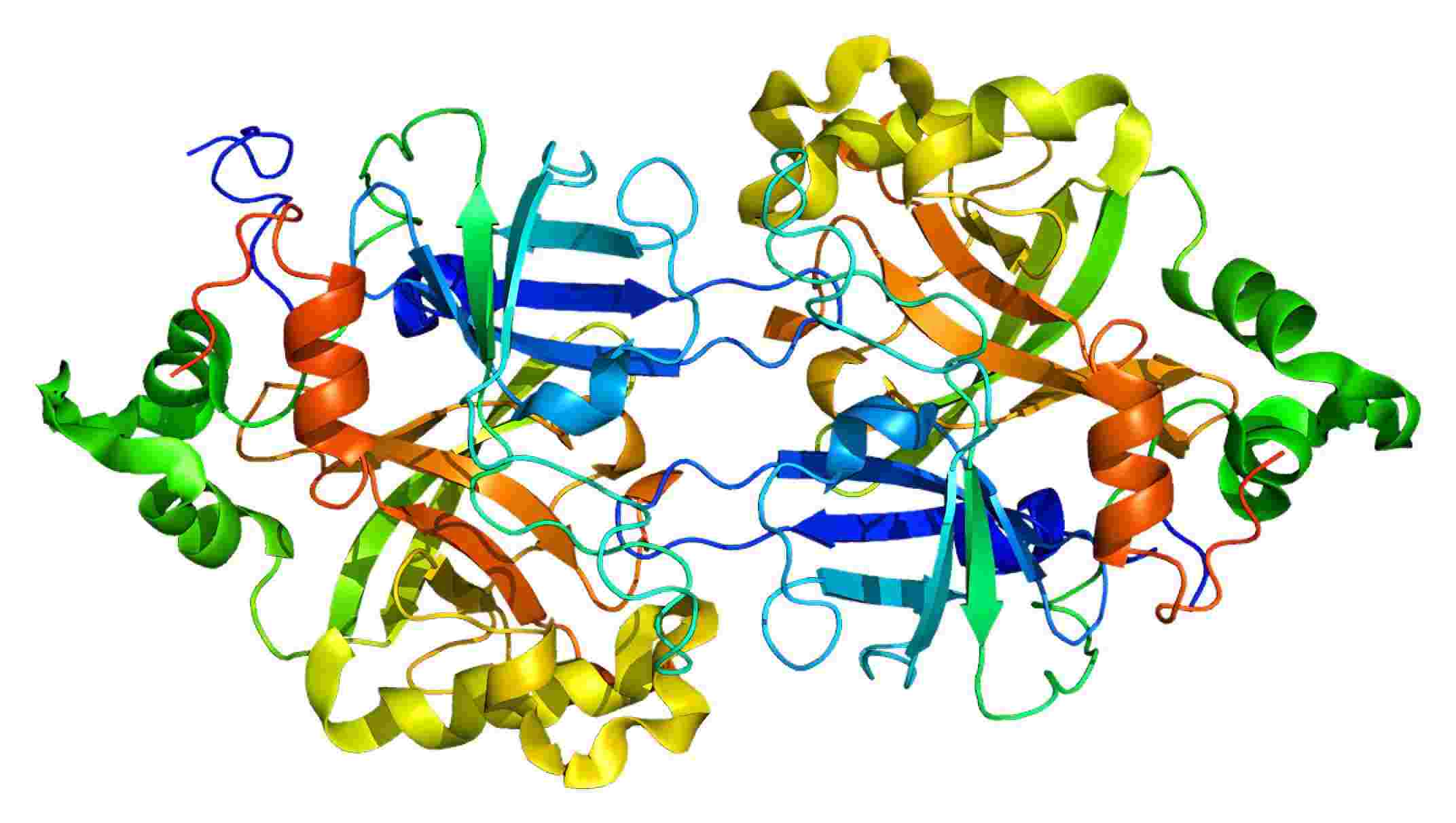 Fig.1 Structure of Factor B. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.1 Structure of Factor B. Distributed under CC BY-SA 3.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Factor B Functional Service
Creative Biolabs provides a comprehensive range of Factor B-related products, encompassing anti-Factor B monoclonal/polyclonal Antibodies, complement Factor B ELISA Assay Kits, and complement Factor B Proteins, Peptides, Lysates, and Vectors. These products are essential for studying Factor B's role in the alternative complement pathway, including its activation, regulation, and involvement in immune response. They are widely used in research on inflammation, immune complex diseases, and complement-related pathologies.
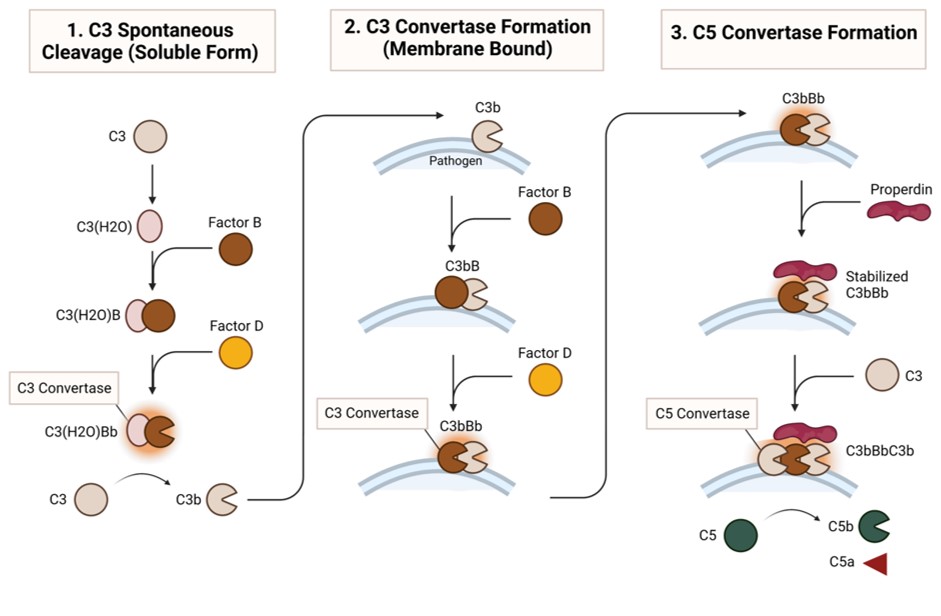 Fig.2 Factor B in initiation of the alternative complement system. Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Fig.2 Factor B in initiation of the alternative complement system. Distributed under CC BY-SA 4.0, from Wiki, without modification.
Research on complement Factor B functional testing has focused on evaluating its role in immune responses using various experimental tools. And it typically focuses on its interaction with complement C3 and its activation by the C3 convertase complex. Purified proteins are usually used to assess the kinetics of Factor B binding and cleavage. ELISA kits are commonly used to quantify Factor B levels and detect their interaction with specific antibodies or other complement proteins. Lysates, which contain native or recombinant Factor B, help study its molecular function in cellular contexts. Factor B vectors are used for transfecting into cells for complement Factor B expression. Moreover, genetic studies on Factor B-deficient mice or human samples help elucidate its involvement in various diseases, such as autoimmune disorders and age-related macular degeneration.
For instance, the functional characterization of anti-Factor B antibodies has demonstrated their ability to enhance alternative pathway C3 convertase activity in vitro, confirming their pathogenic effect in acute postinfectious GN. Besides, crucial antibody binding sites on Factor B have been identified, including one correlated to disease severity.
Creative Biolabs provides specialized Factor B-related services, including Factor B binding assays and a range of additional functional tests, designed to support our clients in clinical research and scientific applications.


 Datasheet
Datasheet Fig.1 Structure of Factor B.
Fig.1 Structure of Factor B. Fig.2 Factor B in initiation of the alternative complement system.
Fig.2 Factor B in initiation of the alternative complement system. 