Chemoenzymatic Labeling with N-Myristoyltransferase
Chemoenzymes have emerged as a powerful tool for the selective labeling and conjugation of target proteins. This technique enables the precise labeling of proteins at specific sites, streamlining the workflows without the need for extensive pre-purification steps. Chemoenzymatic labeling allows proteins to remain in their naturally expressed volumes for an extended period, preserving their functional integrity. Following conjugation, the labeled proteins can be easily isolated while maintaining their active state. N-myristoyltransferase (NMT), a eukaryotic enzyme, has great promise for for bioconjugation applications. NMT possesses an ability to selectively conjugate myristic acid (Myr), in its active form of Myr-CoA, to the N-terminal glycine of target proteins. This targeted modification is facilitated by the recognition of a short peptide sequence, typically (Met)GXXS/TXXX. NMT has desirable properties, including (1) N-terminal specificity for proteins; (2) the ability to accept various analogs of Myr (e.g., ketones-, azide-, alkyne-, sulfur-, and phenyl-modified fatty acids); and (4) orthogonality of target proteins in prokaryotic expression systems.
The following describes the selective labeling of calmodulin (CaM) using NMT and its subsequent conjugation to gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), aiming to help researchers further the understanding of chemoenzymatic labeling methods.
Disclaimer
The procedures outlined in this document are for reference only. Creative Biolabs makes no assurances or warranties regarding the outcomes that may result from the customer's implementation of this guideline.
Materials
 Co-expression and Tagging by 12-Azidododecanoic Acid (12-ADA)
Co-expression and Tagging by 12-Azidododecanoic Acid (12-ADA)
- Bacterial cells (BL21(DE3)).
- Plasmid 1 (encoding the modifying enzymes NMT and methionyl aminopeptidase (metAP))
- Plasmid 2 (CaM engineered to carry an NMT recognition sequence)
- Kanamycin.
- Ampicillin.
- LB agar plates (supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin and 100 μg/mL ampicillin).
- LB media (liquid broth, supplemented with 50 μg/mL kanamycin and 100 μg/mL ampicillin immediately before inoculation).
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS).
- Isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG).
- Myristic acid stock solution (0.5 M in DMSO).
- 12-ADA stock solution (0.5 M in DMSO).
- Centrifuge tubes.
 Extraction of 12-ADA CaM
Extraction of 12-ADA CaM
- Lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 0.5 mM EDTA, 0.5 mM EGTA, 10 mM KCl, 1 mg/mL lysozyme, and 10 units of deoxyribonuclease (DNase)).
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (PIC).
 Conjugation of 12-ADA CaM to AuNP by Click Chemistry
Conjugation of 12-ADA CaM to AuNP by Click Chemistry
- 100 nm NHS-activated AuNP (NHS-AuNP) conjugation kit.
- Alkyne-PEG4-amine crosslinker (0.5 M in DMSO).
- HEPES buffer (pH 7.4, 20 mM).
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA, 2 mg/mL in HEPES).
- Sodium ascorbate.
- CuSO4.
- Iodoacetamide.
- Tris-hydroxypropyltriazolylmethylamine (THPTA).
- Aminoguanidine hydrochloride.
- Tube-O-DIALYZER tubes (1,000 Da MWCO).
- Beaker.
Methods
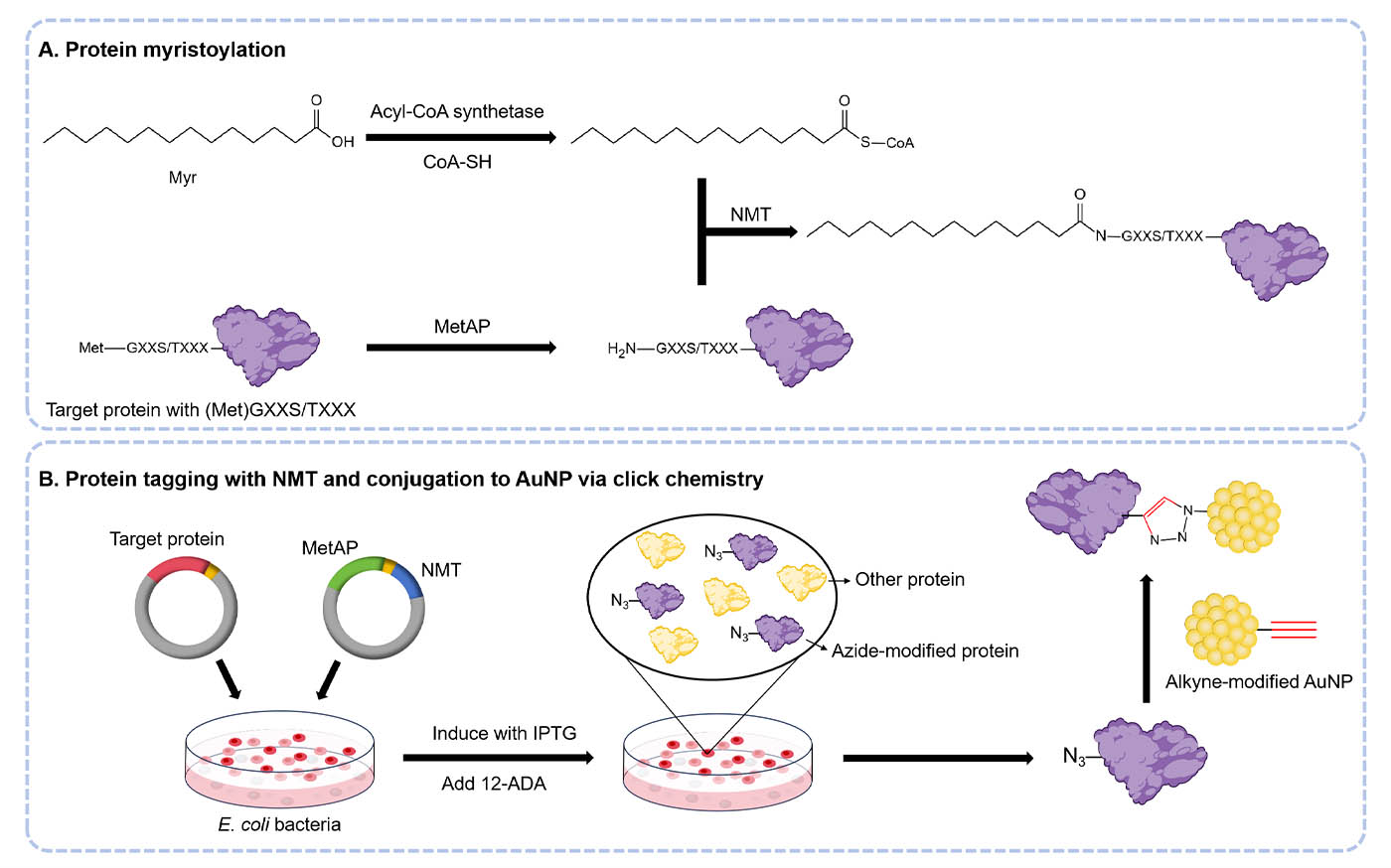
 Co-expression and Tagging by 12-ADA
Co-expression and Tagging by 12-ADA
- Transform bacterial cells (BL21(DE3)) following the instructions of the manufacturer by plasmid 1 and plasmid 2. Plate on LB agar plates (with kanamycin and ampicillin) to select colonies that have successfully incorporated both plasmids. Incubate the plates overnight at 37°C.
- Select a single colony and inoculate 5 ~ 10 mL LB medium (supplemented with both 50 μg/mL kanamycin and 100 μg/mL ampicillin before inoculation). Culture overnight in an orbital shaker maintained at 250 rpm under 37°C.
- Place the overnight culture (5 ~ 10 mL) into a fresh sterile LB (500 mL, with kanamycin and ampicillin) and grow until the optical density at 600 nm (OD600) reaches 0.8 - 1.
- Add IPTG (1 mM in water) to the culture to induce protein expression, and simultaneously supplement with 12-ADA or myristic acid (as a negative control) at a final concentration of 500 μM. Then, incubate the culture for 3-4 hours.
- To harvest the cells, centrifuge the culture at 12,000 × g for 15 minutes under 4°C.
- Add ice-cold PBS (10mL) to resuspend the pellet, centrifuge again, and discard the wash solution (A large culture can be aliquoted into several smaller pellets, ensuring that each pellet contains a volume between 100 to 250 mL).
- Store the cell pellet at -80°C.
 Extraction of 12-ADA CaM
Extraction of 12-ADA CaM
- Add 5 mL lysis buffer (with PIC) per gram of pellet to resuspend the cells, and lyse them by sonication.
- Centrifuge the lysate at 12,500 × g for 20 minutes under 4°C, and retain the supernatant to collect the soluble proteins.
- Detect the protein concentration in the clarified lysate and dilute it to 1-10 mg/mL with lysis buffer.
 Conjugation of 12-ADA CaM to AuNP by Click Chemistry
Conjugation of 12-ADA CaM to AuNP by Click Chemistry
- Mix 48 μL alkyne-PEG4-amine crosslinker with 60 μL AuNP reaction buffer in a centrifuge tube (1.5 mL).
- Add the mixture (90 μL) into a vial containing NHS-AuNPs, and then use a pipette to gently move the particles up and down until all aggregates are removed. Then, stir at room temperature for 4 hours.
- Add the quencher solution (10 μL) and pipet the mixture up and down to stop the reaction.
- Split the mixture into 3 equal parts (33.3 μL per tube).
- Centrifuge the tubes at 200 x g for 20 minutes to settle the alkyne-modified AuNPs. Remove the supernatant (recording the volume) and retain the pellets.
- Add the BSA solution (10 μL) into all tubes and rotate them end-over-end at room temperature for 30 minutes.
- To settle the alkyne-modified AuNPs again, centrifuge the vials at 200 x g for 20 minutes. Then, remove the supernatant and record its volume.
- Centrifuge the vials at 200 × g for 20 min to settle the alkyne-modified AuNPs again and remove the supernatant (recording the volume).
- Add click reagents (3.33 μL sodium ascorbate (400 mM in water), 5.33 μL CuSO4 (25 mM in water), 6.66 μL iodoacetamide (0.5 M in water), 13.33 μL THPTA (50 mM in water), and 13.33 μL aminoguanidine hydrochloride (pH 7.0, 100 mM in water) solutions) and 10 μL clarified lysate (containing 12-ADA-CaM protein) to a tube with the AuNPs. Include negative controls like the non-azide-modified protein.
- Incubate overnight at 4°C under continuous stirring to bioconjugate the 12-ADA-CaM to the alkyne-modified AuNPs.
- Place the conjugates into the Tube-O-DIALYZER tube. Subsequently, immerse the tube in a beaker with HEPES buffer (pH 7.4, 20 mM).
- Dialyze overnight at 4°C under continuous stirring.
- Transfer the dialyzed sample to centrifuge tubes. Then, adjust the sample to 100 μL with AuNP reaction buffer.
Notes
- Procedures should include appropriate negative controls, such as Myr-labeled lysate of the target protein and non-azide-modified protein.
- Protein expression time (from induction by IPTG to harvest) needs to be optimized for different target proteins.
- Optimization of lysis buffer conditions for different target proteins helps to ensure successful extraction and preservation of the natural structure and function of proteins.
- The reagent dosage for the click reaction given in the above procedure is based on three equal parts of AuNPs to save valuable reagents.
- Tracking the exact volume removed during the washing steps is important for downstream applications (e.g., protein activity) as well as for the reproducibility and traceability of experiments.
Recommended products
