Types Structures Signaling Mechanisms Functions Assay Therapeutic Targeting
Anaphylatoxins, including C3a, C4a, and C5a, are bioactive peptides derived from the complement system, playing crucial roles in the innate immune response. The primary anaphylatoxins, C3a, C4a, and C5a, exert their actions through specific anaphylatoxin receptors: C3a receptor (C3aR) and C5a receptors (C5aR1 and C5aR2). Understanding these receptors is critical in comprehending their roles in health and disease. Creative Biolabs explores their structural intricacies, signaling cascades, pathophysiological roles, and emerging therapeutic strategies targeting these receptors in inflammatory/autoimmune disorders.
Types of Anaphylatoxin Receptors
Anaphylatoxins exert their biological effects through specific receptors known as anaphylatoxin receptors. The three primary receptors are:
-
C3aR: C3aR is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) primarily expressed on immune cells such as mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. Its activation leads to various biological effects, including chemotaxis and the release of inflammatory mediators.
-
C4aR: Unlike C3aR and C5aR, C4aR is less well-characterized and is considered to have a weaker biological impact. However, it may still play a role in modulating immune responses at the local tissue level.
-
C5aR1 and C5aR2
-
C5aR1 is a well-characterized GPCR associated with robust pro-inflammatory responses. It is widely distributed on immune cells and tissues, and its activation leads to increased phagocytosis, cytokine release, and enhanced vascular permeability.
-
C5aR2, although it shares some structural similarities with C5aR1, has distinct functions. It may act as a regulatory receptor, modulating the inflammatory response initiated by C5aR1. The balance between C5aR1 and C5aR2 signaling is crucial for maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive inflammation.
Structural Architecture of Anaphylatoxin Receptors
Anaphylatoxin receptors (C3aR and C5aR1/C5aR2) are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) with specialized structural adaptations for recognizing complement-derived peptides C3a and C5a. Their architecture balances conserved GPCR motifs with domain-specific features that enable precise ligand binding and signaling.
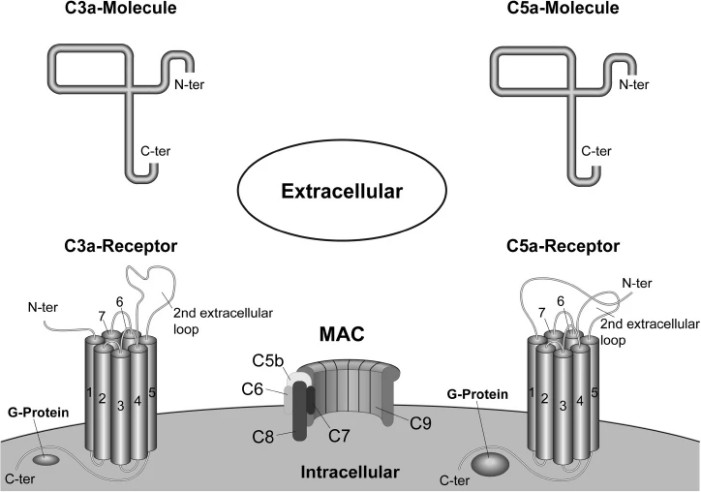 Fig. 1 The two seven-transmembrane-spanning G-protein-coupled receptors C3aR and C5aR.1,3
Fig. 1 The two seven-transmembrane-spanning G-protein-coupled receptors C3aR and C5aR.1,3
Core Structural Features
-
All anaphylatoxin receptors belong to Class A GPCRs, characterized by a seven-transmembrane α-helical bundle (TM1-TM7).
-
The N-terminal extracellular domain (ECD) and three extracellular loops (ECLs) form ligand-binding pockets, while intracellular loops couple to Gαi/o proteins.
-
C5aR1: Binds C5a via a two-site mechanism. The receptor's N-terminal ECD interacts with the disulfide-stabilized core of C5a (residues 1–63), while the C-terminal helical tail of C5a (residues 65–74, including the MQLGR motif) engages ECL2 and ECL3.
-
C3aR: Recognizes C3a through a conserved ECD disulfide network (Cys21–Cys47, Cys22–Cys54, Cys34–Cys55), stabilizing ligand orientation.
Key Structural Techniques
-
NMR/X-ray crystallography
-
Cryo-EM
Signaling Mechanisms of Anaphylatoxin Receptors
Anaphylatoxin receptors orchestrate diverse signaling cascades beyond their canonical chemotactic roles, modulating immune cell activation, transcriptional reprogramming, and inflammatory cross-talk. These pathways are finely tuned by receptor-ligand dynamics, cellular context, and signaling bias.
Table 1 Anaphylatoxin receptors activate pleiotropic pathways through Gαi/o and β-arrestin coupling.
|
Pathway
|
C3aR Effects
|
C5aR1 Effects
|
|
Gαi/o
|
↓ cAMP, ERK activation
|
↑ Chemotaxis, ROS production
|
|
β-Arrestin
|
Receptor internalization
|
NF-κB/MAPK activation
|
|
Cross-talk
|
Synergizes with TLR4
|
Amplifies NLRP3 inflammasome
|
G Protein-Coupled Signaling Networks
Both receptors primarily signal through Gαi/o proteins, but their downstream effectors diverge.
C3aR activation
-
Immediate effects: ↓ cAMP via Gαi, ↑ Ca²⁺ influx through L-type channels (blocked by nifedipine).
-
Kinase activation: PI3K/Akt axis drives FOXO1 phosphorylation, promoting anti-inflammatory gene expression (e.g., FoxP3 in regulatory T cells).
C5aR1 activation
-
ROS production: Gαi-mediated NADPH oxidase activation fuels oxidative bursts in neutrophils/macrophages.
-
MAPK/ERK: Sustained ERK1/2 phosphorylation enhances pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion (TNF-α, IL-6).
β-Arrestin-Biased Signaling
Table 2 Ligand-specific conformational changes enable pathway bias.
|
Receptor
|
Biased Pathway
|
Functional Outcome
|
|
C3aR
|
β-Arrestin-1 Coupling
|
Receptor internalization, NF-κB suppression
|
|
C5aR1
|
β-Arrestin-2 Scaffold
|
NLRP3 inflammasome priming, IL-1β maturation
|
Functions of Anaphylatoxin Receptors
Anaphylatoxin receptors (C3aR, C5aR1, C5aR2) are pivotal mediators of immune responses, bridging innate and adaptive immunity through their interactions with complement fragments C3a and C5a. Their functions span inflammation, immune cell regulation, and tissue homeostasis, with dual roles in protection and pathology.
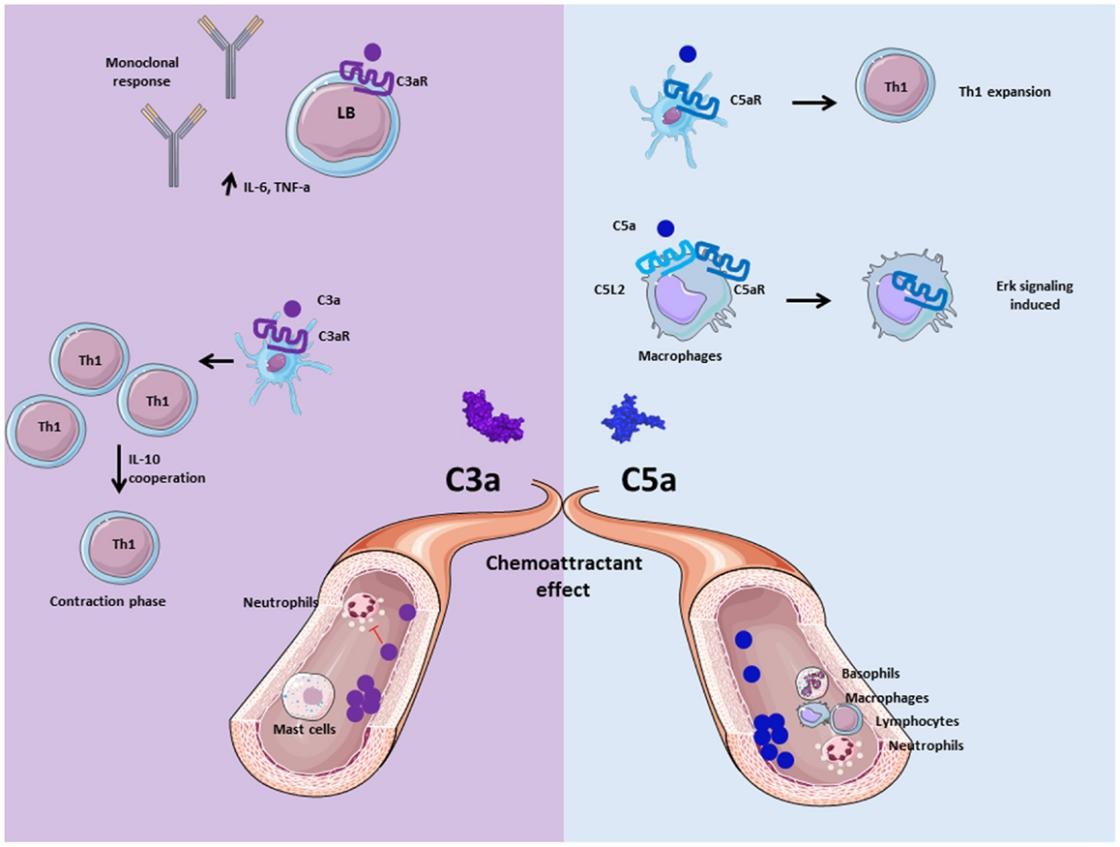 Fig. 2 Role of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a.2,4
Fig. 2 Role of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a.2,4
Protective Roles in Immune Homeostasis
Tolerance maintenance
-
C3aR stabilizes regulatory T cells (Tregs) by activating STAT5, preserving FoxP3 expression to suppress autoimmunity.
-
C5aR2 limits C5aR1-driven inflammation by scavenging excess C5a and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome assembly in dendritic cells (DCs).
Pathogen clearance
-
C3a enhances macrophage phagocytosis of Listeria monocytogenes via PI3K/Akt, reducing bacterial load by 70% in murine models.
-
C5a primes neutrophils for ROS-mediated pathogen killing while promoting DC maturation for antigen presentation.
Anti-inflammatory modulation
-
Low-dose C3a suppresses TNF-α/IL-6 in non-adherent monocytes, while C5aR2-deficient mice exhibit exacerbated Th17 responses in asthma.
Role of Anaphylatoxin Receptors in Disease
Aberrant activation of anaphylatoxin receptors has been implicated in various pathological conditions, including:
Table 3 Pathogenic triggers in autoimmunity and allergy.
|
Receptor
|
Mechanism
|
Disease Link
|
|
C3aR
|
↑ IL-1β via NLRP3 inflammasome
|
Lupus nephritis
|
|
C5aR1
|
↑ Neutrophil priming/ROS
|
ANCA vasculitis
|
|
C5aR2
|
↓ Treg suppression of Th1/Th17
|
Allergic asthma
|
|
C5aR1
|
Drives IL-23/IL-17 axis in DCs
|
Allergic asthma
|
|
C3aR
|
Synergizes with TLR4 to enhance Th2 polarization
|
Allergic asthma
|
Anaphylatoxin receptor-ligand binding assays are valuable for understanding the molecular interactions between receptors and their ligands. With advanced platforms and standard programs, Creative Biolabs provides rapid and customized complement receptor-ligand binding assays to customers worldwide.
This assay is a laboratory test used to assess the interaction between complement receptors and their ligands, which can be performed by radioisotope labeling, receptor-ligand enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunoprecipitation, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
Therapeutic Targeting of Anaphylatoxin Receptors
C3aR, C5aR1, C5aR2 have become critical targets for therapeutic interventions in inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Their role in mediating immune responses makes them attractive candidates for precision medicine approaches. Several approaches are under investigation.
Table 4 Mechanisms of different anaphylatoxins in disease.
|
Disease
|
Mechanism of Action
|
|
C5a Antagonists
|
C5a antagonists, such as Avacopan, have shown promise in clinical trials for treating conditions like ANCA-associated vasculitis. By blocking C5a receptor signaling, these agents aim to reduce inflammation and tissue damage.
|
|
Monoclonal Antibodies
|
Monoclonal antibodies targeting specific anaphylatoxins or their receptors offer a more targeted therapeutic approach. For instance, anti-C5 antibodies can effectively inhibit the effects of C5a, reducing excessive inflammation.
|
|
Small Molecule Inhibitors
|
Research into small molecule inhibitors of C5aR1 and C5aR2 is ongoing. These agents could provide a new avenue for modulating immune responses in various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
|
As structural insights refine drug design, Creative Biolabs continues to help pioneer the next generation of inhibitors (small molecules, mAb, peptide mimetics). We offer solutions for anaphylatoxin-related research including:
If you want more information, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Ehrnthaller, Christian, et al. "New insights of an old defense system: structure, function, and clinical relevance of the complement system." Molecular medicine 17 (2011): 317-329. https://doi.org/10.2119/molmed.2010.00149
-
Merle, Nicolas S., et al. "Complement system part II: role in immunity." Frontiers in immunology 6 (2015): 257. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00257
-
under Open Access license CC BY 2.0, without modification.
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 The two seven-transmembrane-spanning G-protein-coupled receptors C3aR and C5aR.1,3
Fig. 1 The two seven-transmembrane-spanning G-protein-coupled receptors C3aR and C5aR.1,3
 Fig. 2 Role of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a.2,4
Fig. 2 Role of anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a.2,4