C3a Structure C3a Functions C3a Test C3a Deficiency Therapeutic Target
Complement component C3a is a key effector of the complement system and plays a dual role in immune regulation, balancing pro- and anti-inflammatory responses. This 77-residue anaphylatoxin is produced by proteolytic cleavage of C3 and binds to the G-protein-coupled receptor, C3aR, to orchestrate a variety of immune pathways critical for host defense, tissue homeostasis, and disease progression.
Structure of C3a
C3a is a small, highly cationic protein derived from the proteolytic cleavage of the alpha chain of C3, a key molecule in the complement system. Its unique structural attributes enable it to function as an anaphylatoxin, mediating immune responses and inflammation.
C3a arises from enzymatic cleavage of the alpha chain of complement component C3 during activation by C3 convertase. This cleavage also generates other fragments such as:
-
C3b: A large opsonin fragment (~176 kDa) that facilitates phagocytosis and assembly of additional complement components.
-
iC3b: A derivative of C3b involved in immune regulation but lacking convertase activity.
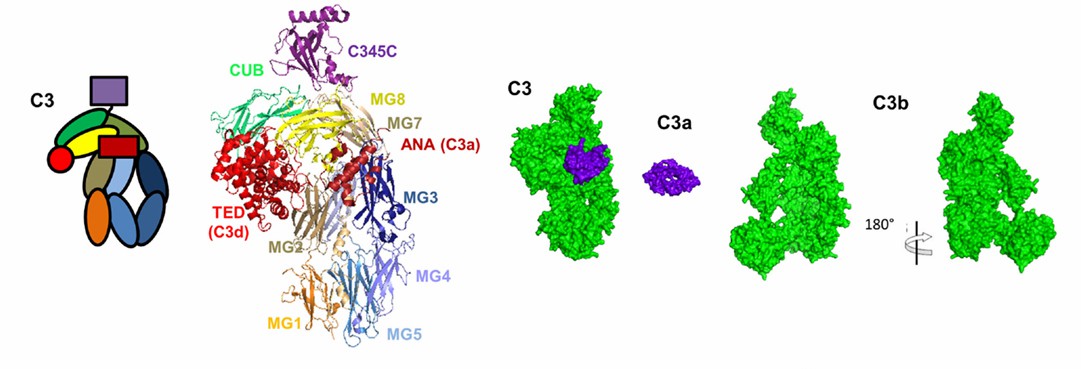 Fig. 1 Structure and domain organization of the central complement component C3 and its cleavage fragments C3b and C3a.1,2
Fig. 1 Structure and domain organization of the central complement component C3 and its cleavage fragments C3b and C3a.1,2
C3a is composed of a single polypeptide chain consisting of 77 amino acid residues, with a molecular weight of approximately 9 kDa. The protein is highly cationic due to its amino acid composition, which includes an unusually basic C-terminal region critical for interaction with cellular receptors. Notably, C3a lacks tryptophan and carbohydrate residues, which distinguishes it from other complement components.
-
C-terminal region: The highly cationic COOH-terminal end plays a pivotal role in binding to the C3aR. This interaction initiates intracellular signaling cascades that mediate immune responses such as chemotaxis and mast cell degranulation.
-
Disulfide knot: The three disulfide bonds stabilize the protein's overall structure and ensure its functional integrity during receptor binding.
-
Flexible N-terminal helix: This region contributes to the dynamic conformational changes required for receptor engagement.
C3a binds specifically to the C3aR, composed of 482 amino acids. The binding of C3a to C3aR triggers downstream signaling pathways that regulate immune responses, including T cell activation, angiogenesis stimulation, and macrophage activation.
Biological Functions of C3a
C3a exerts its effects via C3aR, triggering intracellular signaling cascades that modulate:
Table 1 Biological functions of C3a.
|
Functional Roles
|
Mechanisms
|
|
Innate immunity
|
Enhances vascular permeability, mast cell degranulation, neutrophil respiratory bursts, and macrophage activation.
|
|
Adaptive immunity
|
Regulates T cell differentiation, B cell cytokine production (e.g., IL-6, TNF-α), and dendritic cell-mediated Treg expansion.
|
|
Anti-inflammatory modulation
|
Counters C5a-driven neutrophilic inflammation by suppressing neutrophil migration and degranulation.
|
C3a: Proinflammatory vs. Anti-Inflammatory Roles
C3a is traditionally associated with proinflammatory activity.
-
Chemotaxis: Recruits eosinophils, mast cells, and basophils to sites of infection or injury, enhancing immune cell infiltration.
-
Cytokine and chemokine production: Stimulates release of proinflammatory mediators such as TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 from immune cells.
-
Leukotriene synthesis: Activates basophils to produce leukotrienes, amplifying allergic and inflammatory responses.
-
Respiratory burst: Enhances reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in phagocytes, aiding microbial killing.
-
Platelet aggregation: Contributes to thromboinflammatory processes by activating platelets.
Emerging evidence challenges the dogma of C3a as strictly proinflammatory. C3a paradoxically modulates immune responses to prevent excessive inflammation.
-
Cytokine suppression: Attenuates TNF-α and IL-1β release in LPS-primed cells, limiting systemic inflammation.
-
Immune tolerance: Promotes regulatory T cell differentiation and dendritic cell-mediated immunosuppression.
-
Neutrophil regulation: Counters C5a-driven neutrophilic inflammation by reducing migration and degranulation.
The complement C3a functional assay is a laboratory method crafted to assess the activity and functionality of the C3a component within the complement system across diverse samples, such as human serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, cell lysates, and cell culture supernatants. This evaluation can be performed using hemolytic assays and solid-phase sandwich ELISA techniques.
Creative Biolabs delivers high-quality, tailored functional assays for complement C3a, harnessing advanced technologies and profound scientific expertise to aid clients in progressing complement-based therapeutic developments.
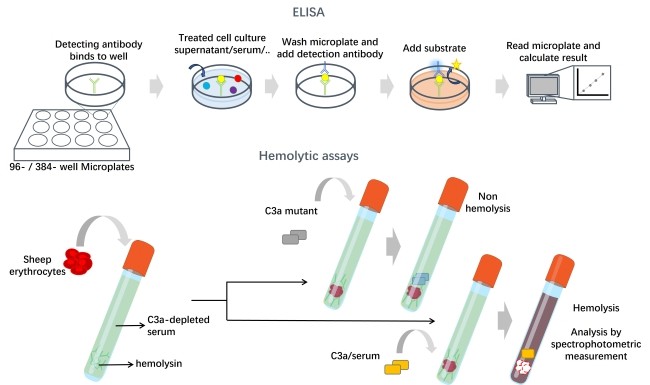 Fig. 2 Workflow of complement C3a functional test.
Fig. 2 Workflow of complement C3a functional test.
Elevated C3a is usually associated with active lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and glomerulonephritis and may guide diagnosis and monitoring. The test may be used in research applications.
-
To study the role of C3a in immune dysregulation, nerve repair, and antimicrobial defense.
-
To evaluate drug candidates targeting C3a-C3aR signaling in preclinical models.
C3a and Disease Pathology
C3a plays a complex and context-dependent role in disease pathology, acting as both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediator depending on the specific condition, disease stage, and cell types involved.
Table 2 Disease-specific roles of C3a.
|
Diseases
|
Roles
|
|
Atherosclerosis
|
-
C3aR deficiency enhances local inflammatory responses in atherosclerotic lesions, suggesting a protective role for C3a signaling.
-
C3a/C3aR axis suppresses systemic and local proinflammatory responses in atherosclerosis.
|
|
Kidney diseases
|
-
C3aR expression is enhanced in various kidney diseases, with increased C3a levels in plasma and urine correlating with disease progression.
-
The C3a/C3aR pathway generally promotes glomerular and tubulointerstitial disease progression.
-
In lupus nephritis, C3aR's role is controversial, with some studies suggesting protective effects and others indicating pathogenic involvement.
|
|
Neurological disorders
|
-
C3aR antagonism alleviates tau pathology and behavioral deficits in a mouse model of tauopathy, suggesting a role in neurodegenerative diseases.
|
C3a is both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediator, and thus requires a nuanced approach to understand its role in disease pathology. This complexity presents challenges and opportunities for the development of targeted therapies for various inflammatory and autoimmune diseases.
C3a as a Therapeutic Target
Innovative strategies currently available to regulate C3a signaling include:
-
C3aR antagonists - Block pro-inflammatory pathways, used in sepsis and acute lung injury.
-
Recombinant C3a agonists - Enhance anti-inflammatory response, applications in autoimmune diseases, transplant rejection.
-
Complement inhibitors - Attenuate C3a-mediated tissue damage, used in CAP.
The tools and innovations we can adopt to advance C3a research.
-
Structural biology: Cryo-electron microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations to map C3a-C3aR interactions.
-
Genetically engineered models: C3aR knockout mice are used to dissect signaling pathways in vivo.
-
High-throughput screening: Identification of small molecule modulators with biased agonism.
As research reveals the paradoxical role of C3a, precise modulation of C3a signaling holds promise for the treatment of inflammatory, infectious, and degenerative diseases. Creative Biolabs offers customized solutions for C3a research:
If you want more information, please feel free to contact us.
References
-
Merle, Nicolas S., et al. "Complement system part I–molecular mechanisms of activation and regulation." Frontiers in immunology 6 (2015): 262. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00262
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.

 Fig. 1 Structure and domain organization of the central complement component C3 and its cleavage fragments C3b and C3a.1,2
Fig. 1 Structure and domain organization of the central complement component C3 and its cleavage fragments C3b and C3a.1,2
 Fig. 2 Workflow of complement C3a functional test.
Fig. 2 Workflow of complement C3a functional test.