C1s Structure C1s Functions C1s Assays C1s in Disease Therapeutic Target
Complement component C1s is a serine protease that occupies a pivotal role in the classical complement pathway. As a key subunit of the C1 complex (C1qr2s2), C1s orchestrates critical enzymatic processes that amplify immune responses against pathogens while maintaining strict specificity to avoid host tissue damage.
Structure of C1s
C1s is a modular serine protease with a complex domain organization that underpins its role in the classical pathway. Its structure enables precise substrate recognition, enzymatic activity, and interactions with other components of the C1 complex (C1q and C1r).
C1s comprises five distinct domains arranged in a linear sequence:
-
CUB1 domain: Involved in protein-protein interactions, particularly with C1r and C1q.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF)-like domain: Contributes to structural stability and facilitates interactions with adjacent domains.
-
CUB2 domain: Plays a role in binding to collagen-like regions of C1q via Ca²⁺-mediated interactions.
-
CCP1: Facilitates substrate recognition and binding.
-
CCP2: Directly interacts with the serine protease (SP) domain to modulate enzymatic activity.
-
Chymotrypsin-like Serine Protease (SP) domain: The catalytic core responsible for cleaving C4 and C2.
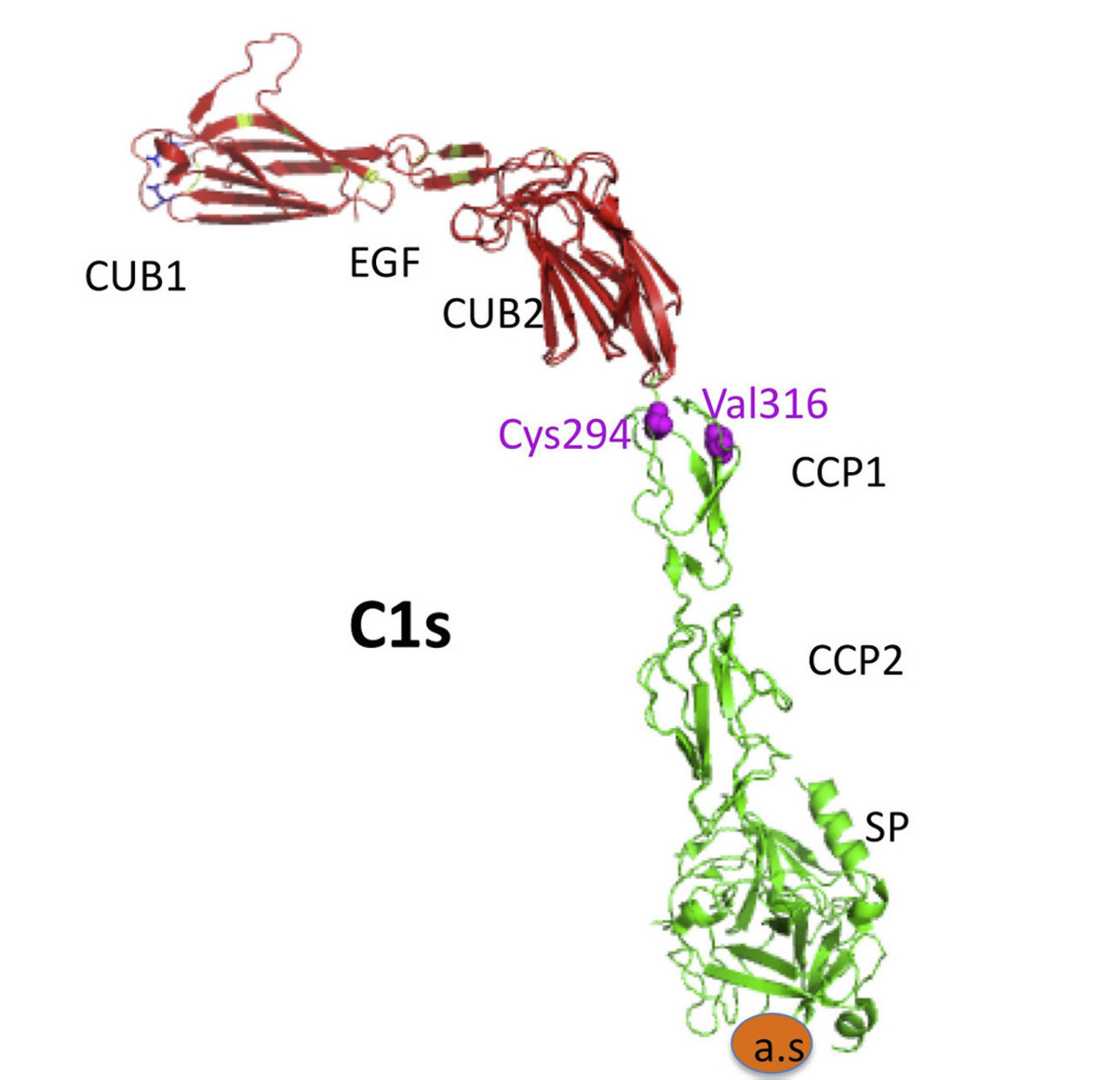 Fig. 1 Structure of C1s.1,3
Fig. 1 Structure of C1s.1,3
Key structural features:
-
CUB1-EGF-CUB2 interface: This interaction is stabilized by Ca²⁺ ions at the interface, ensuring specificity and structural rigidity.
-
CCP2-SP domain assembly: This arrangement restricts access to subsidiary substrate-binding sites in the SP domain, ensuring narrow specificity for C4 and C2.
-
Flexibility and conformational changes: Upon binding to C1q, the C1r-C1s tetramer adopts a more compact conformation, with the C1r-C1s dimers positioned centrally and C1q collagen stems arranged peripherally.
By understanding these structural nuances, researchers can develop targeted therapies to modulate C1s activity in complement-mediated disorders.
Functional Roles of C1s in Complement Activation
C1s is a serine protease that executes critical enzymatic steps in the classical pathway, initiating immune responses against pathogens and immune complexes. Its activation and substrate cleavage are tightly regulated to balance immune defense with host protection.
C1s is activated downstream of C1q binding to activators like antibody-antigen complexes. The process involves:
Table 1 C1s in complement activation.
|
Function
|
Mechanism
|
Description
|
|
Activation Mechanism
|
C1r autoactivation
|
Upon C1q engagement, C1r undergoes autoactivation via intermolecular proteolytic cleavage between neighboring C1 complexes bound to the same surface.
|
|
C1s activation
|
Active C1r cleaves C1s, converting it from a zymogen to an active protease.
|
|
Substrate Cleavage and Cascade Initiation
|
C4 cleavage
|
C1s cleaves C4 into C4a (anaphylatoxin) and C4b (covalent attachment to pathogens).
|
|
C2 cleavage
|
C1s cleaves C2 into C2a (C3 convertase subunit) and C2b (inflammatory mediator).
|
|
Formation of C3 convertase
|
C2b remains noncovalently bound to C4b, stabilizing the C4bC2a complex, which acts as the classical pathway C3 convertase.
|
While primary role of C1s is in the classical pathway, it also cleaves non-complement proteins:
-
MHC I: Modulates T-cell responses.
-
LRP6: Triggers Wnt signaling, influencing cell growth and neuronal connectivity.
-
HMGB1: Reduces autoimmunity by degrading danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs).
C1s Assays
C1s activity can be assessed through multiple experimental approaches, each with distinct advantages and limitations.
Table 2 Multiple experimental approaches for C1s assays.
|
Approaches
|
Principle
|
Protocol
|
Advantages
|
Limitations
|
|
Functional chromogenic assays
|
Measures enzymatic activity via cleavage of synthetic substrates.
|
-
Activation: Inhibit C1-esterase inhibitor (C1-INH) using monospecific antiserum to activate C1s in plasma.
-
Substrate: Use amidolytic chromogenic substrates to detect proteolytic activity.
-
Detection: Quantify substrate cleavage via colorimetric or fluorometric methods.
|
|
-
Cross-reactivity with other proteases (e.g., C1r, MASP2)
|
|
Hemolytic reconstitution assays
|
Restores C1s activity in deficient serum to measure functional recovery.
|
-
Deficient serum: Use C1s-depleted serum (e.g., C1s-Dpl).
-
Reconstitution: Add purified C1s to deficient serum and measure restored hemolytic activity (e.g., CH50 assay).
-
Validation: Confirm specificity by adding purified C1s and observing dose-dependent hemolysis.
|
-
Directly measures the role of C1s in classical pathway activation
|
-
Labor-intensive
-
Requires standardized deficient serum
|
|
C2/C4 cleavage assays
|
Quantifies C1s-mediated cleavage of C2 and C4.
|
-
Substrate preparation: Use purified C2 or C4 proteins.
-
Reaction: Incubate C1s with substrates, then separate products via SDS-PAGE or Western blot.
-
Detection: Identify cleavage products (C2a/C2b, C4a/C4b) using specific antibodies.
|
-
Directly links C1s activity to substrate cleavage
|
-
Semi-quantitative
-
Prone to interference from other proteases
|
|
ELISA for activated C1s
|
Detects activated C1s using conformation-specific antibodies.
|
-
Antibodies: Use polyclonal or monoclonal antibodies targeting activated C1s.
-
Detection: Perform Western blot or sandwich ELISA to quantify activated C1s in samples.
|
-
Specific to activated C1s
-
Avoiding detection of zymogen forms
|
-
Limited commercial availability of validated antibodies
|
|
Pathway-specific functional assays
|
Measures classical pathway activity, indirectly assessing C1s function.
|
-
Immune complexes: Coat microtiter plates with IgM or antigen-antibody complexes.
-
Activation: Add serum, then detect downstream products (e.g., C9) via ELISA.
-
Interpretation: Reduced C9 indicates impaired C1s activity.
|
-
Clinically relevant
-
Widely used
|
-
Does not isolate C1s activity from other components
|
|
LC-MS/MS and Gelatin Zymography
|
Quantifies C1s protein levels or activity via proteomic analysis.
|
-
LC-MS/MS: Identify and quantify C1s in complex samples using mass spectrometry.
-
Gelatin Zymography: Detect proteolytic activity in gels containing gelatin.
|
-
High sensitivity for protein detection
|
-
Does not confirm functional activity
|
These methods provide a robust toolkit for studying C1s in experimental settings, balancing specificity, sensitivity, and practicality.
C1s in Disease and Immunity
C1s plays a pivotal role in both immune defense and disease pathogenesis, making it a critical target for therapeutic intervention and diagnostic biomarker development.
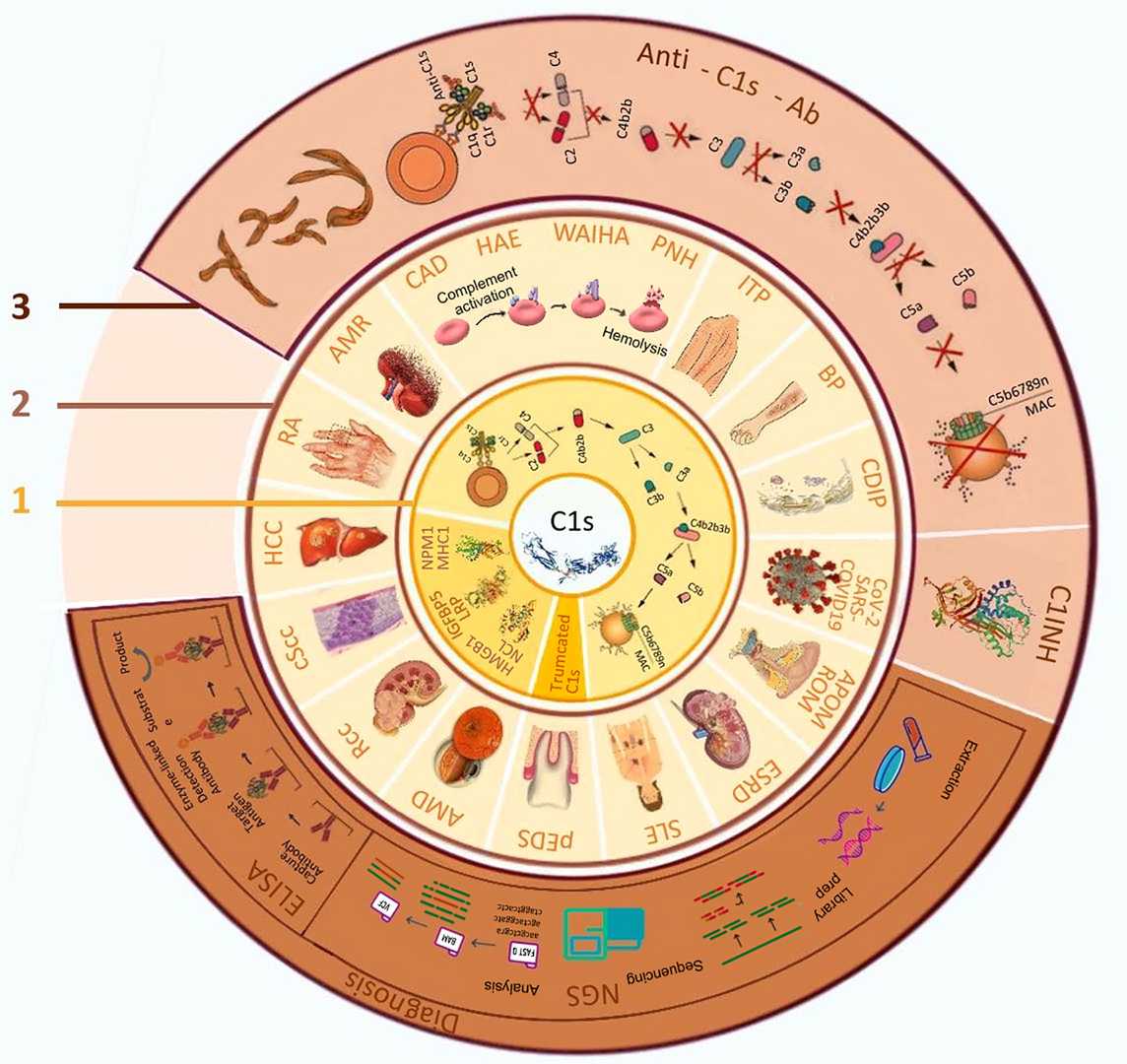 Fig. 2 The biological function of C1s, related diseases and its application in diagnosis and treatment.2,3
Fig. 2 The biological function of C1s, related diseases and its application in diagnosis and treatment.2,3
-
C1s deficiency predisposes to SLE due to impaired immune complex clearance.
-
C1s activation contributes to inflammation and tissue damage, with therapeutic targeting under exploration.
-
C1s modulates T-cell responses and reduces autoimmunity by degrading DAMPs.
Table 3 Clinical implications summary
|
Disease
|
C1s Role
|
Diagnostic Biomarkers
|
|
CAD
|
Initiates hemolysis via C4/C2 cleavage
|
C4, CH50, C3d+ erythrocytes
|
|
SLE
|
Deficiency impairs immune complex clearance
|
Elevated plasma C1s
|
|
RA/Other Autoimmune
|
Drives inflammation via complement activation
|
C4, anti-C1s autoantibodies
|
By leveraging the dual role of C1s in immune activation and tissue regulation, researchers are advancing both diagnostic tools and targeted therapies to address complement-mediated diseases.
C1s as a Therapeutic Target
C1s has emerged as a high-value therapeutic target due to its central role in classical pathway activation and its involvement in diverse pathological conditions.
-
Small-molecule inhibitors: Target the CCP2-SP domain interface or Ca²⁺-dependent interactions to block C1s activity.
-
Monoclonal antibodies
-
Gene therapy and RNA interference: CRISPR-Cas9 and RNAi techniques to modulate C1s expression, offering precision in complement regulation.
-
Combination therapies: Pairing C1s inhibitors with other complement modulators (e.g., C5 inhibitors) for synergistic effects.
C1s is a master regulator of the classical pathway. Its intricate structure, precise enzymatic function, and involvement in disease pathogenesis make it a compelling focus for therapeutic innovation. As research advances, C1s inhibitors may emerge as transformative tools in treating autoimmune disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and complement-mediated inflammation.
For Creative Biolabs, leveraging this knowledge to develop customized solutions for complement system research is important. If you need help with research, please contact our team of experts.
References
-
Kouser, Lubna, et al. "Emerging and novel functions of complement protein C1q." Frontiers in immunology 6 (2015): 317. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00317
-
Ye, Jun, et al. "Complement C1s as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target: Progress and propective." Frontiers in immunology 13 (2022): 1015128. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1015128
-
under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only.
Related Sections:

 Fig. 1 Structure of C1s.1,3
Fig. 1 Structure of C1s.1,3
 Fig. 2 The biological function of C1s, related diseases and its application in diagnosis and treatment.2,3
Fig. 2 The biological function of C1s, related diseases and its application in diagnosis and treatment.2,3