Induced Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Modeling & Pharmacodynamics Service
Animal models are useful if they reproduce all or some of the clinical features of a disease. In systemic lupus erythematosus studies and preclinical tests of new therapeutics, spontaneous mouse models, as well as induced SLE models are commonly used based on different research requirements. Unlike NZB/W or MRL/lpr mouse models, in which genetic factors play a central role, induced mouse models develop lupus due to exposure to certain environmental triggers.
The Pristane-Induced Lupus (PIL) Model
Intraperitoneal injections of pristane (2,6,10,14-tetramethylpentadecane, or TMPD), an isoprenoid alkane found at high concentration in mineral oil, is a standard method to induce systemic lupus with characteristic organ involvement and autoantibodies (auto-abs) in various mouse strains, such as BALB/c and C57BL/6. However, different strains show diverse clinical presentations, suggesting that environment has a considerable importance in lupus. TMPD-treated BALB/c mice, for instance, are characterized by: 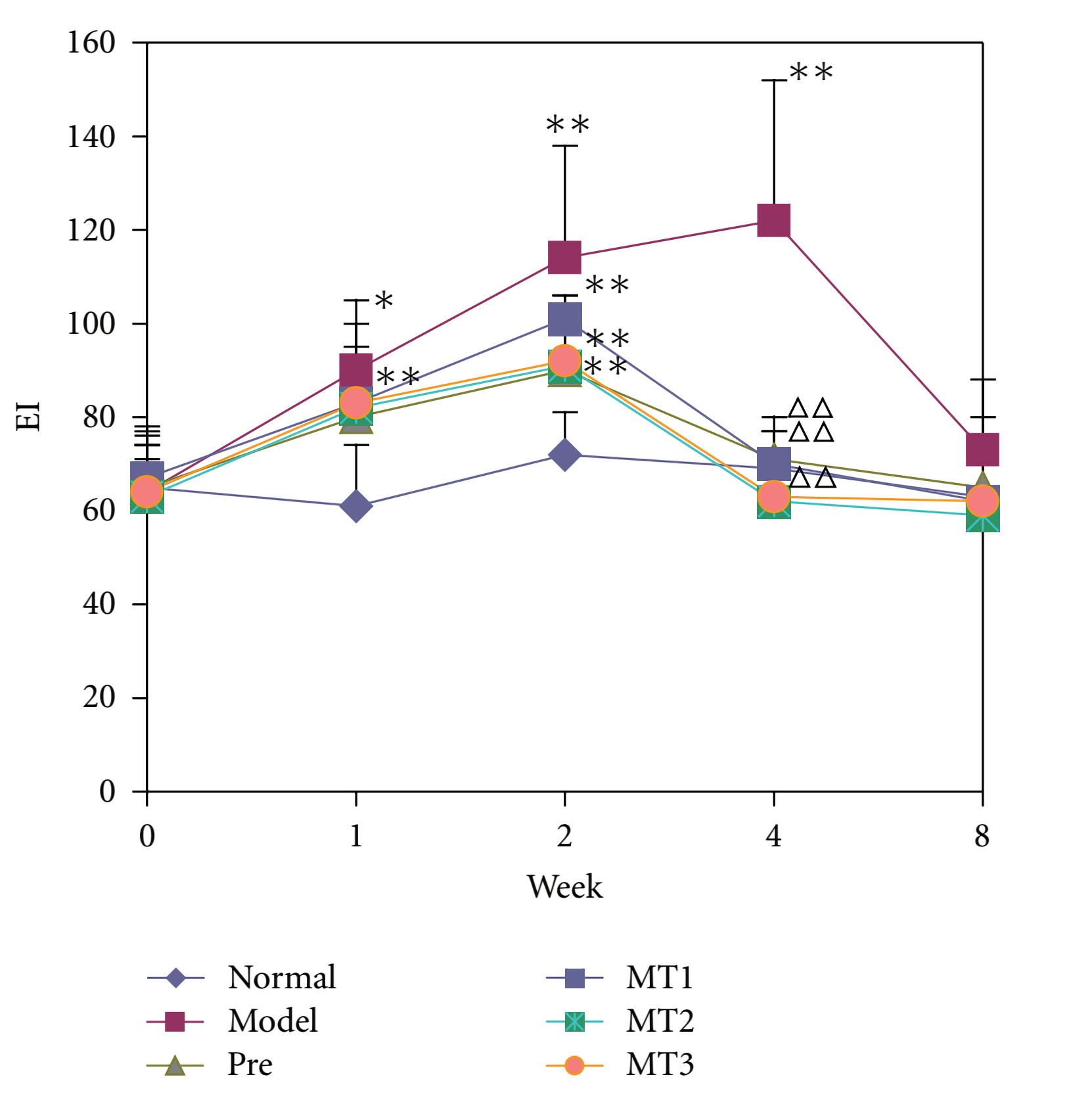 Fig.1 Levels of IgM Antihistone antibodies detected by ELISA in sera
Fig.1 Levels of IgM Antihistone antibodies detected by ELISA in sera
of the pristane-induced lupus mice. Normal, normal control group;
Model, PIL model group; Pre, prednisone-treatment group;
MT1-3, melatonin group. (Zhou et al. 2010)
- Arthritis, similar to symptoms seen in human SLE.
- Immune-complex deposition in the kidney leading to severe proteinuria and nephritis.
- Production of antinuclear antibodies (ANA) and diverse lupus autoantibodies, including anti-dsDNA and anti-Sm.
- TMPD-lupus is associated with abnormal production of IFNα and ß, which appears to have a central role in SLE.
Induced Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease Model
Various models of induced graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) have been used as models of lupus, including chronic and acute models. Similar to the pristane-induced model, these models require only a single injection of donor cells to induce a lupus-like syndrome. Pathological features associated with these models include:
- Production of a range of autoantibodies similar to those seen in human SLE.
- Glomerulonephritis caused by the deposition of immune complexes in the kidney.
- Production of antinuclear antibodies (ANA).
- More severe symptoms in females than males.
Compared to existing spontaneous murine models, GVHD models offer advantages such as they are reproducible and predictable, they exhibit rapid disease onset and relatively short time course. What's more, the severity is dependent on the number of allografted cells. These respects of the GVHD model render it particularly suitable for the study of lupus and the testing drug effects.
Creative Biolabs provides assessments including but not limited to:
- Cytokines measurements
- Anti-DNA antibody and autoantibodies measurements (ELISA)
- Histology of joints, lungs, and kidneys
- Assessment of nephritis
- Assessment of lymphoproliferation
Meanwhile, in order to meet our customers' specific requirements and their various research objectives, Creative Biolabs also offers other rodent inflammatory & immunological disease models listed as follows that you may be interested in:
- Carrageenan Air Pouch Model
- Carrageenan-Induced Paw Edema Model
- Imiquimod (IMQ)-Induced Psoriasis Rodent Model
- Chemical-Induced Rodent Contact Hypersensitivity Model
- Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (PCA) Model
- Delayed Type Hypersensitivity (DTH) Rodent Model
- Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis (AIA) Rodent Model
- Collagen-Induced Arthritis (CIA) Rodent Model
- Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis (CAIA) Model
- Cecum Ligation and Puncture (CLP)-Induced Sepsis Model
- LPS-Induced Rodent Sepsis Model
- Spontaneous Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) Mouse Models
Supported by seasoned experts and sufficient technical skills, Creative Biolabs is proud to offer the most comprehensive services for pharmacology and pharmacodynamic studies. Contact us or send us an inquiry for more information or a formal quote.
Reference
- Zhou, L.L.; et al. Regulatory effect of melatonin on cytokine disturbances in the pristane-induced lupus mice. Mediators of Inflammation.2010, (2010-7-8), 2010(962-9351).
For Research Use Only.
