Conjugation Based on Cysteine Residues
Cysteine has a highly reactive thiol side chain that can be oxidized with another molecule of cysteine to form an inter- or intramolecular disulfide bond, which contributes to the secondary and tertiary structure of proteins. The unique properties of cysteine, including high nucleophilicity, low redox potential, and low abundance, make it a valuable target for the strategies of protein bioconjugation. Classical methods, such as nucleophilic substitution, Michael addition, disulfide bond exchange, and photocatalytic reactions, enable the conjugation of cysteine-containing peptides or proteins with various molecules (e.g., cytotoxic drugs and carriers). Among these methods, the use of maleimide-based crosslinkers to prepare antibody-drug conjugates (ADC) is the most prevalent approach. The following outlines a method for preparing peptide-carrier conjugates utilizing cysteine residues.
Disclaimer
The technology and procedures described in this document are meant only as guidelines. Regarding the possible results of the client following this recommendation, Creative Biolabs makes no guarantees or warranties.
Materials
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA).
- Cysteine-containing peptide.
- m-Maleimidobenzoyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl ester (MBS).
- Dimethylformamide (DMF).
- Sodium azide.
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4, 0.01 M).
- PBS (pH 7, 0.01 M).
- Dialysis tubing (Avg. flat width 43 mm, 12,000 Da MWCO, with 50 mm dialysis tubing closures).
- Centrifuge tubes (1 mL/5 mL).
- Beaker (50 mL).
Methods
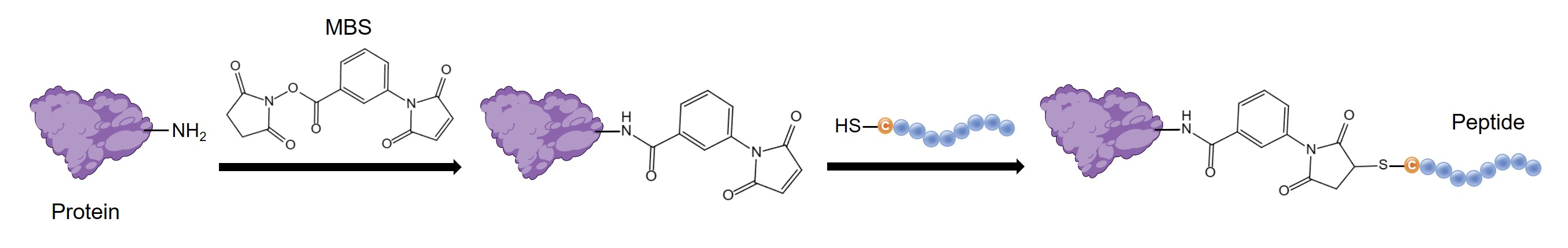
- Dissolve 5 mg BSA in 0.5 mL of PBS (pH 7, 0.01 M).
- Prepare an MBS stock solution (10 mg/mL in DMF).
- Dropwise add 100 μL of MBS stock solution to the BSA solution under constant stirring. Then, mix continuously at room temperature for 30 minutes.
- Remove excess MBS through the dialysis process. Transfer the entire conjugate solution to the 12,000 Da MWCO dialysis tubing and seal it with dialysis tubing closures.
- Place the dialysis device into a 50 mL beaker containing 30 mL PBS (pH 7.4, 0.01 M) and dialyze for 2 hours in a refrigerated environment. Repeat the procedure twice with the last dialysis lasting overnight.
- Dissolve 5 mg cysteine-containing peptide into 100 μL DMF.
- Transfer the conjugate solution into a 5 mL centrifuge tube, and then add the cysteine-containing peptide solution.
- Incubate the mixture overnight at room temperature.
- Dialyze the mixture according to step 4 and step 5.
- Store aliquots in a refrigerator or freezer with sodium azide (0.02% ).
Notes
- It is recommended to use cysteine-containing peptides with a purity of >90%.
- To prepare a PBS solution (pH 7.4, 0.01 M), combine 8.064 g of sodium chloride (NaCl) and 0.201 g of potassium chloride (KCl) in a 1 L volumetric flask, carefully add distilled water to the scale mark, and then shake well.
Recommended products
